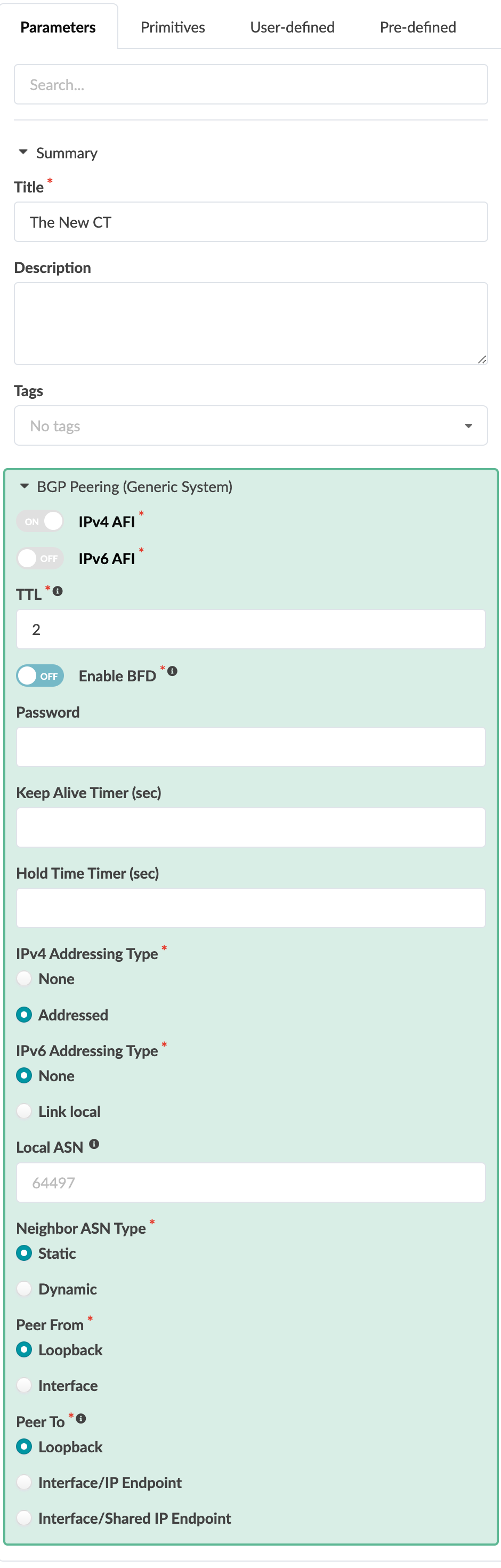
Primitive: BGP Peering (Generic System)
The BGP peering (generic system) primitive creates a BGP peering session with a generic system. The generic system is inherited from Apstra generic system properties, such as loopback and ASN (addressed, link-local peer). This primitive connects to a virtual network (single) or IP link connectivity point primitive.
The following parameters must be configured:
-
IPv4 AFI
-
IPv6 AFI
-
BGP Time to Live (TTL)
-
When you set TTL to 0, nothing is configured and the device defaults are used.
-
When you set TTL to 1, Cisco NX-OS and FRR-based BGP (SONiC) renders disable-connected-check. Otherwise, TTL values render ebgp-multihop on specific BGP neighbors.
-
-
Enable BFD - Enable BFD with interval: 1 sec, multiple: 3 sec
-
This enables BFD for the BGP peering. Multihop BFD is only supported for Junos, which is activated by default. For non-Junos devices, set TTL to 1.
-
-
BGP Password
-
BGP Keep Alive Timer (seconds)
-
BGP Hold Time Timer (seconds)
-
IPv4 Addressing Type (none, addressed)
-
IPv6 Addressing Type (none, (addressed if IPv6 applications are enabled) link local)
-
Local ASN - Configured on a per-peer basis. It allows a router to appear to be a member of a second autonomous system (AS) by prepending a local-as AS number, in addition to its real AS number, announced to its eBGP peer, resulting in an AS path length of two.
-
Neighbor ASN Type (static, dynamic)
-
Peer From (loopback, interface)
-
Peer To (loopback, interface/IP endpoint, interface/shared IP endpoint)
-
Loopback: use this option to peer with the loopback address of a single remote system.
-
Interface/IP endpoint: use this option to peer with the IP address of a single remote system link or routed vlan interface.
-
Interface/Shared IP endpoint: use this option for any scenario where the remote peer IP address is shared across multiple remote systems.
-
You can connect a routing policy primitive to a BGP peering (generic system).