ON THIS PAGE
Deploying the Apstra Virtual Appliance on Nutanix
This guide explains how to deploy the Apstra VM Image for Linux KVM image and install it on Nutanix.
Download the Image
Download the 6.0 Apstra VM Image for Linux KVM (QCOW2) from the Software Downloads page.
Select the 6.0 version from the VERSION drop-down window.
An example filename for the 6.0 version is aos_server_6.0.0-189.qcow2.gz.
Extract the disk image and then move it to the location where you want to install it.
Upload the Image
Log into the Nutanix Prism Central console.
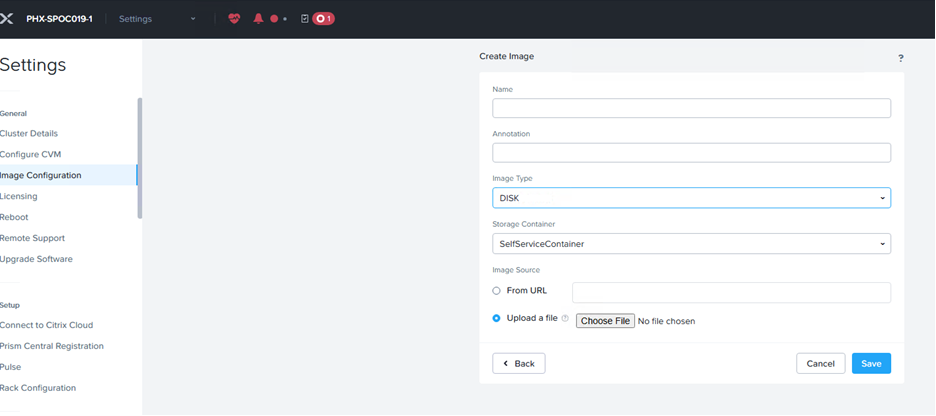
Navigate to the Image Configuration screen, or similar screen, depending on your version of Nutanix.
Specify the name of the image.
Select the image type as DISK.
Select SelfServiceContainer from the Storage Container drop-down window.
Select Upload a file and then click Choose File to upload the qcow2 file that you extracted from the .gz file.
Deploy the VM
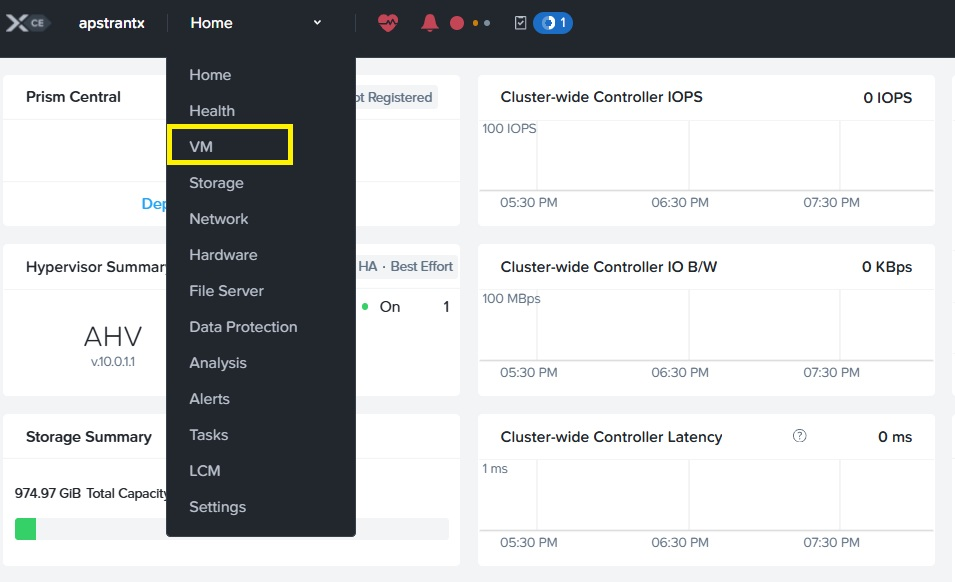
In the Prism Central console, navigate to the VM section.
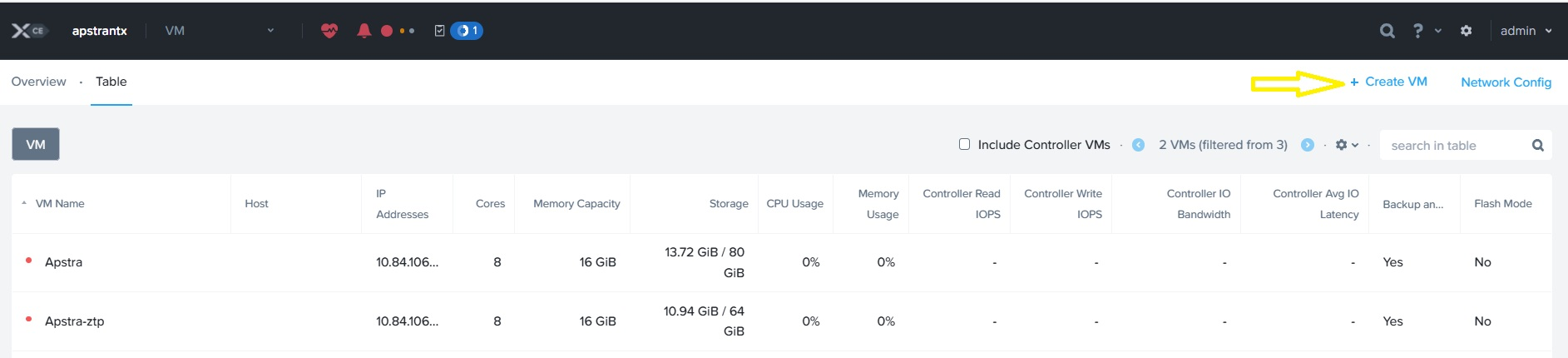
Click Table and then select Create VM to start the wizard.
Enter the name of the VM in the Name edit box.
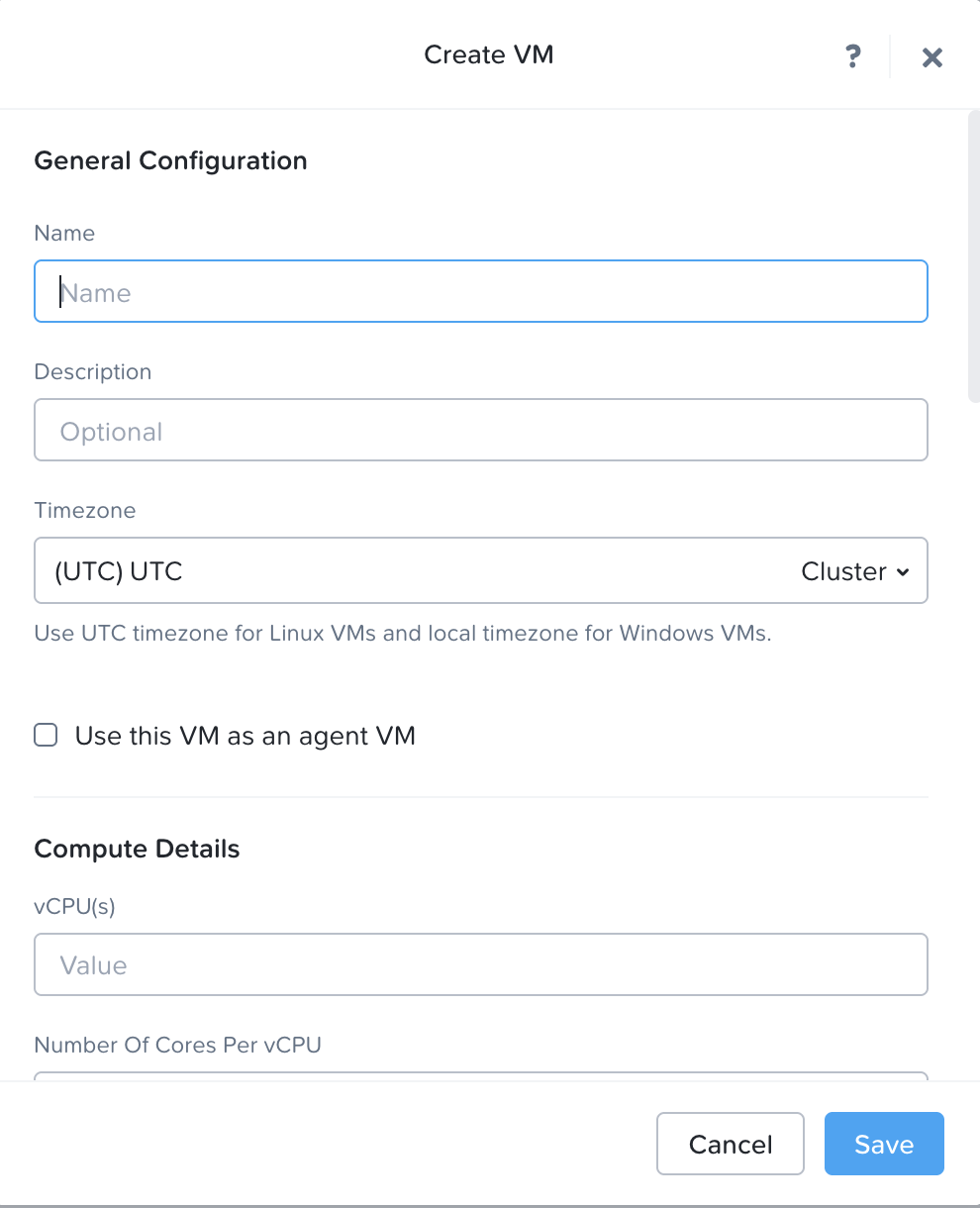
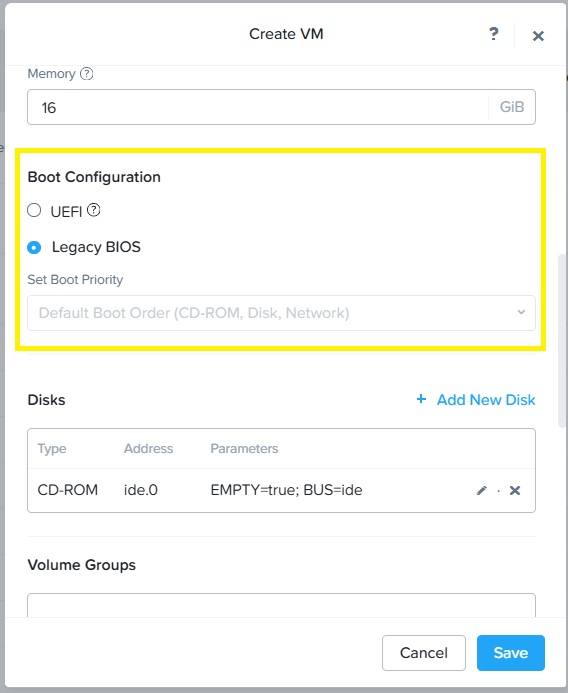
Select Legacy BIOS in the Boot Configuration section.
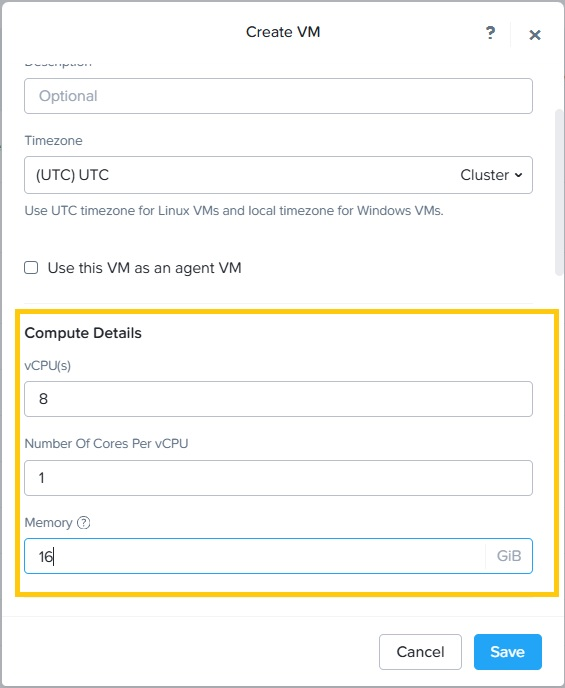
- Specify the number of vCPU(s) and cores per vCPU, and memory details.
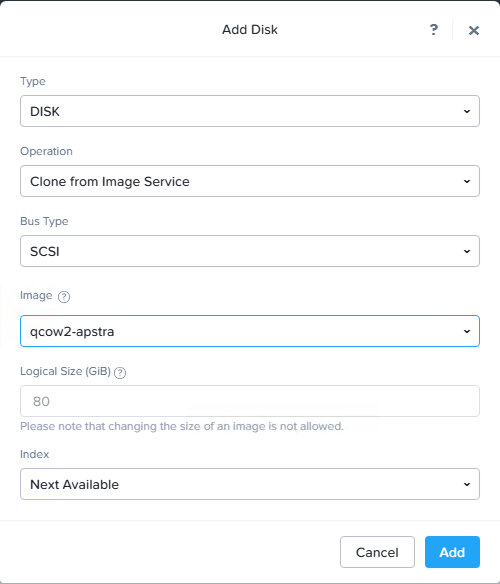
Add a disk to the VM:
Select DISK from the Type drop-down window.
Select Clone from Image Service from the Operation drop-down window.
Select SCSI from the Bus Type drop-down window.
Select qcow2-apstra from the Add Diskdrop-down window.
Select Next Available from the Index drop-down window, and then click Add.
- Click Add New NIC in the Network Adapters
(NIC) section to add a NIC.
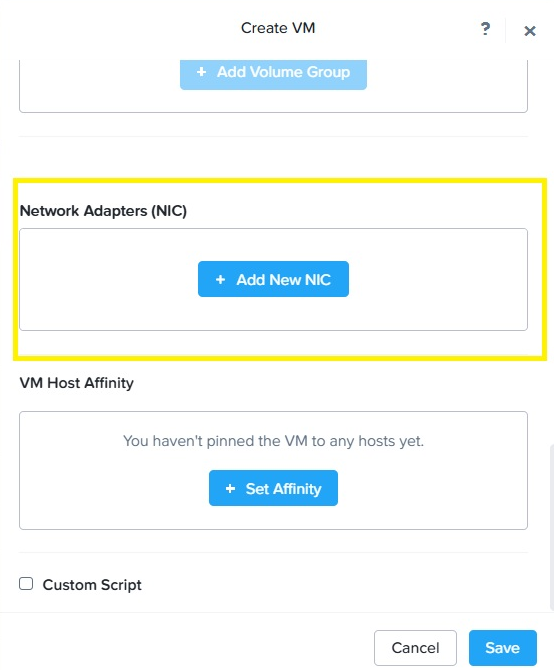
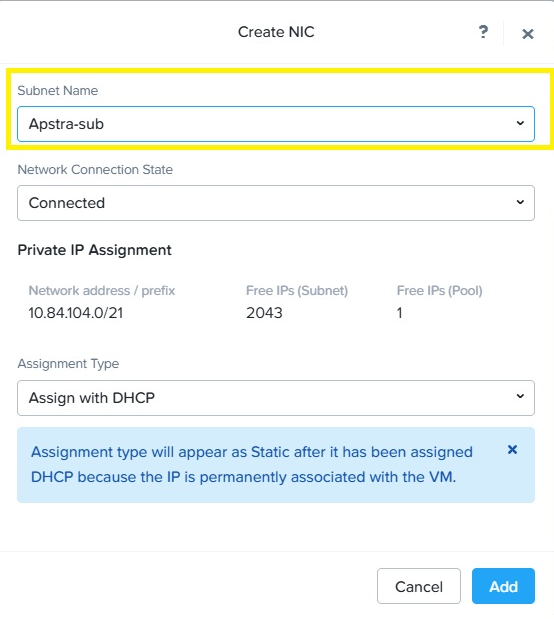
Select the available subnet name from the drop-down window.
Save the VM settings, and then right-click on the VM to power it on.
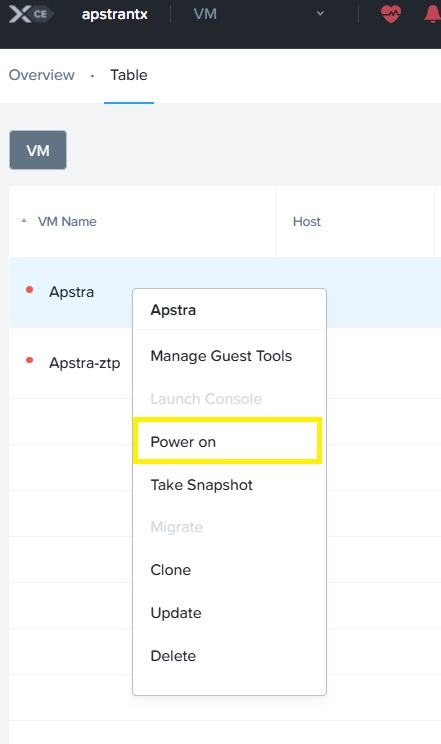
Right-click on the VM, and then select Launch Console for access.