Connecting Power to a DC-Powered MX960 Router with Normal-Capacity Power Supplies
Do not mix AC and DC power supply modules within the same device. Mixing currents can damage the device.
Before you perform DC power procedures, ensure there is no power to the DC circuit. To ensure that all power is off, locate the circuit breaker on the panel board that services the DC circuit, switch the circuit breaker to the off position, and tape the switch handle of the circuit breaker in the off position.
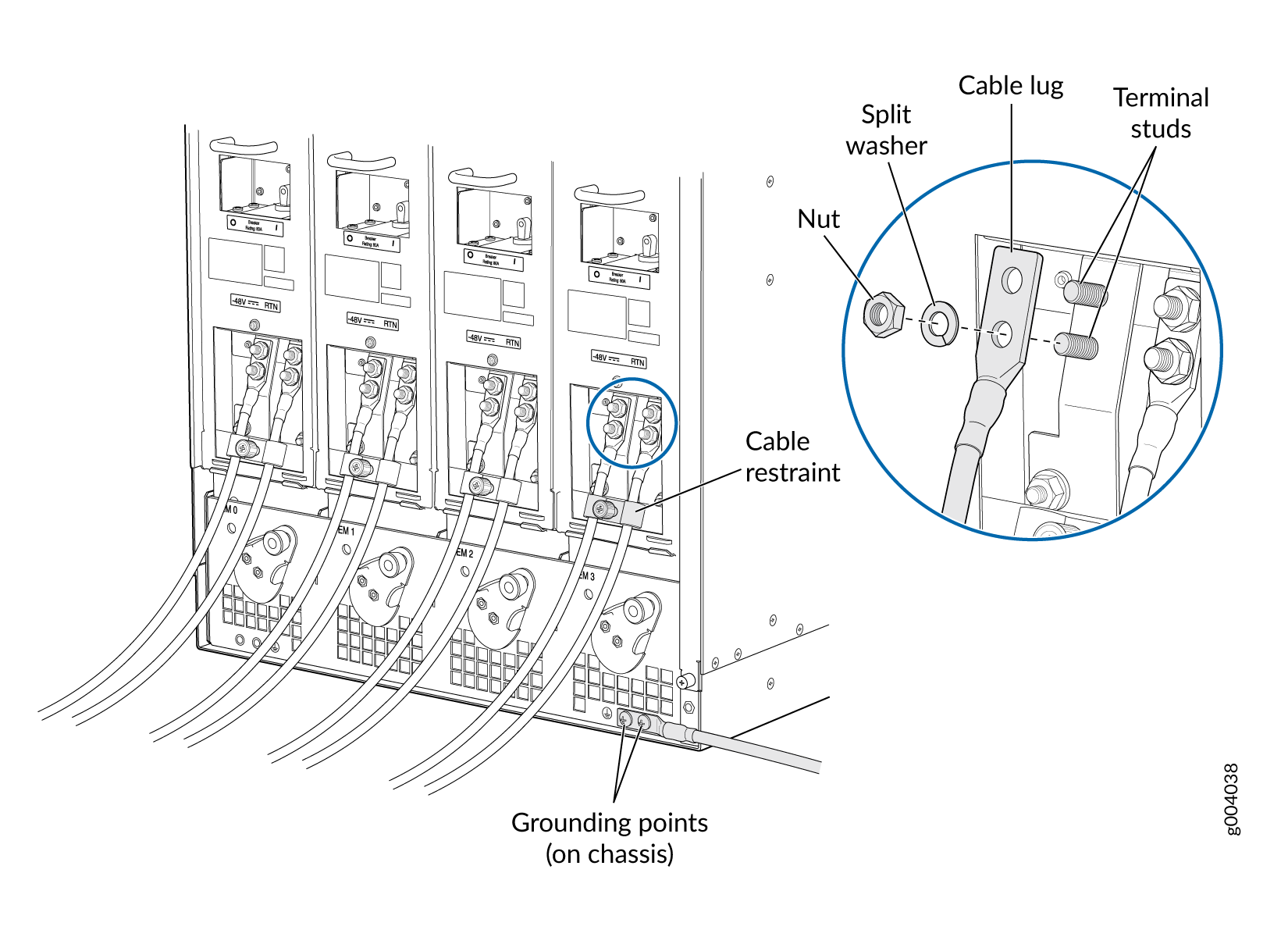
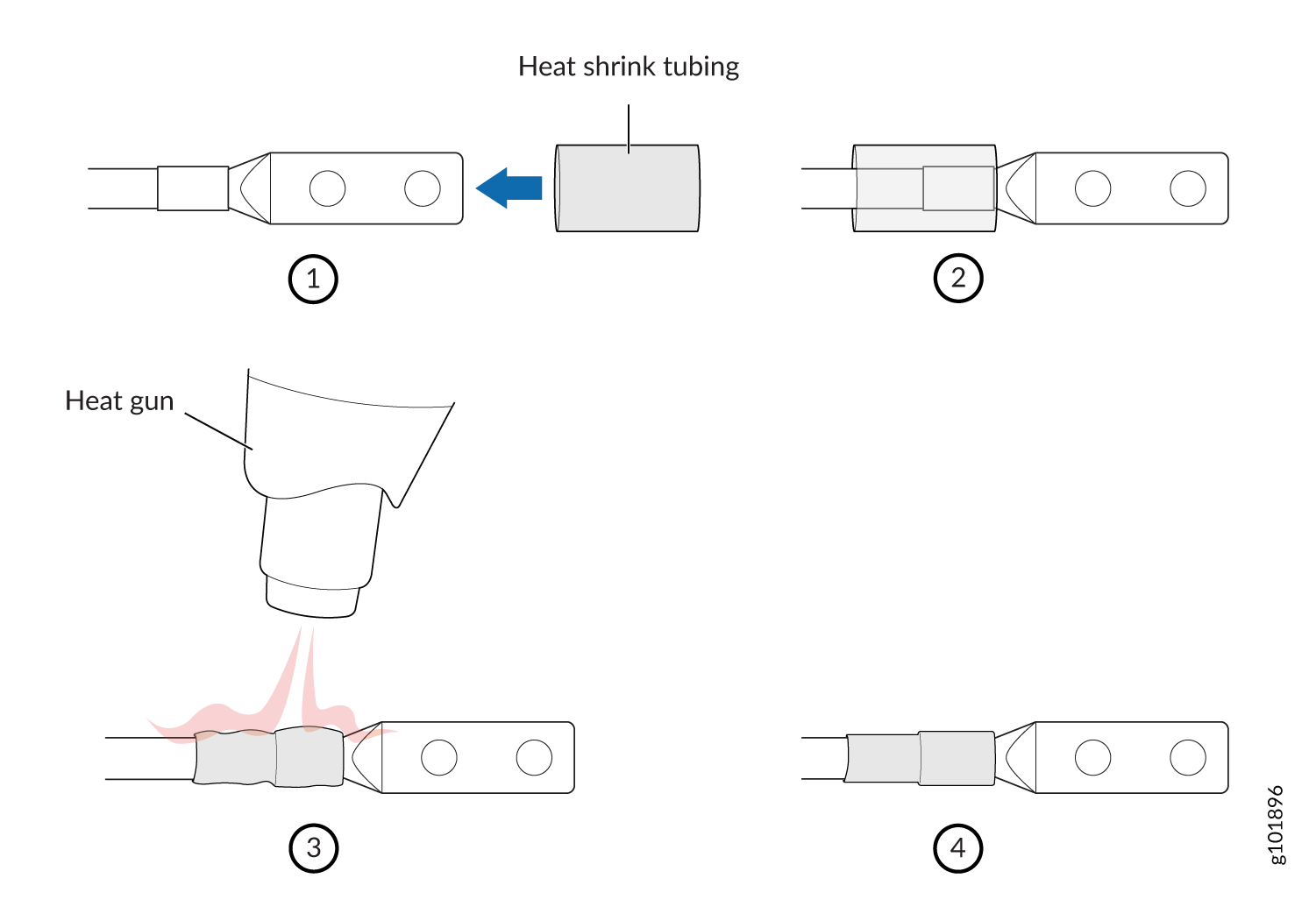
You connect DC power to the router by attaching power cables from the external DC power sources to the terminal studs on the power supply faceplates. You must provide the power cables (the cable lugs are supplied with the router).
To connect the DC source power cables to the router: