EX4400 Site Guidelines and Requirements
Environmental Requirements and Specifications for EX4400 Switches
You must install the switch in a rack or cabinet. You must house it in a dry, clean, well-ventilated, and temperature-controlled environment.
Follow these environmental guidelines:
Keep the site as dust-free as possible, because dust can clog air intake vents and filters, reducing the efficiency of the switch cooling system.
Maintain ambient airflow for normal switch operation. If the airflow is blocked or restricted, or if the intake air is too warm, the switch might overheat, leading to the switch temperature monitor shutting down the device to protect the hardware components.
Table 1 provides the required environmental conditions for normal switch operation for EX4400.
Altitude |
Relative Humidity |
Temperature |
Seismic |
|---|---|---|---|
No performance degradation up to 6000 feet at 104° F (1828.8 meters at 40° C) |
Normal operation ensured in relative humidity range of 5% through 90%, noncondensing |
|
Tested for Zone 4 earthquake according to NEBS GR-63-CORE, Issue 5. |
Install the EX4400 only in restricted-access areas, such as dedicated equipment rooms and equipment closets, in accordance with Articles 110-16, 110-17, and 110-18 of the National Electrical Code, ANSI/NFPA 70. Only skilled and instructed persons must access the device.
General Site Guidelines
Efficient device operation requires proper site planning. For the device to operate properly, you must ensure maintenance and proper layout of the equipment, rack or cabinet, and wiring closet.
To plan and create an acceptable operating environment for your device and prevent environmentally caused equipment failures:
Keep the area around the chassis free from dust and conductive material, such as metal flakes.
Follow the prescribed airflow guidelines to ensure that the cooling system functions properly. Ensure that the exhaust from other equipment does not blow into the intake vents of the device.
Follow the prescribed electrostatic discharge (ESD) prevention procedures to prevent damaging the equipment. Static discharge can cause components to fail completely or intermittently over time.
Install the device in a secure area, so that only authorized personnel can access the device.
Site Electrical Wiring Guidelines
Table 2 describes the factors you must consider while planning the electrical wiring at your site.
You must provide a properly grounded and shielded environment and use electrical surge-suppression devices.
Avertissement Vous devez établir un environnement protégé et convenablement mis à la terre et utiliser des dispositifs de parasurtension.
|
Site Wiring Factor |
Guidelines |
|---|---|
|
Signaling limitations |
If your site experiences any of the following problems, consult experts in electrical surge suppression and shielding:
|
|
Radio frequency interference |
To reduce or eliminate RFI from your site wiring, do the following:
|
|
Electromagnetic compatibility |
If your site is susceptible to problems with electromagnetic compatibility (EMC), particularly from lightning or radio transmitters, seek expert advice. Strong sources of electromagnetic interference (EMI) can cause:
|
Rack Requirements
You can mount the device on two-post racks or four-post racks.
|
Rack Requirement |
Guidelines |
|---|---|
|
Rack type |
A U is the standard rack unit defined by the Electronic Components Industry Association (ECIA) (http://www.ecianow.org). You can mount the device on a rack that provides bracket holes or hole patterns spaced at 1U (1.75 in. or 4.45 cm) increments and meets the size and strength requirements to support the weight. |
|
Mounting bracket hole spacing |
The holes in the mounting brackets are spaced at 1U (1.75 in. or 4.45 cm) so that the device can be mounted in any rack that provides holes spaced at that distance. |
|
Rack size and strength |
Ensure that the:
|
|
Rack connection to building structure |
|
Cabinet Requirements
You can mount the device in a cabinet that contains a 19-in. rack.
|
Cabinet Requirement |
Guidelines |
|---|---|
|
Cabinet size and clearance |
|
|
Cabinet airflow requirements |
When you mount the device in a cabinet:
|
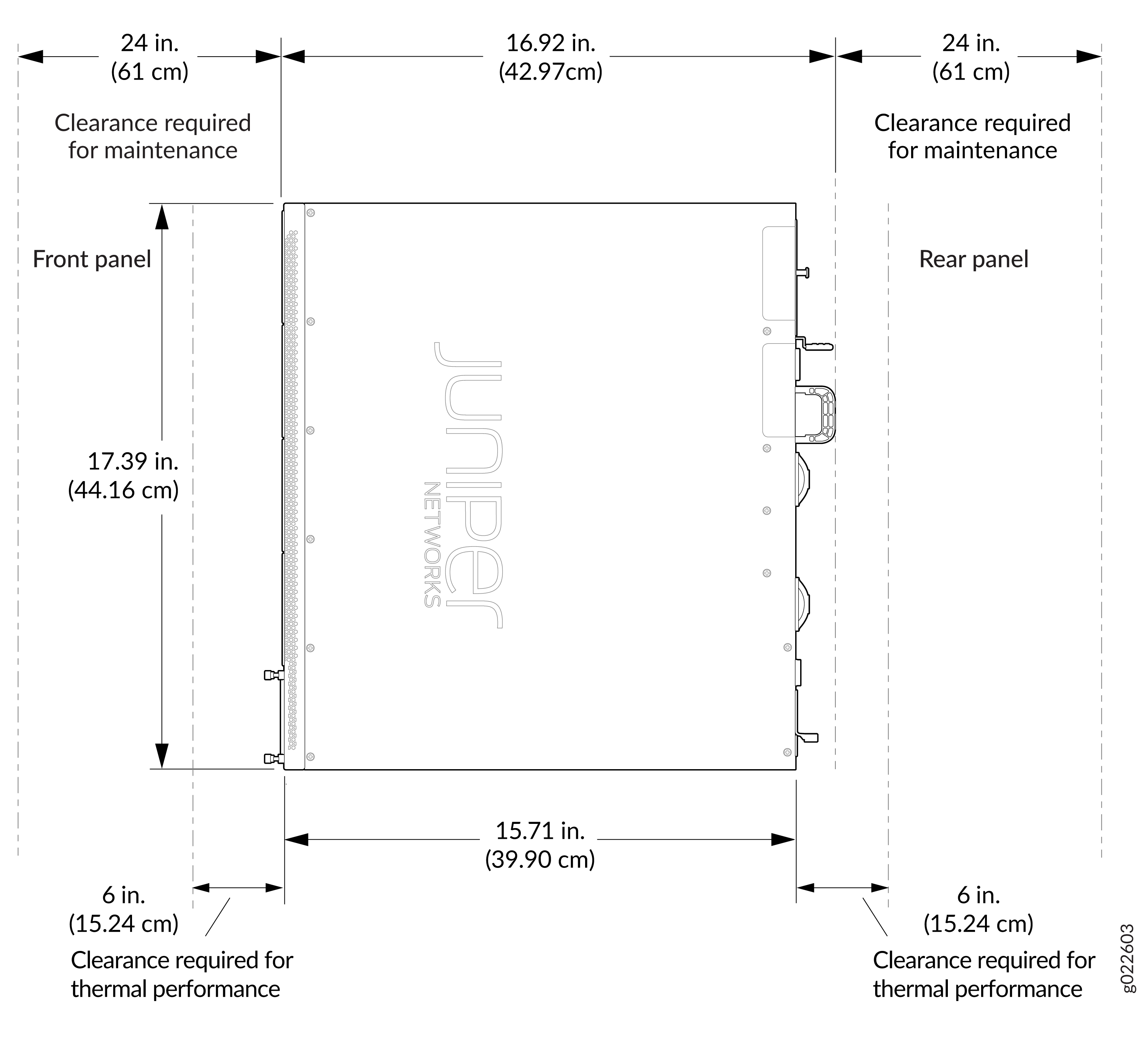
Clearance Requirements for Hardware Maintenance for EX4400 Switches
When planning the site for installing an EX4400 switch, follow these clearance requirements (see Figure 1):
For the cooling system to function properly, ensure that the airflow around the chassis is unrestricted.
If you are mounting the switch on a rack or cabinet along with other equipment, ensure that the hot air exhaust from other equipment does not blow into the cold air intake vents of the chassis.
Leave at least 6 in. (15.2 cm) clearance in front of and behind the chassis for airflow.
Leave at least 24 in. (61 cm) clearance in front of and behind the switch for service personnel to remove and install hardware components.
Figure 1: Clearance Requirements for Hardware Maintenance for EX4400 (AFO and AFI) Switches