Supported Topologies
Apstra ConnectorOps supports non-HA (single SRX hanging from border leaf) or Multinode High Availability (MNHA) (two peer SRXs) mode topologies.
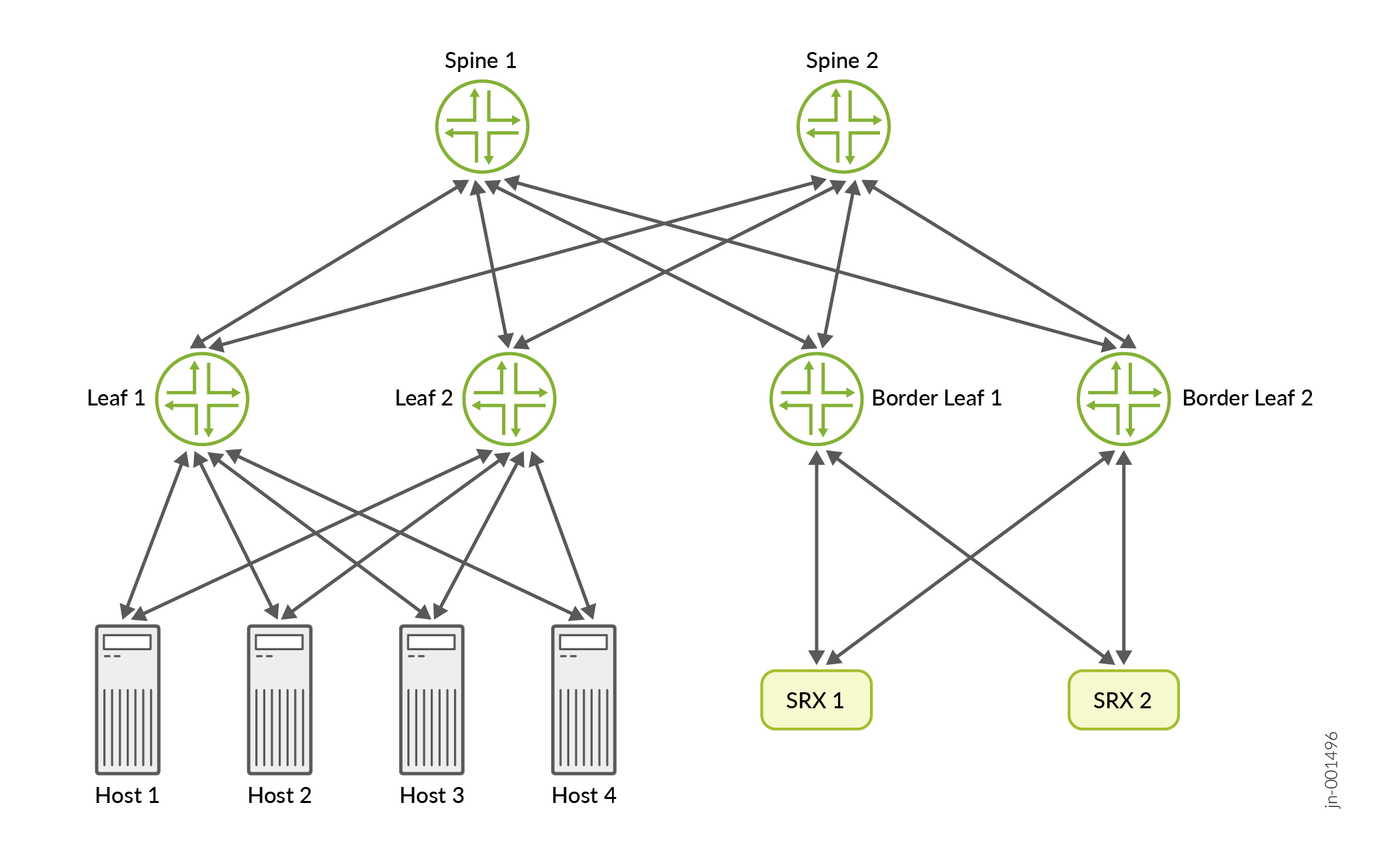
MNHA mode topology
This MNHA topology shows a dual border-leaf design with two SRX Firewalls for high-availability. Each SRX connects to a both border leaves, to provide fabric redundancy.
Traffic from local hosts moves through leaf/spine layers to the border, then passes through either SRX for inspection and policy enforcement. The redundant paths ensure that the fabric can keep routing and enforcing security policies even if a border leaf or SRX fails.
Non-HA topology
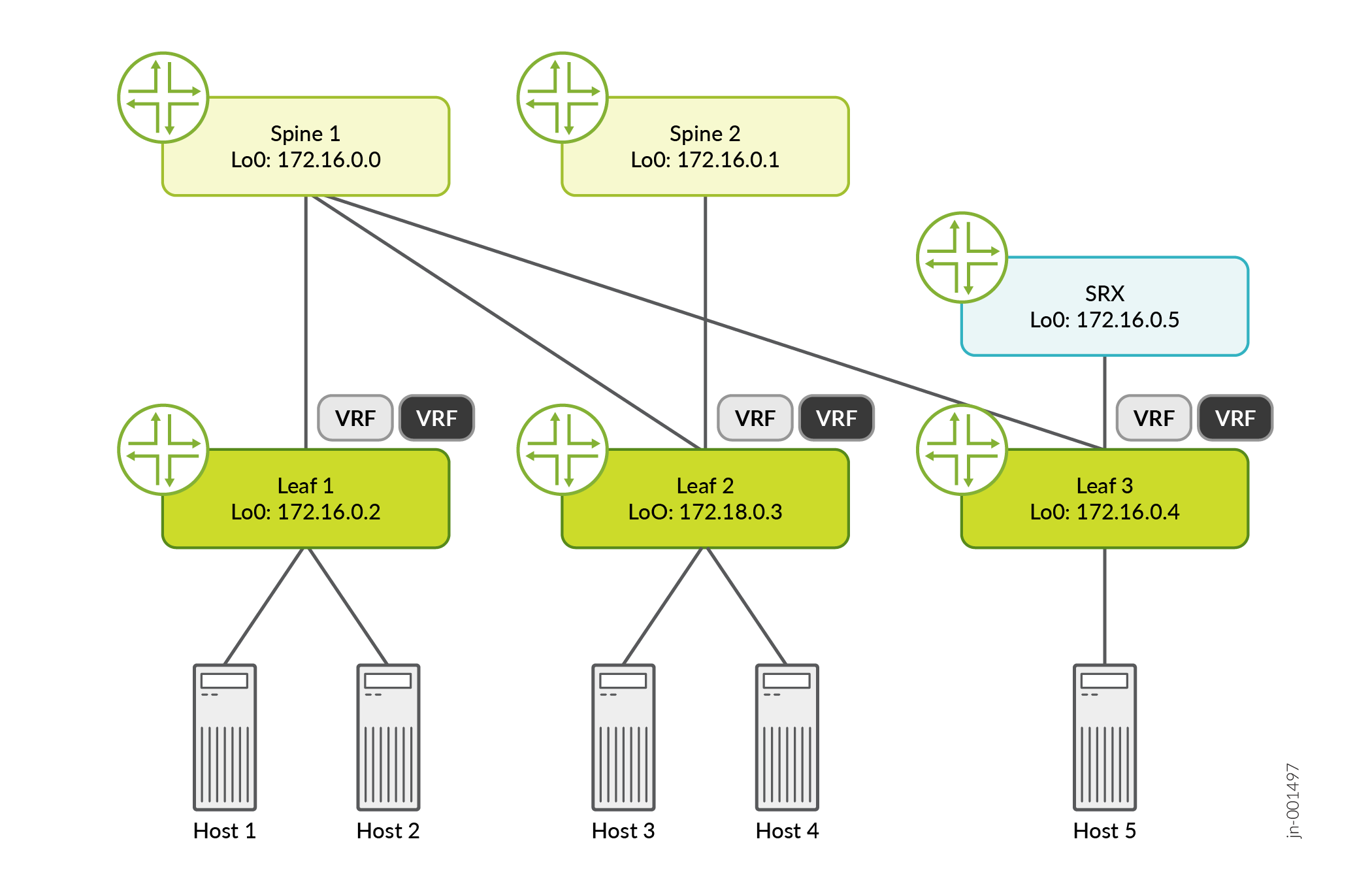
In this topology, the EVPN-VXLAN fabric is designed for edge-routed bridging (ERB), with SRXs functioning in an enhanced border leaf (EBL) position. EBL extends the traditional border leaf role to provide traffic inspection for VXLAN tunnels at the network edge.
VXLAN traffic originating at the LEAF-1 device traverses through the SRX Series Firewalls that function as EBLs. In this use case, the SRX Series Firewall is placed at the border, that is, at the entry and exit point of the campus or data centre, to provide stateful inspection to the VXLAN encapsulated packets traversing through it.
Host-1 is mapped to VN-Blue with its own VRF, and Host-4 to VN-Green with an isolated VRF.
When pinging from Host-1 to Host-4 (or the reverse), the traffic is routed from Host-1 to LEAF-1, lands on LEAF-3 via the spine layer, and establishes a VXLAN tunnel between LEAF-1 and LEAF-3. Upon reaching LEAF-3, the traffic is automatically directed to the SRX for policy enforcement and inter-VRF route-leak inspection. Following inspection, the traffic is returned through LEAF-3, forwarded to LEAF-2 via the spines, and ultimately lands Host-4.
