Creating a Custom Telemetry Collector
SUMMARY This topic describes the steps that are required to create a custom telemetry collector.
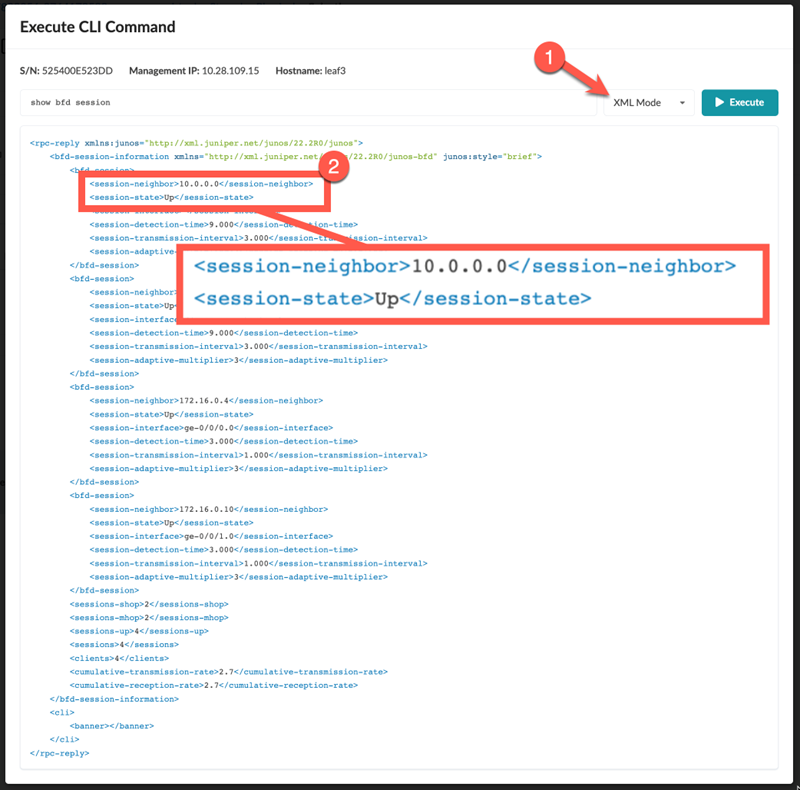
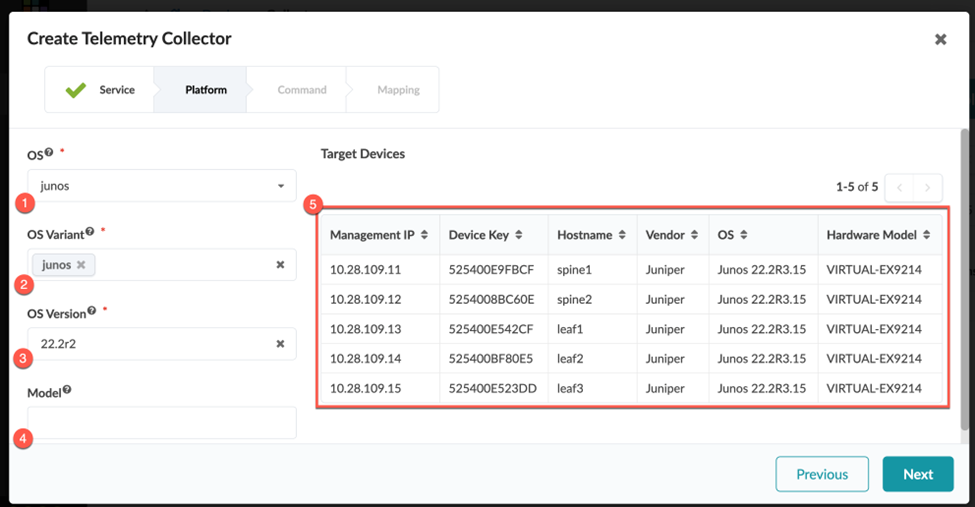
In this topic, we'll walk you through creating your own custom telemetry service using BFD as an example. In our example, the telemetry service collects the state of the BFD sessions you just configured. Our goal is to alert operations that a BFD session is down.
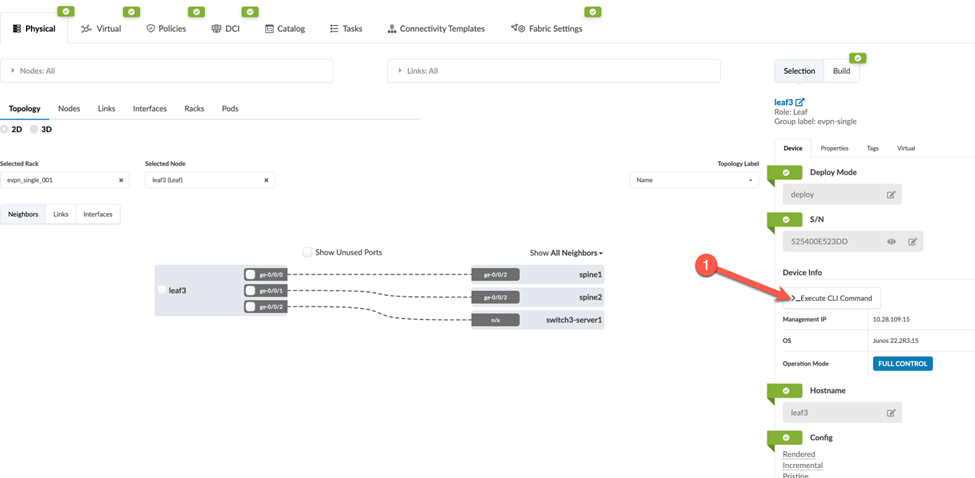
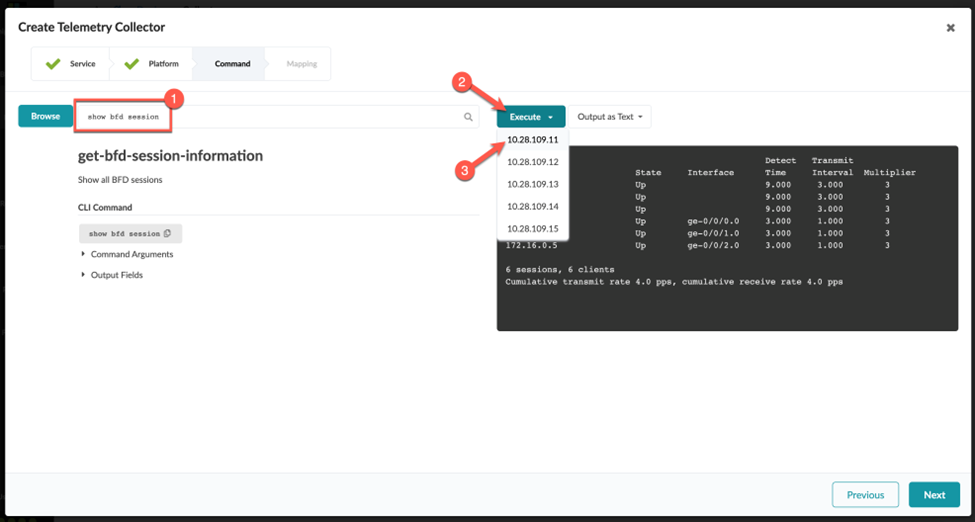
Execute the CLI Command
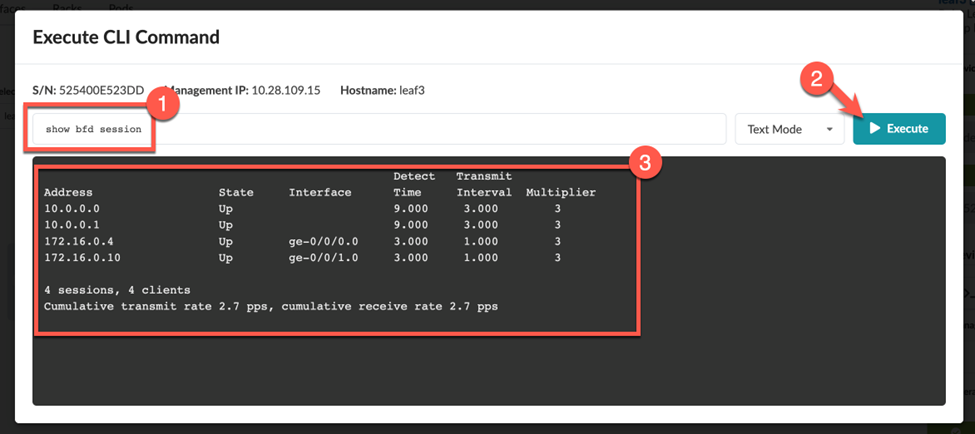
You can execute CLI commands from within the staged or active blueprint (shown in our example), or from the Devices > Managed Devices page.
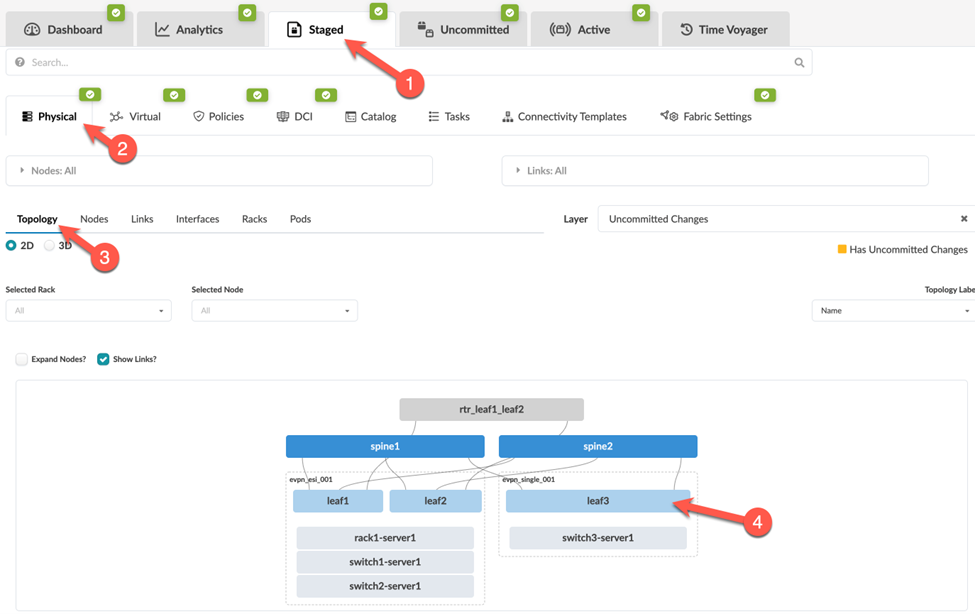
To use the CLI command feature, navigate to a deployed Junos device in your blueprint as follows:
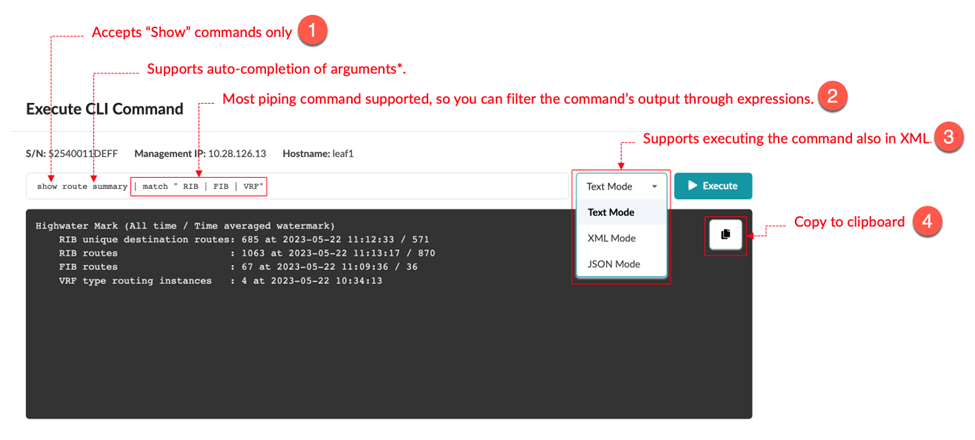
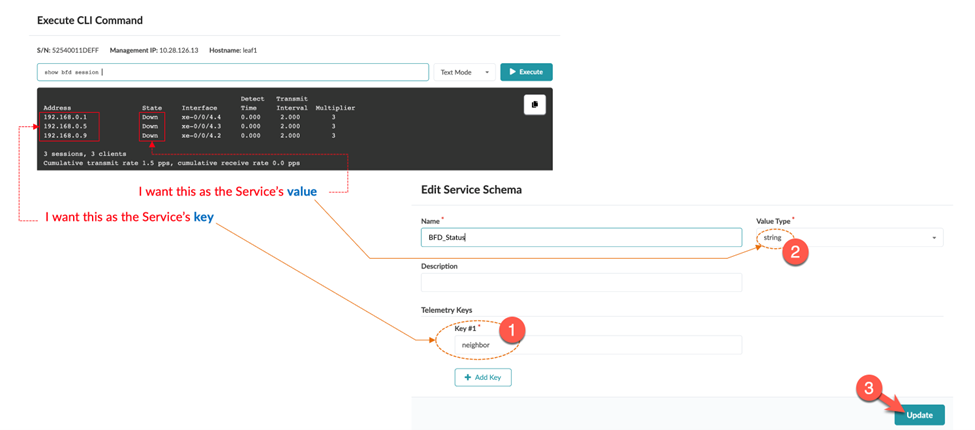
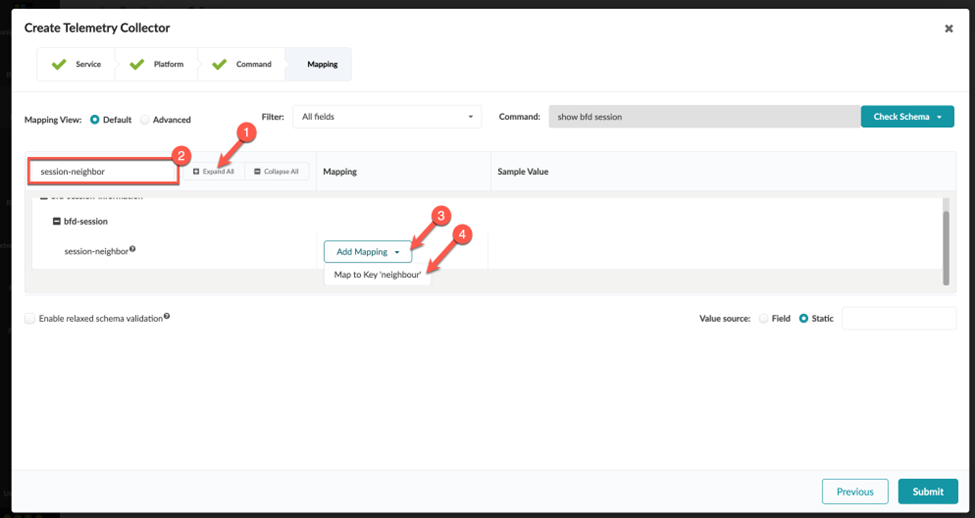
Identify the Key and Value of Interest from the CLI Output
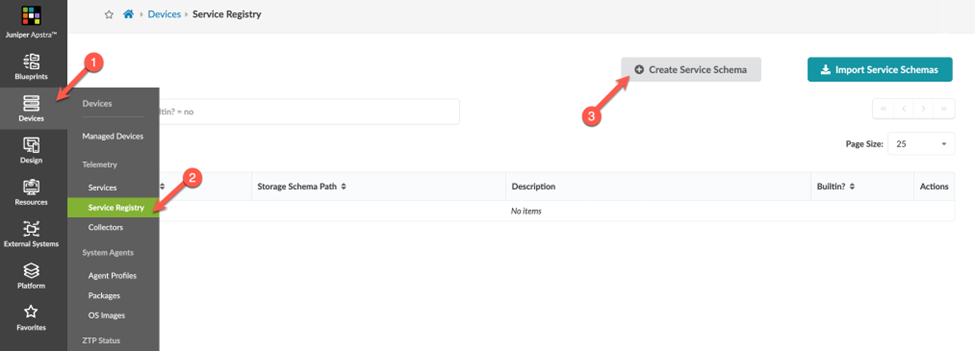
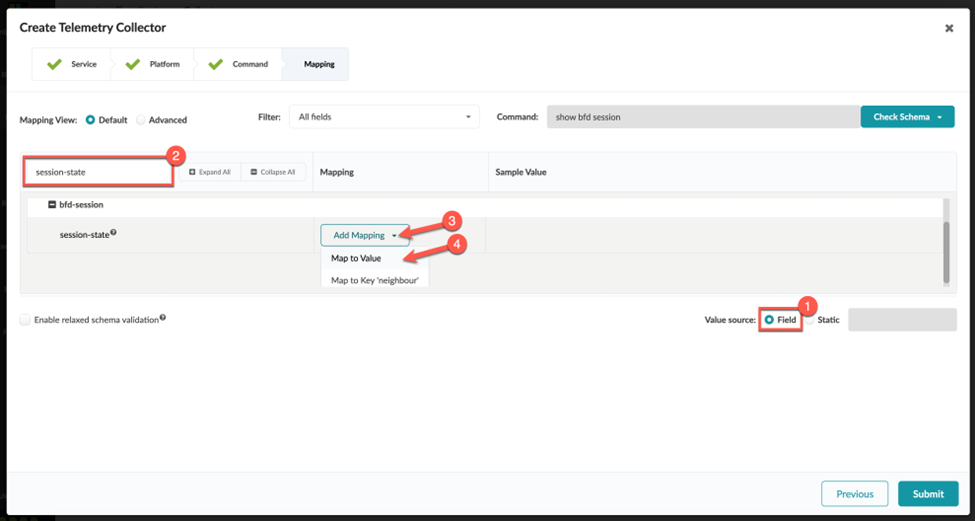
Create a Service Schema
A single telemetry service schema can have multiple collectors associated with it.
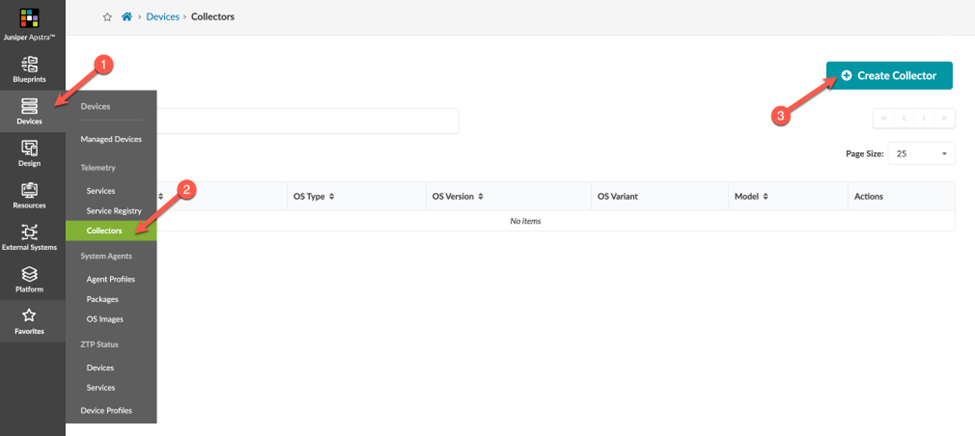
Create a Collector
A single telemetry service schema can have multiple collectors associated with it.
Validate That the Collector Is Working
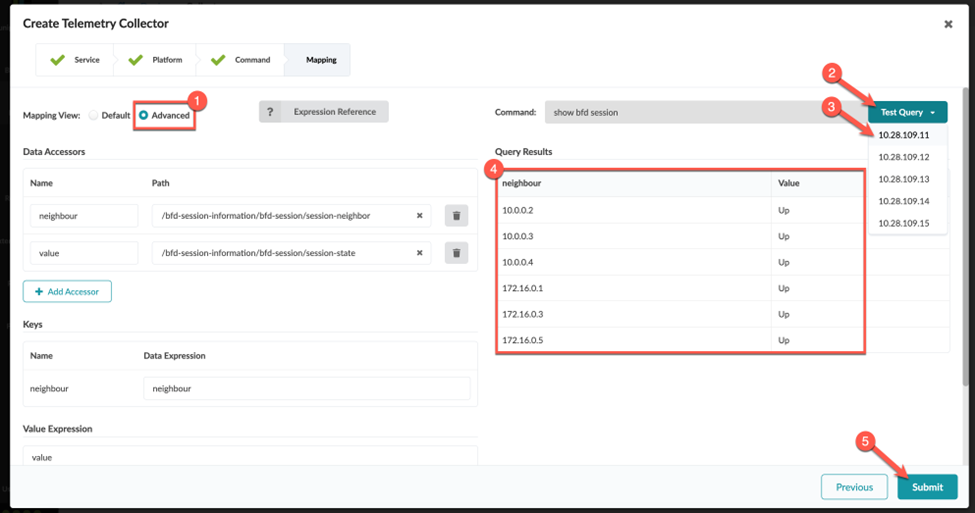
Congratulations! You successfully created a collector.
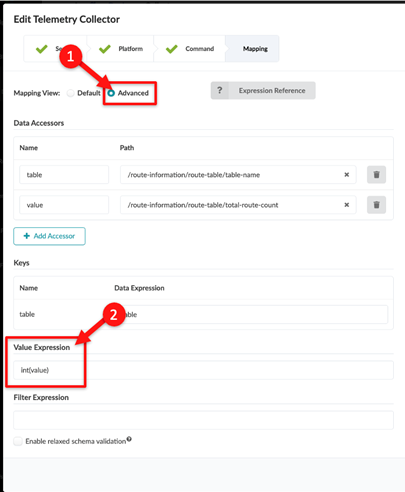
When you define the integer (number) values for a collector, you might need to enter a value expression for the collector to function. This is because Junos occasionally reports number data as a string. Before the collector can be processed, you must perform a conversion from string to integer on the Apstra side.