Maintaining the JRR200 Cables and Connectors
Maintaining JRR200 Route Reflector Network Cables
Purpose
For optimum performance, verify the condition of the network cables.
Action
On a regular basis:
Secure excess cable in tidy loops that do not obstruct access to the device. Do not allow fastened loops of cable to dangle from the connector, because this stresses the cable at the fastening point. Putting fasteners on the loops helps maintain their shape.
Keep the cable connections clean and free of dust and other particles, which can cause drops in the received power level. Always inspect cables and clean them if necessary before connecting an interface.
Label both ends of the cables to identify them.
The following guidelines apply specifically to fiber-optic cables that connect to optical transceivers that are installed in Juniper Networks devices:
When you unplug a fiber-optic cable, always cover the cable connector with the rubber safety cap.
Anchor fiber-optic cables to avoid stress on the connectors. Be sure to secure fiber-optic cables so that they do not support their own weight as they hang to the floor. Never let fiber-optic cable hang free from the connector.
Avoid bending fiber-optic cable beyond its bend radius. An arc smaller than a few inches can damage the cable and cause problems that are difficult to diagnose.
Frequent plugging and unplugging of fiber-optic cable into and out of optical instruments can cause damage to the instruments that is expensive to repair. Instead, attach a short fiber extension to the optical equipment. Any wear and tear due to frequent plugging and unplugging is then absorbed by the short fiber extension, which is easy and inexpensive to replace.
Keep fiber-optic cable connections clean. Small microdeposits of oil and dust in the canal of the transceiver or cable connector could cause loss of light, reducing signal power and possibly causing intermittent problems with the optical connection.
To clean the transceivers, use an appropriate fiber-cleaning device, such as RIFOCS Fiber Optic Adaptor Cleaning Wands (part number 946). Follow the directions for the cleaning kit you use.
After you clean an optical transceiver, make sure that the connector tip of the fiber-optic cable is clean. Use only an approved alcohol-free fiber-optic cable cleaning kit, such as the Opptex Cletop-S Fiber Cleaner. Follow the directions for the cleaning kit you use.
Replacing an SFP+ Transceiver on JRR200 Route Reflector
Small form-factor pluggable plus transceivers (SFP+) are enhanced SFP transceivers that provides support for data rates of up to 10 Gbps for fiber-optic or copper interfaces. You can remove and replace the SFP+ transceivers without powering off the device or disrupting device functions.
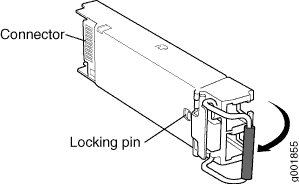
Removing an SFP+ Transceiver
To remove an SFP+ transceiver:
After removing a transceiver from the chassis, wait at least 30 seconds before reinserting it or inserting a transceiver into a different slot.
See Also
Installing an SFP+ Transceiver
To install an SFP+ transceiver:
