MX960 Flexible PIC Concentrator Description
A Flexible PIC Concentrator (FPC) occupies two Dense Port Concentrator (DPC) slots on an MX Series router. The MX960 router has 11 dedicated DPC slots and one multifunction slot that supports either a DPC, FPC, or Switch Control Board (SCB). The dedicated DPC slots are numbered 0 though 5, and 7 though 11, left to right. The multifunction slot is labeled 2/6. Up to six FPCs can be installed vertically in any two slots that support FPCs (see Figure 1). The interface corresponds to the lowest numbered DPC slot for which the FPC is installed.
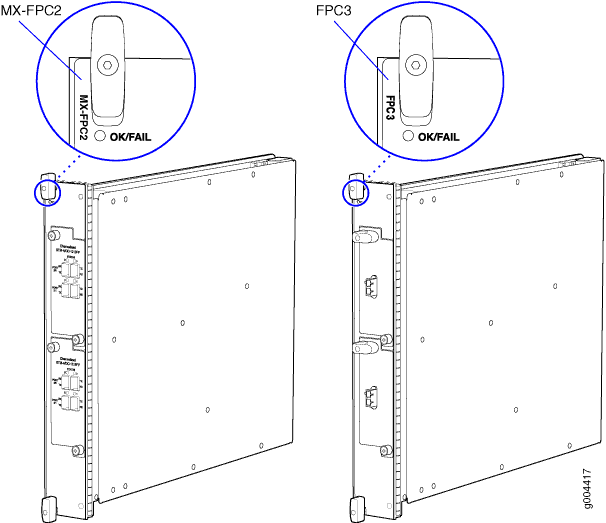
Figure 2 shows the typical FPCs supported on the MX960 router.
If a slot is not occupied by a DPC, an FPC, or an SCB, a blank panel must be installed to shield the empty slot and to allow cooling air to circulate properly through the router.
Each FPC supports up to two PICs. On an FPC2, one Packet Forwarding Engine receives incoming packets from the PICs installed on the FPC and forwards them through the switch planes to the appropriate destination port. On an FPC3, two Packet Forwarding Engines receive incoming packets from the PICs installed on the FPC and forward them through the switch planes to the appropriate destination port. The FPCs interface with the power supplies and SCBs.
FPCs are hot-removable and hot-insertable, as described in MX960 Component Redundancy. When you install an FPC into a functioning router, the Routing Engine downloads the FPC software, the FPC runs its diagnostics, and the PICs, housed on the FPC, are enabled. Forwarding continues uninterrupted during this process. When you remove or install an FPC, packet forwarding between other DPCs or FPCs is not affected.
FPC Components
Each FPC consists of the following components:
-
FPC card carrier, which includes two PIC slots
-
Up to two Packet Forwarding Engines, each consisting of one I-chip for Layer 3 processing and one Layer 2 network processor
-
Midplane connectors and power circuitry
-
Processor subsystem (PMB), which includes a 1.2-GHz CPU, system controller, 1 GB of SDRAM, and two Gigabit Ethernet interfaces
-
Two LEDs, located on the craft interface above the FPC, that display the status of the FPC and are labeled OK and FAIL
-
FPC online/offline button, located on the craft interface above the FPC
