Installing the Optional SATA Solid-State Drive in SRX340 and SRX345 Services Gateways
The SRX340 and SRX345 services gateways allows optional installation of a 100 GB serial advanced technology attachment (SATA) solid-state drive (SSD), which can be used for storing traffic log entries. The SATA SSD is not hot-swappable.
Use only a Juniper-qualified SATA SSD.
Before you install the SSD, ensure that you have taken the necessary precautions to prevent electrostatic discharge (ESD) damage (see Prevention of Electrostatic Discharge Damage).
To install the SSD:
- Power off the services gateway.
- Attach an ESD grounding strap to your bare wrist and connect the strap to the ESD point on the chassis.
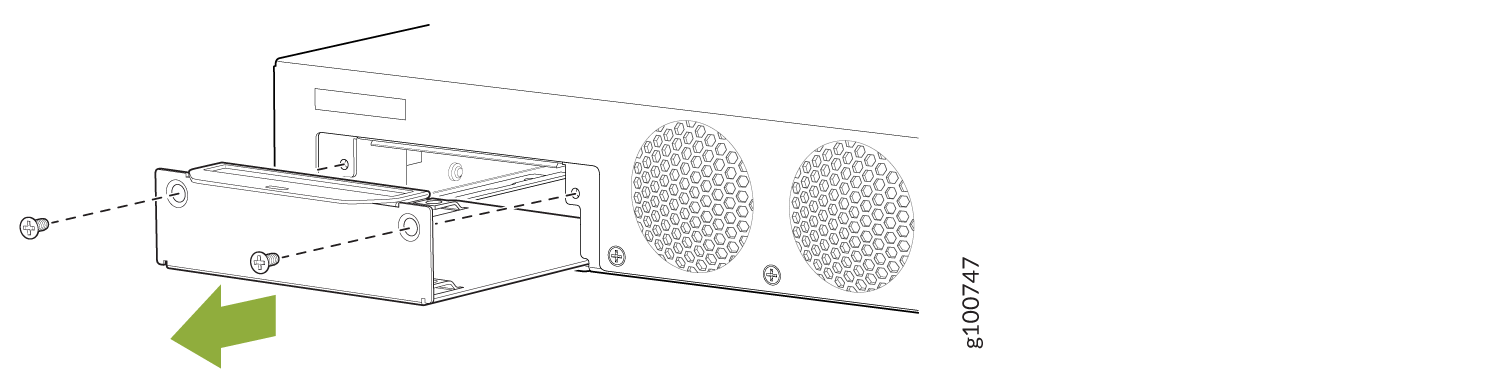
- Remove the two screws securing the SSD cover plate located
on the rear panel, and remove the SSD tray from the slot.Figure 1: Removing the SSD Tray
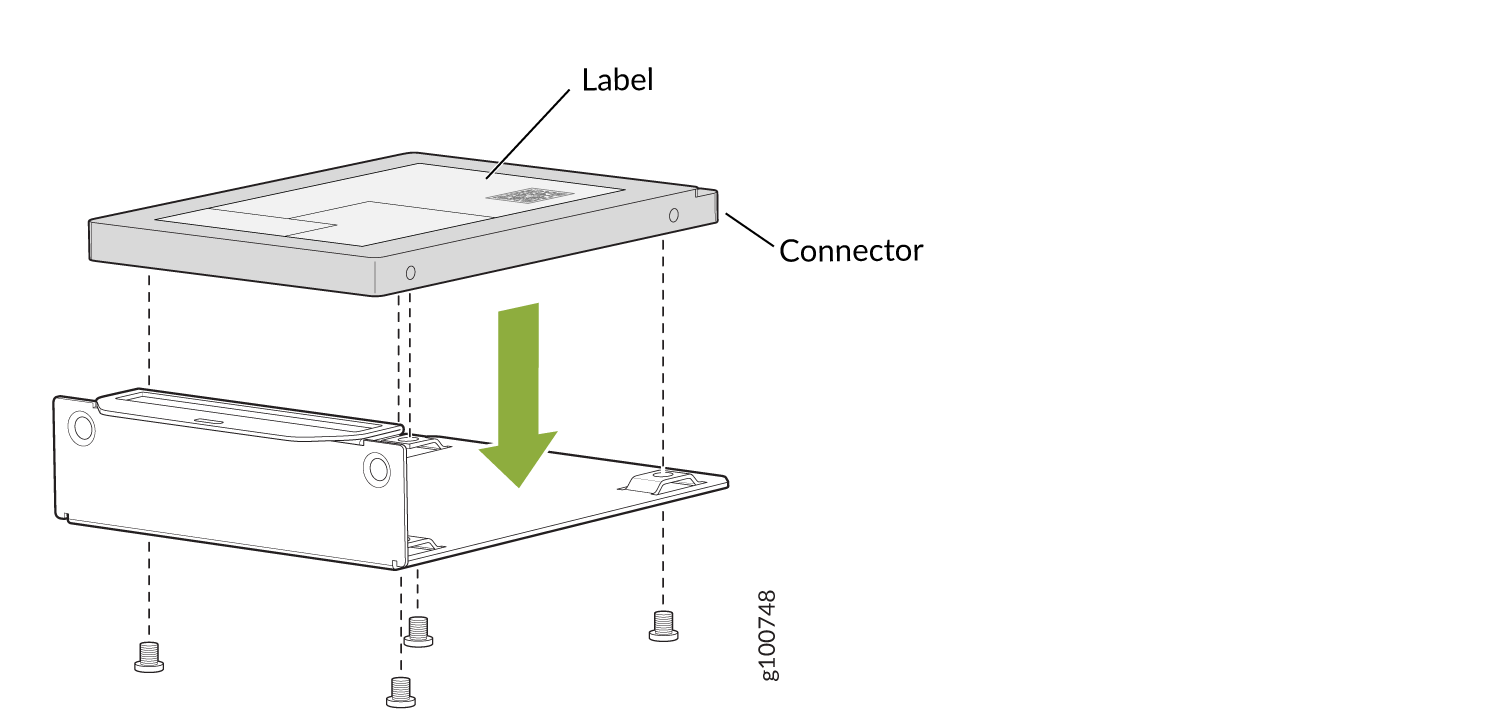
- Place the SSD on the tray, with the label facing up. Secure
the SSD to the tray by using four M3x6 mm screws. Apply between 4.5
in.-lb (0.51 N-m) and 6 in.-lb (0.67 N-m) of torque to each screw.Figure 2: Securing the SSD to the SSD Tray
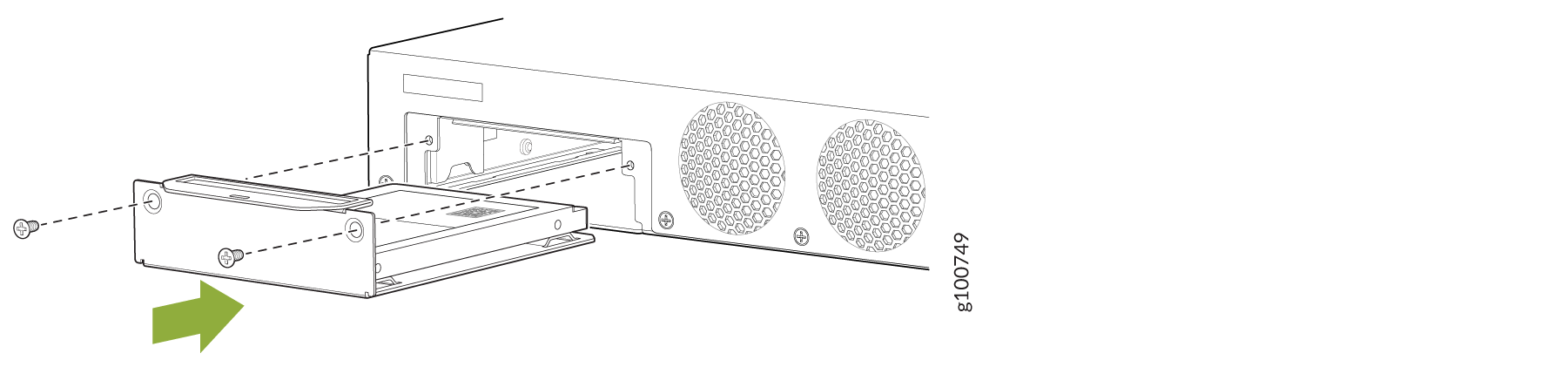
- Slide the SSD tray into the slot and secure the cover
plate.Figure 3: Installing the SSD
- Power on the services gateway.
If the SSD is unformatted, the SSD is formatted during the bootup process. A single partition in the Unix (UFS) format is created, which occupies the entire SSD. The partition is mounted on the /var/ssd directory automatically. A symbolic link (symlink) from the /mfs/var/traffic-log directory to the /var/ssd/traffic-log directory is created.
- Verify that the SSD information is displayed in the output
of the
show chassis hardware detailandshow system storage detailcommands.user@host> show chassis hardware detail Hardware inventory: Item Version Part number Serial number Description Chassis CZ2916AF0098 SRX345 Routing Engine REV 0x07 650-065042 CZ2916AF0098 RE-SRX345 da0 7718 MB ATP CG eUSB Nand Flash ad0 95396 MB SFSA100GQ1AA4TO-C-LB-21 000060158419A3000068 Hard Disk usb0 (addr 1) product 0x0000 0 vendor 0x0000 uhub0 usb0 (addr 2) product 0x1000 4096 vendor 0x090c umass0 FPC 0 FPC PIC 0 8xGE,8xGE SFP Base PIC Xcvr 12 REV 01 740-021308 AD154130TYA SFP+-10G-SR FPC 1 REV 01 650-073957 AG49041294 FPC PIC 0 LTE for AA mPIM FPC 2 REV 06 750-064613 BCAN2181 FPC PIC 0 1x Serial mPIM (RoHS) FPC 3 REV 09 750-064612 BCBB9371 FPC PIC 0 1x VDSL2 mPIM (RoHS) FPC 4 REV 06 750-064611 BCAZ1189 FPC PIC 0 1x T1E1 mPIM (RoHS) Power Supply 0user@host> show system storage detail Filesystem 1024-blocks Used Avail Capacity Mounted on /dev/da0s1a 592690 400812 144464 74% / devfs 1 1 0 100% /dev /dev/md0 20012 11884 6528 65% /junos /cf/packages 592690 400812 144464 74% /junos/cf/packages devfs 1 1 0 100% /junos/cf/dev /dev/md1 1383532 1383532 0 100% /junos /cf 20012 11884 6528 65% /junos/cf devfs 1 1 0 100% /junos/dev/ /cf/packages 592690 400812 144464 74% /junos/cf/packages1 procfs 4 4 0 100% /proc /dev/bo0s3e 189432 20 174258 0% /config /dev/bo0s3f 5239224 27584 4792504 1% /cf/var /dev/md2 1056324 100514 871306 10% /mfs /cf/var/jail 5239224 27584 4792504 1% /jail/var /cf/var/jails/rest-api 5239224 27584 4792504 1% /web-api/var /cf/var/log 5239224 27584 4792504 1% /jail/var/log devfs 1 1 0 100% /jail/dev /dev/md3 1884 4 1730 0% /jail/mfs /dev/ssd 96138198 3406 88443738 0% /var/ssd
