Maintaining Fiber Optic Cables on the LWC
Connect a Fiber-Optic Cable to an LWC Device
Before you connect a fiber-optic cable to an optical transceiver installed in an LWC device, ensure that you have taken the necessary precautions for safe handling of lasers (see Laser and LED Safety Guidelines and Warnings for the LWC Devices).
You can connect fiber-optic cables to the field-replaceable unit (FRU) optical transceivers installed in LWC devices.
Do not look directly into a fiber-optic transceiver or into the ends of fiber-optic cables. Fiber-optic transceivers and fiber-optic cables connected to transceivers emit laser light that can damage your eyes.
Do not stare into the laser beam or view it directly with optical instruments even if the interface has been disabled.
To connect a fiber-optic cable to an optical transceiver installed in an LWC device:
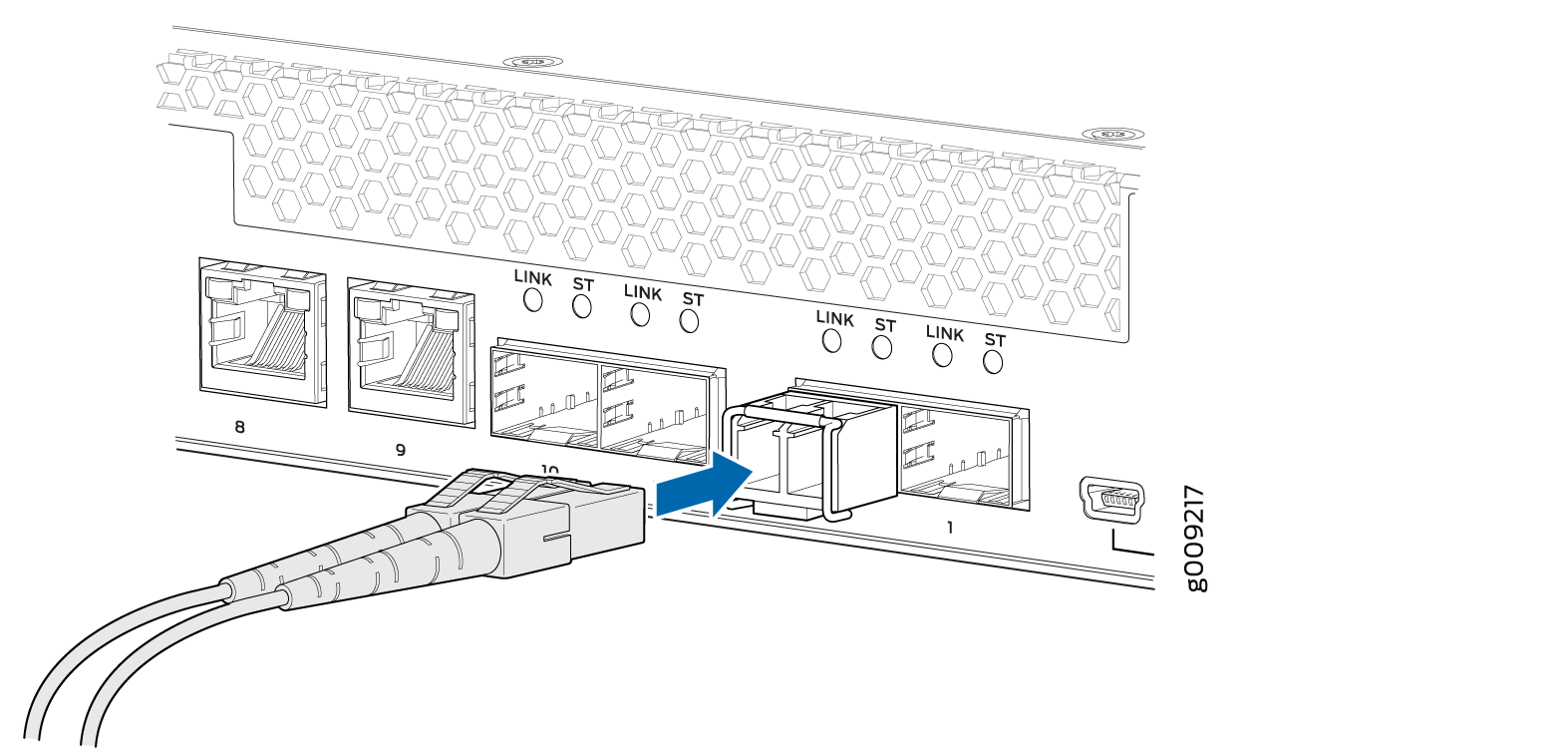
Disconnect a Fiber-Optic Cable from an LWC Device
Before you disconnect a fiber-optic cable from an optical transceiver installed in an LWC device, ensure that you have taken the necessary precautions for safe handling of lasers (see Laser and LED Safety Guidelines and Warnings for the LWC Devices).
Ensure that you have the following parts and tools available:
Rubber safety cap to cover the transceiver
Rubber safety cap to cover the fiber-optic cable connector
To disconnect a fiber-optic cable from an optical transceiver installed in the LWC device:
Maintaining Fiber-Optic Cables in an LWC Device
To maintain fiber-optic cables in LWC devices:
When you unplug a fiber-optic cable from a transceiver, place rubber safety caps over the transceiver and on the end of the cable.
Anchor fiber-optic cable to avoid stress on the connectors. When attaching a fiber-optic cable to a transceiver, be sure to secure the fiber-optic cable so that it is not supporting its own weight as it hangs to the floor. Never let a fiber-optic cable hang free from the connector.
Do not bend fiber-optic cables beyond their minimum bend radius. Bending the cables beyond their minimum bend radius can damage the cables and cause problems that are difficult to diagnose.
Frequent plugging and unplugging of fiber-optic cables in and out of optical instruments can damage the instruments, which are expensive to repair. Attach a short fiber extension to the optical equipment. Any wear and tear due to frequent plugging and unplugging is then absorbed by the short fiber extension, which is easier and less expensive to replace than the instruments.
Keep fiber-optic cable connections clean. Microdeposits of oil and dust in the canal of the transceiver or cable connector can cause loss of light, reduction in signal power, and possibly intermittent problems with the optical connection.
To clean the transceiver canal, use an appropriate fiber-cleaning device such as RIFOCS Fiber Optic Adaptor Cleaning Wands (part number 946). Follow the directions in the cleaning kit you use.
After cleaning the transceiver, make sure that the connector tip of the fiber-optic cable is clean. Use only an approved alcohol-free fiber-optic cable cleaning kit such as the Cletop-S® Fiber Cleaner. Follow the directions in the cleaning kit you use.
