Connect the QFX5120 to the Network
Install a Transceiver
Before you install a transceiver in a device, ensure that you have taken the necessary precautions for safe handling of lasers (see Laser and LED Safety Guidelines and Warnings).
Ensure that you have a rubber safety cap available to cover the transceiver.
The transceivers for Juniper Networks devices are hot-removable and hot-insertable field-replaceable units (FRUs). You can remove and replace the transceivers without powering off the device or disrupting the device functions.
After you insert a transceiver or after you change the media-type configuration, wait for 6 seconds for the interface to display operational commands.
We recommend that you use only optical transceivers and optical connectors purchased from Juniper Networks with your Juniper Networks device.
The Juniper Networks Technical Assistance Center (JTAC) provides complete support for Juniper-supplied optical modules and cables. However, JTAC does not provide support for third-party optical modules and cables that are not qualified or supplied by Juniper Networks. If you face a problem running a Juniper device that uses third-party optical modules or cables, JTAC may help you diagnose host-related issues if the observed issue is not, in the opinion of JTAC, related to the use of the third-party optical modules or cables. Your JTAC engineer will likely request that you check the third-party optical module or cable and, if required, replace it with an equivalent Juniper-qualified component.
Use of third-party optical modules with high-power consumption (for example, coherent ZR or ZR+) can potentially cause thermal damage to or reduce the lifespan of the host equipment. Any damage to the host equipment due to the use of third-party optical modules or cables is the users’ responsibility. Juniper Networks will accept no liability for any damage caused due to such use.
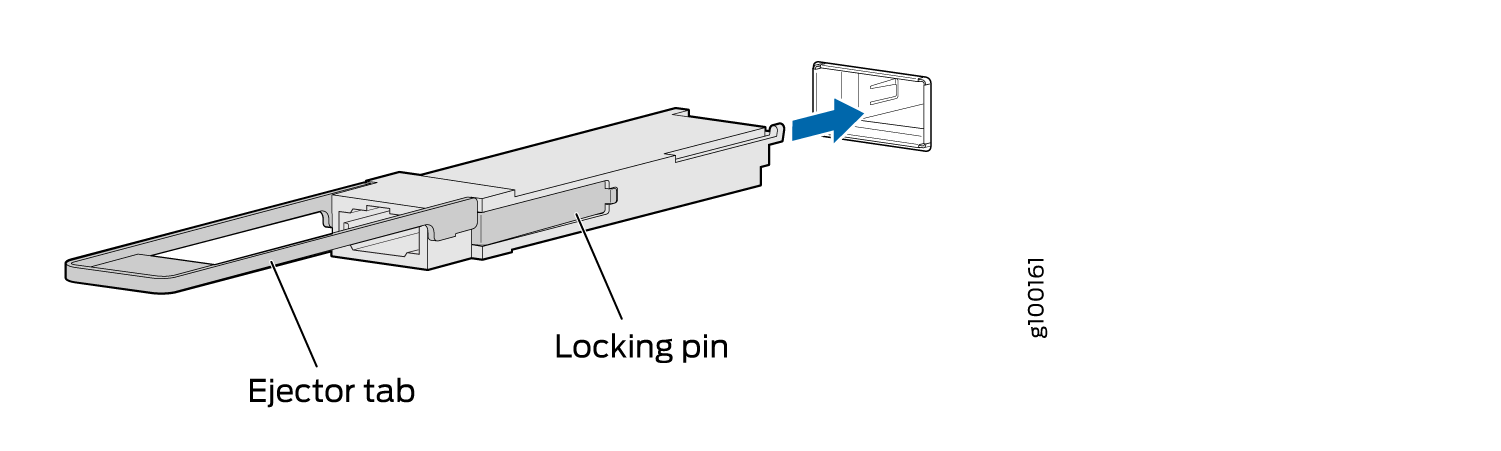
Figure 1 shows how to install a QSFP+ transceiver. The procedure is the same for all types of transceivers except the QSFP28 and CFP transceivers.
To install a transceiver:
To prevent electrostatic discharge (ESD) damage to the transceiver, do not touch the connector pins at the end of the transceiver.
1 — Ejector lever | 3 — Port |
2 — Transceiver |
Install a QSFP28 Transceiver
Before you install a transceiver in a device, ensure that you have taken the necessary precautions for safe handling of lasers (see Laser and LED Safety Guidelines and Warnings).
Ensure that you have a rubber safety cap available to cover the transceiver.
The transceivers for Juniper Networks devices are hot-removable and hot-insertable field-replaceable units (FRUs). You can remove and replace the transceivers without powering off the device or disrupting the device functions.
After you insert a transceiver or after you change the media-type configuration, wait for 6 seconds for the interface to display operational commands.
We recommend that you use only optical transceivers and optical connectors purchased from Juniper Networks with your Juniper Networks device.
The Juniper Networks Technical Assistance Center (JTAC) provides complete support for Juniper-supplied optical modules and cables. However, JTAC does not provide support for third-party optical modules and cables that are not qualified or supplied by Juniper Networks. If you face a problem running a Juniper device that uses third-party optical modules or cables, JTAC may help you diagnose host-related issues if the observed issue is not, in the opinion of JTAC, related to the use of the third-party optical modules or cables. Your JTAC engineer will likely request that you check the third-party optical module or cable and, if required, replace it with an equivalent Juniper-qualified component.
Use of third-party optical modules with high-power consumption (for example, coherent ZR or ZR+) can potentially cause thermal damage to or reduce the lifespan of the host equipment. Any damage to the host equipment due to the use of third-party optical modules or cables is the users’ responsibility. Juniper Networks will accept no liability for any damage caused due to such use.
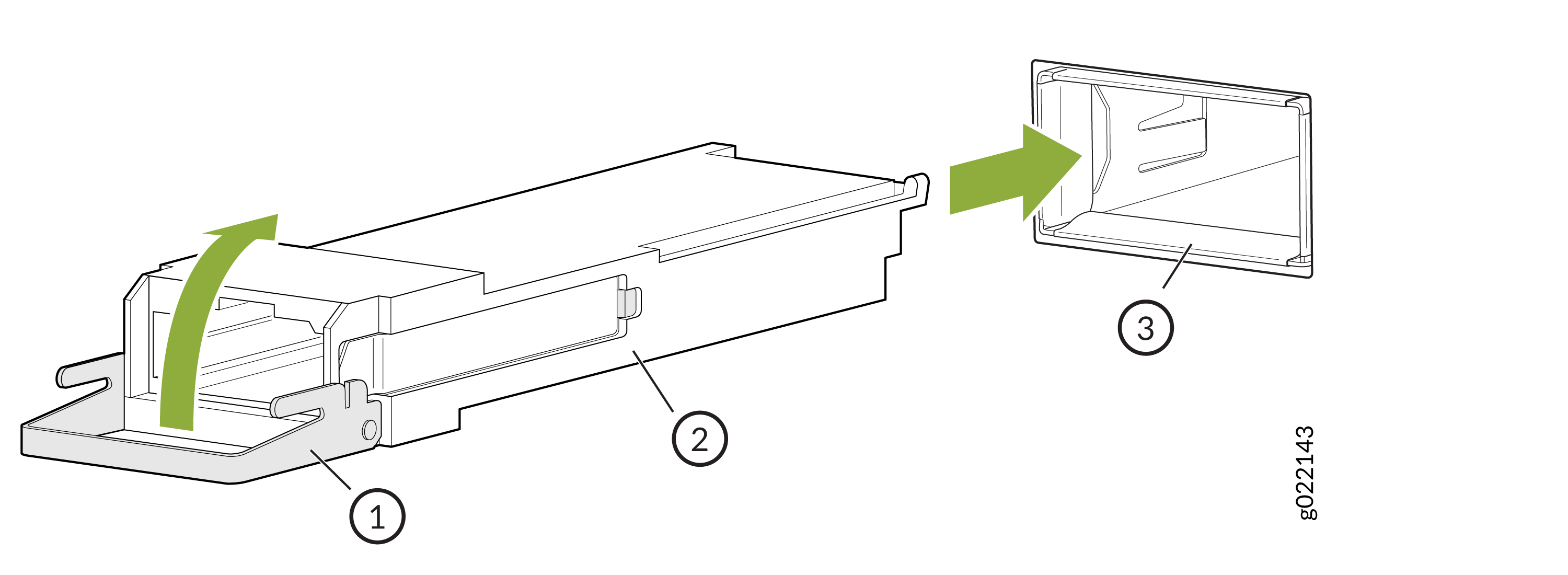
To install a QSFP28 transceiver (see Figure 2):
Connect a Fiber-Optic Cable
Before you connect a fiber-optic cable to an optical transceiver installed in a device, take the necessary precautions for safe handling of lasers (see Laser and LED Safety Guidelines and Warnings).
To connect a fiber-optic cable to an optical transceiver installed in a device:
Do not look directly into a fiber-optic transceiver or into the ends of fiber-optic cables. Fiber-optic transceivers and fiber-optic cables connected to transceivers emit laser light that can damage your eyes.