Processor: State
The State processor checks that a value is one of the specified anomalous states. It outputs DSS with anomaly values, such as 'true' if the value is in the specified states, and otherwise, it returns 'false'. (previously called 'state_check' and 'in_state'). The State processor supports multiple reference states and output is 'true' when input is in any of the specified states.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Input Types | Table( discrete state, accumulate=True or False) |
| Output Types | Table (discrete state) |
| Graph Query (graph_query) |
One or more queries on graph specified as strings, or a list of such queries. (String will be deprecated in a future release.) Multiple queries should provide all the named nodes referenced by the expression fields (including additional_properties). Graph query is executed on the "operation" graph. Results of the queries can be accessed using the "query_result" variable with the appropriate index. For example, if querying property set nodes under name "ps", the result will be available as "query_result[0]["ps"]". In collector processors ( In other processors it is used for general parameterization and it is only supported as a list of queries.
graph_query: "node("system", role="leaf", name="system").
out("hosted_interfaces").
node("interface", name="iface").out("link").
node("link", role="spine_leaf")"
graph_query: ["node("system", role="leaf", name="system")",
"node("system", role="spine", name="system")"]
Non-collector processors containing the
graph_query: [node("property_set", label="probe_propset", name="ps")]
duration: int(query_result[0]["ps"].values["accumulate_duration"])
Another example is a that probes can validate a compliance requirement; the compliance value may change over time and/or it can be used by more than one probe. Also, a probe can validate NOS versions on devices. In this case, property sets can be used to define the current NOS version requirement. If it changes tomorrow: change the property set value, instead of going under the probe stage. |
| Anomalous States | Expression that evaluates to DS value or list of DS values which is used for the check. For example, it can be: "'true'" (expression evaluating to a string) or "['missing', 'unknown', 'down']" (expression evaluating to a list of strings). |
| Anomaly MetricLog Retention Duration | Retain anomaly metric data in MetricDb for specified duration in seconds |
| Anomaly MetricLog Retention Size | Maximum allowed size, in bytes of anomaly metric data to store in MetricDB |
| Anomaly Metric Logging | Enable metric logging for anomalies |
| Enable Streaming (enable_streaming) | Makes samples of output stages streamed if enabled. An optional boolean that defaults to False. If set to True, all output stages of this processor are streamed in the generic protobuf schema. |
| Raise Anomaly (raise_anomaly) | Outputs “true” and “false” values, “true” meaning an appropriate item is anomalous, and "false" meaning the item is not anomalous. When Raise Anomaly is set to True, an actual anomaly is generated in addition to a sample in the output. |
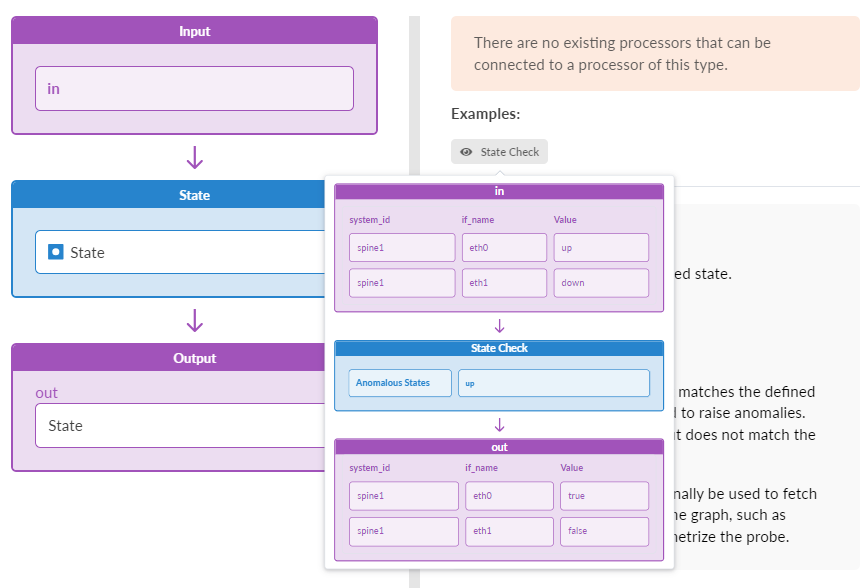
Example: State
state: '"up"'
Sample Input (DS)
[if_name=eth0] : "up" [if_name=eth1] : "down" [if_name=eth3] : "up"
Sample Output (DSS)
[if_name=eth0] : "false" [if_name=eth1] : "true" [if_name=eth3] : "false"
If expression is used for the state field, then it's evaluated for each input item, and it results into item-specific state value. Properties of the respective output item are extended by the state property with value of the evaluated expression.
state: expected_if_state
Sample Input (DS):
[if_name=eth0,expected_if_state=up] : "up" [if_name=eth1,expected_if_state=down] : "down" [if_name=eth3,expected_if_state=up] : "down"
Sample Output (DSS)
[if_name=eth0,state=up] : "false" [if_name=eth1,state=down] : "false" [if_name=eth3,state=up] : "true"
