ON THIS PAGE
Set Up the Example ConnectorOps Topology
Use the following steps to set up the exact topology used in this Apstra ConnectorOps Setup Guide. There are many ways to configure the routing and design of your fabric, and this is just one example. All the configurations done in this process are specific to this topology.
If you are using your own topology, see the Prerequisites for everything ConnectorOps needs to render SRX configurations in Apstra. High-level steps:To Create a Routing Policy for Your Fabric
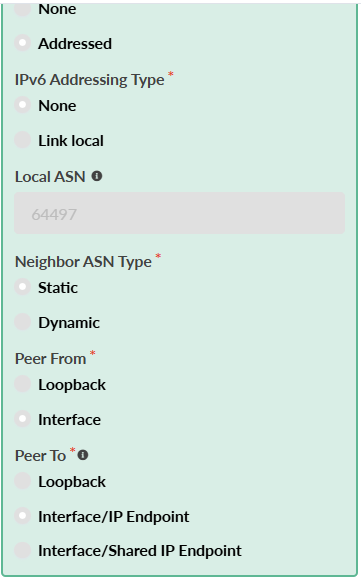
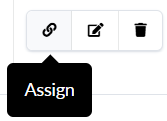
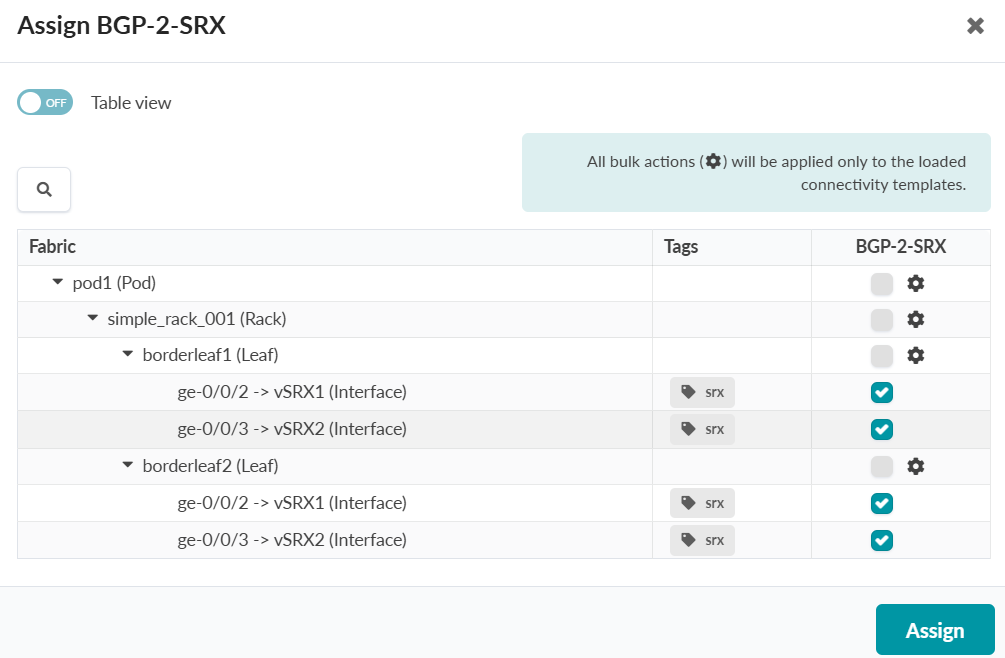
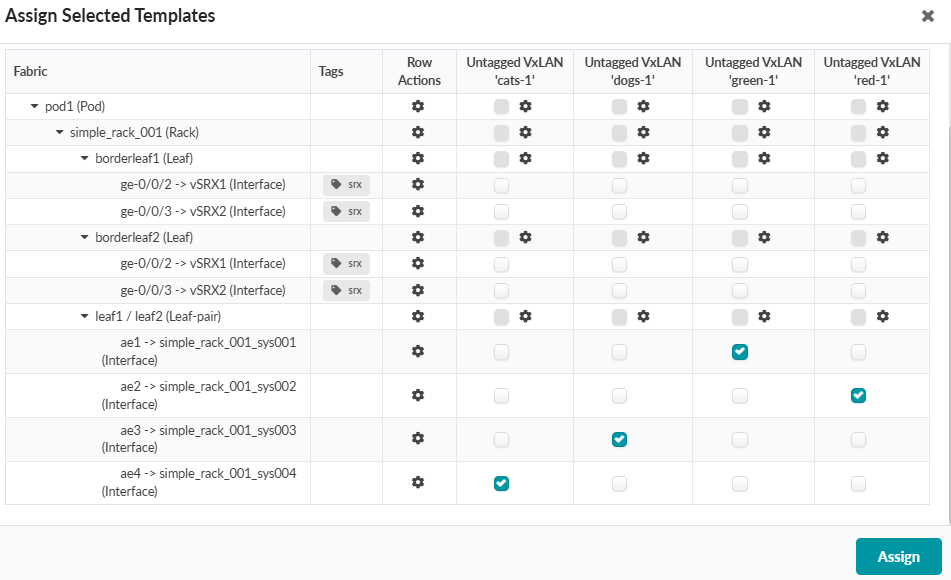
To Create and Assign a Connectivity Template Between the SRXs and Border Leaves
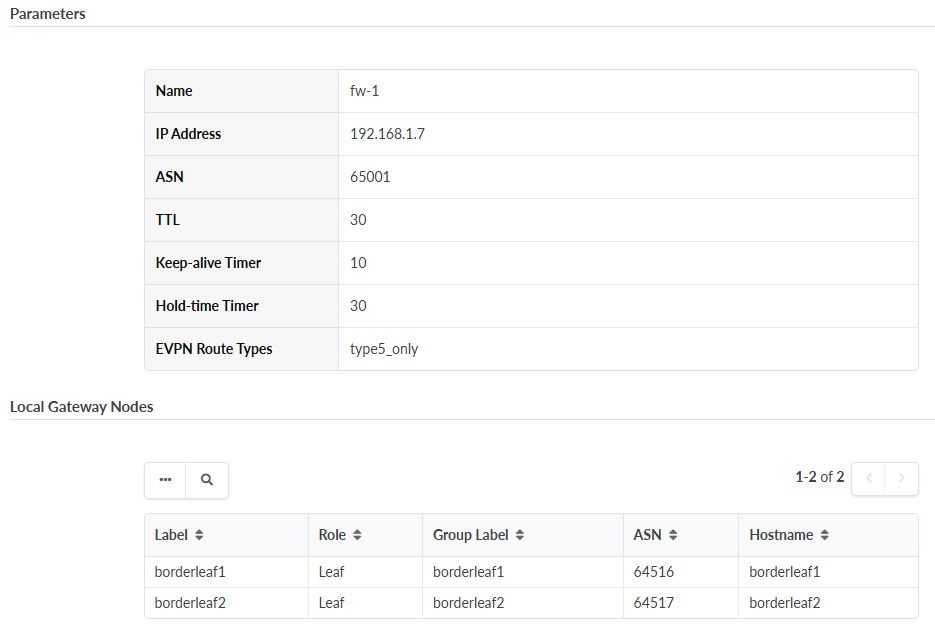
To Create External (Over the Top) Gateways in Apstra, and Designate them as Firewalls for Each SRX
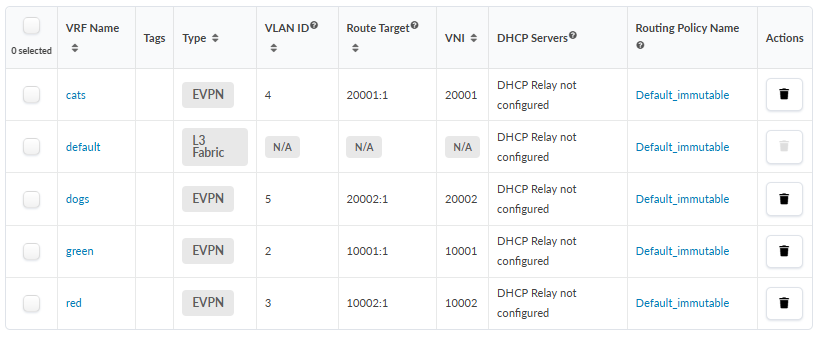
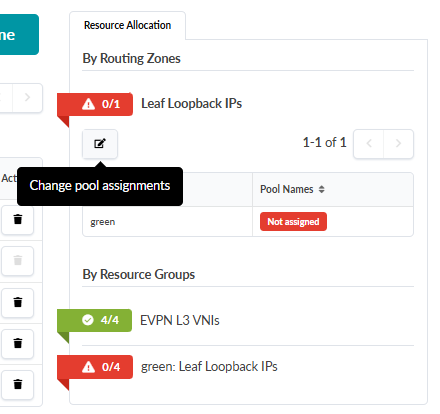
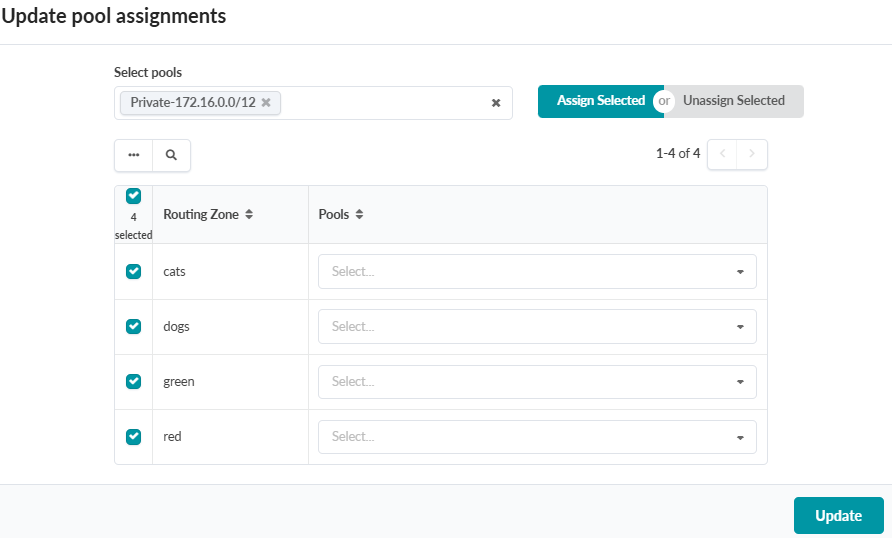
To Create VNs and Assign Routing Zones to Nodes
To Configure Security Policies
The following are the exact Security Policies applied on the SRX devices in this example topology for end-to-end routing.
set groups COMMON security address-book global address FW-1 172.16.1.6/32 set groups COMMON security address-book global address FW-2-lo 172.16.1.7/32 set groups COMMON security address-book global address FW-2-ge-0-0-0 192.168.0.19/32 set groups COMMON security address-book global address FW-2-ge-0-0-1 192.168.0.23/32 set groups COMMON security address-book global address BGP-0 172.16.0.4/32 set groups COMMON security address-book global address BGP-1 172.16.0.5/32 set groups COMMON security address-book global address green 210.210.0.0/16 set groups COMMON security address-book global address red 200.200.0.0/16 set groups COMMON security address-book global address cats 221.221.0.0/16 set groups COMMON security address-book global address dogs 220.220.0.0/16 set groups COMMON security address-book global address-set FW-2 address FW-2-lo set groups COMMON security address-book global address-set FW-2 address FW-2-ge-0-0-0 set groups COMMON security address-book global address-set FW-2 address FW-2-ge-0-0-1 set groups COMMON security policies from-zone evpn to-zone evpn policy HA-ICL match source-address FW-2 set groups COMMON security policies from-zone evpn to-zone evpn policy HA-ICL match destination-address FW-1 set groups COMMON security policies from-zone evpn to-zone evpn policy HA-ICL match application any set groups COMMON security policies from-zone evpn to-zone evpn policy HA-ICL then permit set groups COMMON security policies from-zone evpn to-zone evpn policy HA-ICL then log session-init set groups COMMON security policies from-zone evpn to-zone evpn policy HA-ICL then log session-close set groups COMMON security policies from-zone evpn to-zone evpn policy G2R match source-address green set groups COMMON security policies from-zone evpn to-zone evpn policy G2R match destination-address red set groups COMMON security policies from-zone evpn to-zone evpn policy G2R match application junos-ping set groups COMMON security policies from-zone evpn to-zone evpn policy G2R match application junos-ssh set groups COMMON security policies from-zone evpn to-zone evpn policy G2R match source-l3vpn-vrf-group GREEN set groups COMMON security policies from-zone evpn to-zone evpn policy G2R match destination-l3vpn-vrf-group RED set groups COMMON security policies from-zone evpn to-zone evpn policy G2R then permit set groups COMMON security policies from-zone evpn to-zone evpn policy G2R then log session-init set groups COMMON security policies from-zone evpn to-zone evpn policy G2R then log session-close set groups COMMON security policies from-zone evpn to-zone evpn policy R2G match source-address red set groups COMMON security policies from-zone evpn to-zone evpn policy R2G match destination-address green set groups COMMON security policies from-zone evpn to-zone evpn policy R2G match application junos-http set groups COMMON security policies from-zone evpn to-zone evpn policy R2G match application junos-ping set groups COMMON security policies from-zone evpn to-zone evpn policy R2G match source-l3vpn-vrf-group RED set groups COMMON security policies from-zone evpn to-zone evpn policy R2G match destination-l3vpn-vrf-group GREEN set groups COMMON security policies from-zone evpn to-zone evpn policy R2G then permit set groups COMMON security policies from-zone evpn to-zone evpn policy R2G then log session-init set groups COMMON security policies from-zone evpn to-zone evpn policy R2G then log session-close set groups COMMON security policies from-zone evpn to-zone evpn policy D2C match source-address dogs set groups COMMON security policies from-zone evpn to-zone evpn policy D2C match destination-address cats set groups COMMON security policies from-zone evpn to-zone evpn policy D2C match application any set groups COMMON security policies from-zone evpn to-zone evpn policy D2C match source-l3vpn-vrf-group DOGS set groups COMMON security policies from-zone evpn to-zone evpn policy D2C match destination-l3vpn-vrf-group CATS set groups COMMON security policies from-zone evpn to-zone evpn policy D2C then permit set groups COMMON security policies from-zone evpn to-zone evpn policy C2D match source-address cats set groups COMMON security policies from-zone evpn to-zone evpn policy C2D match destination-address dogs set groups COMMON security policies from-zone evpn to-zone evpn policy C2D match application junos-ping set groups COMMON security policies from-zone evpn to-zone evpn policy C2D match source-l3vpn-vrf-group CATS set groups COMMON security policies from-zone evpn to-zone evpn policy C2D match destination-l3vpn-vrf-group DOGS set groups COMMON security policies from-zone evpn to-zone evpn policy C2D then permit set groups COMMON security policies from-zone evpn to-zone evpn policy FINAL-EVPN-DENY match source-address any set groups COMMON security policies from-zone evpn to-zone evpn policy FINAL-EVPN-DENY match destination-address any set groups COMMON security policies from-zone evpn to-zone evpn policy FINAL-EVPN-DENY match application junos-vxlan set groups COMMON security policies from-zone evpn to-zone evpn policy FINAL-EVPN-DENY then deny set groups COMMON security policies from-zone evpn to-zone evpn policy infra description "control plane permit" set groups COMMON security policies from-zone evpn to-zone evpn policy infra match source-address any set groups COMMON security policies from-zone evpn to-zone evpn policy infra match destination-address any set groups COMMON security policies from-zone evpn to-zone evpn policy infra match application junos-bgp set groups COMMON security policies from-zone evpn to-zone evpn policy infra match application junos-ping set groups COMMON security policies from-zone evpn to-zone evpn policy infra match application bfd-mhop set groups COMMON security policies from-zone evpn to-zone evpn policy infra then permit set groups COMMON security policies from-zone evpn to-zone evpn policy infra then log session-init set groups COMMON security policies from-zone evpn to-zone evpn policy infra then log session-close set groups COMMON security policies from-zone evpn to-zone untrust policy C2EXT match source-address cats set groups COMMON security policies from-zone evpn to-zone untrust policy C2EXT match destination-address any set groups COMMON security policies from-zone evpn to-zone untrust policy C2EXT match application junos-http set groups COMMON security policies from-zone evpn to-zone untrust policy C2EXT match application junos-http-ext set groups COMMON security policies from-zone evpn to-zone untrust policy C2EXT match application junos-https set groups COMMON security policies from-zone evpn to-zone untrust policy C2EXT match application junos-dns-udp set groups COMMON security policies from-zone evpn to-zone untrust policy C2EXT match application junos-dns-tcp set groups COMMON security policies from-zone evpn to-zone untrust policy C2EXT match application junos-ping set groups COMMON security policies from-zone evpn to-zone untrust policy C2EXT match source-l3vpn-vrf-group CATS set groups COMMON security policies from-zone evpn to-zone untrust policy C2EXT then permit set groups COMMON security policies global policy infra-reject-log description "final touch" set groups COMMON security policies global policy infra-reject-log match source-address any set groups COMMON security policies global policy infra-reject-log match destination-address any set groups COMMON security policies global policy infra-reject-log match application any set groups COMMON security policies global policy infra-reject-log then reject set groups COMMON security policies global policy infra-reject-log then log session-init set groups COMMON security policies global policy infra-reject-log then log session-close set groups COMMON security l3vpn vrf-group GREEN vrf GREEN set groups COMMON security l3vpn vrf-group RED vrf RED set groups COMMON security l3vpn vrf-group CATS vrf CATS set groups COMMON security l3vpn vrf-group DOGS vrf DOGS set security policies pre-id-default-policy then log session-close set security zones security-zone trust tcp-rst set security zones security-zone untrust screen untrust-screen set security zones security-zone evpn host-inbound-traffic system-services all set security zones security-zone evpn host-inbound-traffic protocols all set security zones security-zone evpn interfaces ge-0/0/0.0 set security zones security-zone evpn interfaces ge-0/0/1.0 set security zones security-zone evpn interfaces lo0.0 set apply-groups COMMON
After setting up this topology, proceed to Deploy
ConnectorOps and Verify Connectivity.