Root Causes
Root Cause Overview
Root Cause Identification (RCI) automatically determines root causes of complex network issues. RCI leverages the datastore for realtime network status, and automatically correlates telemetry with each active blueprint intent. Root cause use cases include the following:
| Root Cause | Description |
|---|---|
| Link broken | Symptoms: Both interfaces are operationally down, LLDP is missing on both sides, BGP peered across that link is operationally down. |
| Link miscabled | Symptoms: LLDP indicates wrong neighbors, BGP peered across that link is operationally down. |
| Operator shut interface | Symptoms: Both interfaces on the link are operationally down; the interface in question is administratively down; LLDP missing on both sides, BGP peered across that link is operationally down. |
| Disconnection between 2 devices |
Symptoms: Union of symptoms for link broken / link miscabled / operator shut interface for all constituent links between a spine and a leaf For instance, if there are 3 links between a spine and a leaf, then 2 could be miscabled and 1 is broken - this results in a disconnection between that spine and that leaf. |
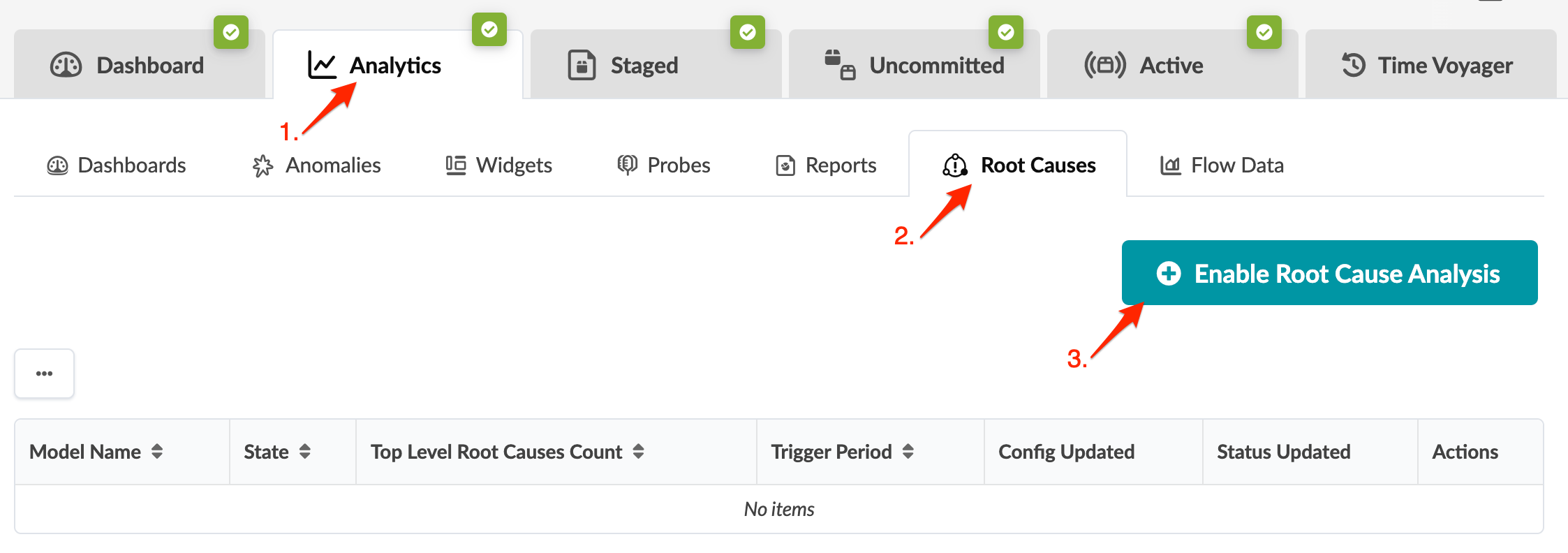
Enable Root Cause Analysis
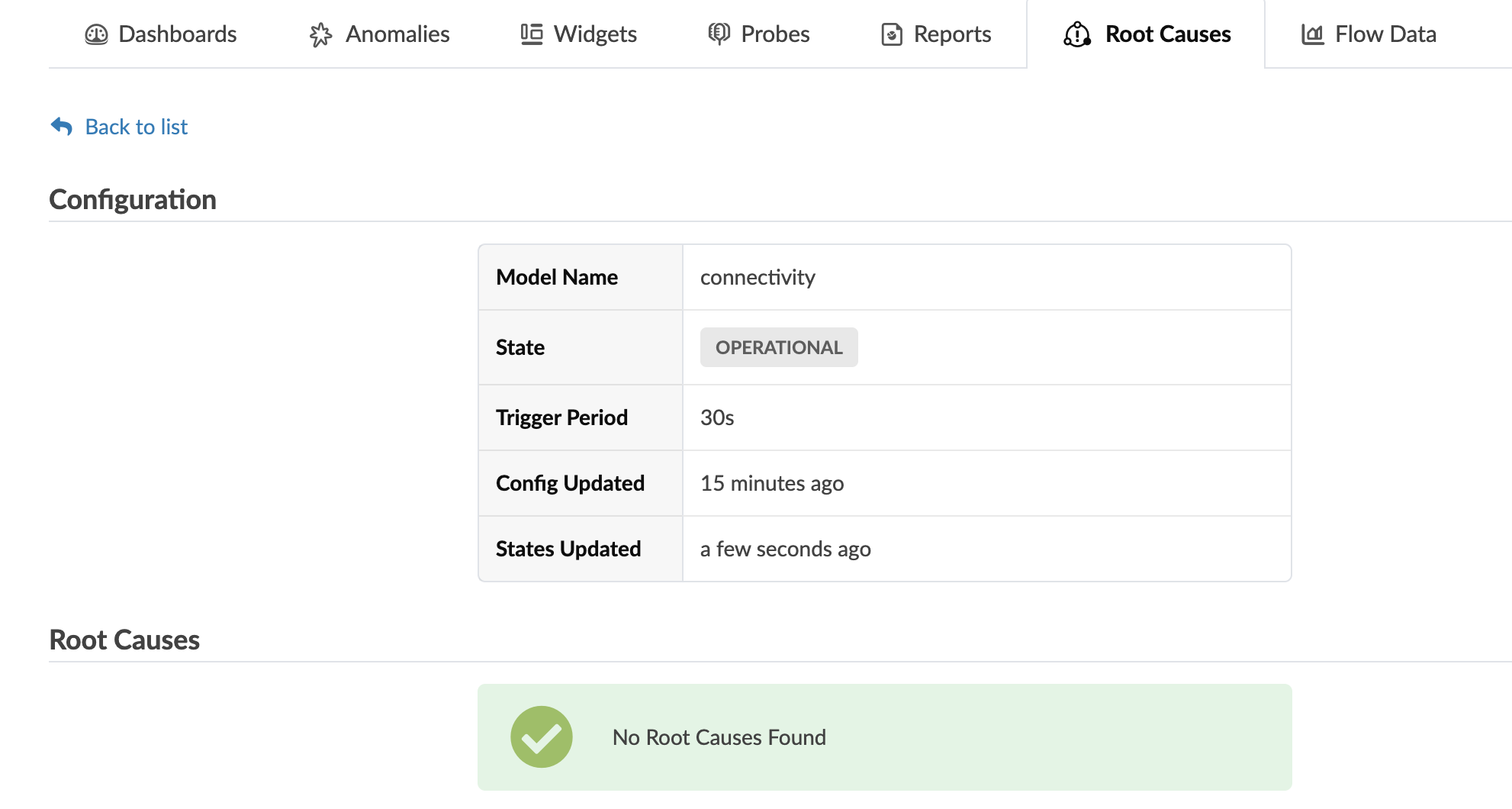
View Root Cause Analysis
To view root cause analysis using the GUI:
From the blueprint, navigate to Analytics > Root Causes and click the model name connectivity in the table.
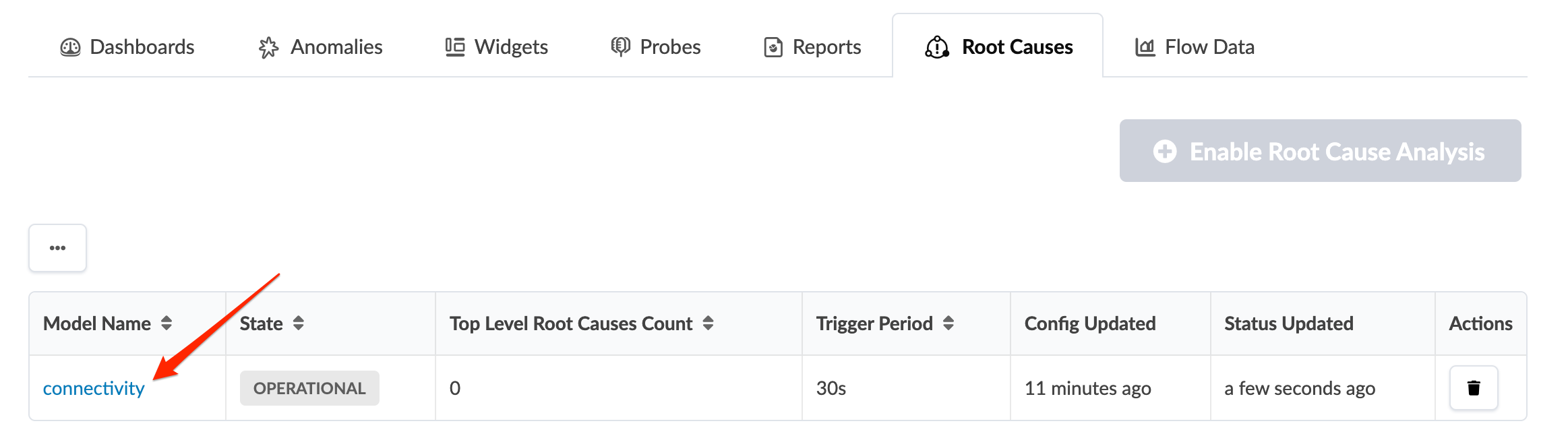
Root cause analysis runs periodically and produces zero or more root causes. Any root causes that are found include a description, a timestamp of when it was detected and a list of symptoms.