Configuring VSTP
Virtual Spanning-Tree Protocol works with VLANs that require device compatibility.
Understanding VSTP
When using VSTP, we recommend that you enable VSTP on all VLANs that can receive VSTP bridge protocol data units (BPDUs).
Benefits of VSTP
VSTP has the following benefits:
-
Connects devices that are not part of the network
-
VSTP and RSTP are the only spanning-tree protocols that can be configured concurrently on a device.
VSTP Restrictions
VSTP has the following restrictions:
-
Devices running Layer 2 next-generation (L2NG) software support 510 VLANs on VSTP.
-
SRX Series Firewalls support only STP, RSTP, and MSTP; VSTP is not supported.
-
In devices that does not support Enhanced Layer 2 Software (ELS), VSTP can support up to 253 VLANs.
Recommended Uses of VSTP
You can use Juniper Networks devices with VSTP, which maintains a separate spanning tree instance per VLAN. One Spanning Tree per VLAN allows fine grain load balancing but requires more BPDU CPU processing as the number of VLANs increases. Juniper Networks devices only inter-operate with PVST+ and Rapid-PVST+. For more information, see VSTP and RPVST+ convergence on native-vlan 1 for EX Switches .
We recommend that you enable both VSTP and RSTP on the EX Series or QFX Series interface.
VSTP and RSTP are the only spanning-tree protocols that can be configured concurrently on a device. The maximum number of VLANs that can be supported by VSTP on a switch depends upon whether you are using Junos OS for EX Series and QFX Series switches with support for the Enhanced Layer 2 Software (ELS) configuration style or Junos OS that does not support ELS. For ELS details, see Using the Enhanced Layer 2 Software CLI. For additional VLANs, use RSTP.
The maximum number of VLANs supported by VSTP on a switch depends upon whether you are using Junos OS for EX Series and QFX Series switches with support for the Enhanced Layer 2 Software (ELS) configuration style or Junos OS that does not support ELS.
See Also
Global and Specific VSTP Configurations for Switches
Juniper Networks devices provide Layer 2 loop prevention through Spanning Tree Protocol (STP), Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP), Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP), and VLAN Spanning Tree Protocol (VSTP). The default factory configuration for devices that support ELS uses RSTP. This topic describes options for configuring VSTP on devices that support ELS.
When you configure VSTP, we recommend that you enable VSTP on all VLANs that can receive VSTP bridge protocol data units (BPDUs).
- Where Can I Configure VSTP?
- VSTP Commands to Configure All Interfaces
- VSTP Commands to Configure Specific Interfaces
- VSTP Commands to Disable Interfaces
Where Can I Configure VSTP?
You can configure VSTP at the global level:
For all interfaces on the switch
For all interfaces within all VLANs
For all interfaces within a specified VLAN
For all interfaces within a specified VLAN group
You can configure or disable VSTP for specific interfaces:
For a specific interface on the switch
For a specific interface within all VLANs
For a specific interface within a specified VLAN
For a specific interface within a specified VLAN group
-
If you configure VSTP on an interface at both the global and the specific VLAN level, the interface configuration that is defined at the specific VLAN level overrides the interface configuration that is defined at the global level.
-
If you specify VSTP to be configured on an interface that is not configured to belong to the VLAN (or VLANs), an error message is displayed.
-
If STP is needed on all the VLANs and the VLANs configured in the system are more than the maximum allowed VLANs for VSTP, then you must use RSTP instead of VSTP.
VSTP Commands to Configure All Interfaces
Command to configure VSTP on an individual interface on a switch:
[edit protocols vstp] user@switch@ set interface interface-name
Command to configure all VSTP interfaces on a switch:
[edit protocols vstp] user@switch# set interface all
Command to configure all VSTP interfaces for all VLANs:
When you issue the set protocols vstp vlan all interface
all command, you might not receive an error message when you
have exceed the limit of 5119 vports.
[edit protocols vstp] user@switch# set vlan all interface all
Command to configure all VSTP interfaces within a specified VLAN:
[edit protocols vstp] user@switch# set vlan (vlan-id |vlan-range |open-set-of-values) interface all interface all
When you configure VSTP with the set
protocol vstp vlan vlan-id interface interface-name command, the VLAN named default is excluded. You must manually configure a
VLAN with the name default to run VSTP.
Command to configure all VSTP interfaces within a specified VLAN group:
[edit protocols vstp] user@switch# set vlan-group vlan-group-name vlan (vlan-id |vlan-range |open-set-of-values) interface all
VSTP Commands to Configure Specific Interfaces
Command to configure a specific interface on a switch:
[edit protocols vstp] user@switch# set interface interface-name
Command to configure a specific interface within all VLANs:
[edit protocols vstp] user@switch# set vlan all interface interface-name
Ensure that the interface is a member of all VLANs before you add the interface to the VSTP configuration. If the interface is not a member of all VLANs, this VSTP configuration will fail when you try to commit it.
Command to configure a specific interface within a specific VLAN:
[edit protocols vstp] user@switch# set vlan vlan-id-or-vlan-range interface interface-name
Command to configure a specific interface within a specific VLAN group:
[edit protocols vstp] user@switch# set vlan-group vlan-group-name vlan (vlan-id |vlan-range |open-set-of-values) interface interface-name
VSTP Commands to Disable Interfaces
Command to disable VSTP on an individual interface on a switch:
[edit protocols vstp] user@switch@ set interface interface-name disable
Command to disable VSTP on a specific interface within a specific VLAN on a switch:
[edit protocols vstp] user@switch@ set vlan vlan-id interface interface-name disable
Command to disable one specific VSTP interface on all the VLANs on the switch:
[edit protocols vstp] user@switch@ set vlan all interface interface-name disable
Command to disable a specific VSTP interface within a specific VLAN group:
[edit protocols vstp] user@switch@ set vlan-group group group-name vlan (vlan-id |vlan-range | open-set-of-values) interface interface-name disable
You cannot disable the VSTP VLAN parameters for all VSTP interfaces.
Example: Configuring VSTP on a Trunk Port with Tagged Traffic
In 802.1ad provider bridge networks (stacked VLANs), single-tagged access ports and double-tagged trunk ports can co-exist in a single spanning tree context. In this mode, the VLAN Spanning Tree Protocol (VSTP) can send and receive untagged Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) bridge protocol data units (BPDUs) on Gigabit Ethernet (ge), 10 -Gigabit Ethernet (xe), and aggregated Ethernet (ae) interfaces. The untagged RSTP BPDUs interoperate with tagged VSTP BPDUs sent over the double-tagged trunk ports.
Double-tagging can be useful for Internet service providers, allowing them to use VLANs internally while mixing traffic from clients that are already VLAN-tagged.
This example shows how to configure the VSTP to send and receive standard untagged Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) bridge protocol data units (BPDUs) on access trunks that interoperate with tagged VSTP BPDUs sent over the double-tagged trunk ports.
Requirements
This example uses the following hardware and software components:
Two CE devices (MX Series routers with DPCE or MPC cards)
Two PE devices (MX Series routers with DPCE or MPC cards)
Junos OS Release 12.3 or later running on the PE devices
Overview
This example shows how to configure VSTP on a trunk port with tagged traffic.
Topology
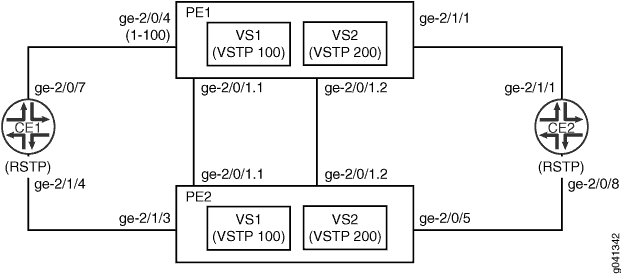
Figure 1 shows a sample topology in which two customer edge (CE) bridges are dual-homed to two provider edge (PE) devices. All of the PE-CE links are single-tagged trunks using C-VLANs 1-100. The core link between Devices PE1 and PE2 is a double-tagged trunk that carries traffic from both CE devices, using S-VLANs 100 and 200 to distinguish the CE traffic.
Two VSTP instances are created on the PE devices, one for each S-VLAN. The CE devices run the standard RSTP. The PE devices run VSTP on the core link while sending standard untagged RSTP BPDUs toward the CE devices.
Configuration
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure this example, copy the
following commands, paste them into a text file, remove any line breaks,
change any details necessary to match your network configuration,
and then copy and paste the commands into the CLI at the [edit] hierarchy level.
Device PE1
set interfaces ge-2/0/1 flexible-vlan-tagging set interfaces ge-2/0/1 encapsulation flexible-ethernet-services set interfaces ge-2/0/1 unit 1 vlan-id 100 set interfaces ge-2/0/1 unit 1 family bridge interface-mode trunk set interfaces ge-2/0/1 unit 1 family bridge inner-vlan-id-list 1-100 set interfaces ge-2/0/1 unit 2 vlan-id 200 set interfaces ge-2/0/1 unit 2 family bridge interface-mode trunk set interfaces ge-2/0/1 unit 2 family bridge inner-vlan-id-list 1-100 set interfaces ge-2/0/4 encapsulation ethernet-vpls set interfaces ge-2/0/4 unit 0 description to_CE1 set interfaces ge-2/0/4 unit 0 family bridge interface-mode trunk set interfaces ge-2/0/4 unit 0 family bridge vlan-id-list 1-100 set interfaces ge-2/1/1 unit 0 description to_CE2 set interfaces ge-2/1/1 unit 0 family bridge interface-mode trunk set interfaces ge-2/1/1 unit 0 family bridge vlan-id-list 1-100 set routing-instances vs1 instance-type virtual-switch set routing-instances vs1 interface ge-2/0/1.1 set routing-instances vs1 interface ge-2/0/4.0 set routing-instances vs1 protocols vstp vlan 100 interface ge-2/0/1 set routing-instances vs1 protocols vstp vlan 100 interface ge-2/0/4 access-trunk set routing-instances vs1 bridge-domains bd vlan-id-list 1-100 set routing-instances vs2 instance-type virtual-switch set routing-instances vs2 interface ge-2/0/1.2 set routing-instances vs2 interface ge-2/1/1.0 set routing-instances vs2 protocols vstp vlan 200 interface ge-2/0/1 set routing-instances vs2 protocols vstp vlan 200 interface ge-2/1/1 access-trunk set routing-instances vs2 bridge-domains bd vlan-id-list 1-100
Device PE2
set interfaces ge-2/0/1 flexible-vlan-tagging set interfaces ge-2/0/1 encapsulation flexible-ethernet-services set interfaces ge-2/0/1 unit 1 vlan-id 100 set interfaces ge-2/0/1 unit 1 family bridge interface-mode trunk set interfaces ge-2/0/1 unit 1 family bridge inner-vlan-id-list 1-100 set interfaces ge-2/0/1 unit 2 vlan-id 200 set interfaces ge-2/0/1 unit 2 family bridge interface-mode trunk set interfaces ge-2/0/1 unit 2 family bridge inner-vlan-id-list 1-100 set interfaces ge-2/1/3 description to_CE1 set interfaces ge-2/1/3 unit 0 family bridge interface-mode trunk set interfaces ge-2/1/3 unit 0 family bridge vlan-id-list 1-100 set interfaces ge-2/0/5 description to_CE2 set interfaces ge-2/0/5 unit 0 family bridge interface-mode trunk set interfaces ge-2/0/5 unit 0 family bridge vlan-id-list 1-100 set routing-instances vs1 instance-type virtual-switch set routing-instances vs1 interface ge-2/0/1.1 set routing-instances vs1 interface ge-2/1/3.0 set routing-instances vs1 protocols vstp vlan 100 interface ge-2/0/1 set routing-instances vs1 protocols vstp vlan 100 interface ge-2/1/3 access-trunk set routing-instances vs1 bridge-domains bd vlan-id-list 1-100 set routing-instances vs2 instance-type virtual-switch set routing-instances vs2 interface ge-2/0/1.2 set routing-instances vs2 interface ge-2/0/5.0 set routing-instances vs2 protocols vstp vlan 200 interface ge-2/0/1 set routing-instances vs2 protocols vstp vlan 200 interface ge-2/0/5 access-trunk set routing-instances vs2 bridge-domains bd vlan-id-list 1-100
Device CE1
set interfaces ge-2/0/7 unit 0 description to_PE1 set interfaces ge-2/0/7 unit 0 family bridge interface-mode trunk set interfaces ge-2/0/7 unit 0 family bridge vlan-id-list 1-100 set interfaces ge-2/1/4 unit 0 description to_PE2 set interfaces ge-2/1/4 unit 0 family bridge interface-mode trunk set interfaces ge-2/1/4 unit 0 family bridge vlan-id-list 1-100 set protocols rstp interface ge-2/0/7 set protocols rstp interface ge-2/1/4 set bridge-domains bd vlan-id-list 1-100
Device CE2
set interfaces ge-2/0/8 unit 0 description to_PE2 set interfaces ge-2/0/8 unit 0 family bridge interface-mode trunk set interfaces ge-2/0/8 unit 0 family bridge vlan-id-list 1-100 set interfaces ge-2/1/1 unit 0 description to_PE1 set interfaces ge-2/1/1 unit 0 family bridge interface-mode trunk set interfaces ge-2/1/1 unit 0 family bridge vlan-id-list 1-100 set protocols rstp interface ge-2/0/8 set protocols rstp interface ge-2/1/1 set bridge-domains bd vlan-id-list 1-100
Configuring PE1, PE2, CE1, and CE2
Step-by-Step Procedure
The following example requires you to navigate various levels in the configuration hierarchy. For information about navigating the CLI, see Using the CLI Editor in Configuration Mode in the CLI User Guide.
To configure Device PE1:
Configure the network interfaces.
[edit interfaces] user@PE1# set ge-2/0/1 flexible-vlan-tagging user@PE1# set ge-2/0/1 encapsulation flexible-ethernet-services user@PE1# set ge-2/0/1 unit 1 vlan-id 100 user@PE1# set ge-2/0/1 unit 1 family bridge interface-mode trunk user@PE1# set ge-2/0/1 unit 1 family bridge inner-vlan-id-list 1-100 user@PE1# set ge-2/0/1 unit 2 vlan-id 200 user@PE1# set ge-2/0/1 unit 2 family bridge interface-mode trunk user@PE1# set ge-2/0/1 unit 2 family bridge inner-vlan-id-list 1-100 user@PE1# set ge-2/0/4 encapsulation ethernet-vpls user@PE1#set ge-2/0/4 unit 0 description to_CE1 user@PE1# set ge-2/0/4 unit 0 family bridge interface-mode trunk user@PE1#set ge-2/0/4 unit 0 family bridge vlan-id-list 1-100 user@PE1# set ge-2/1/1 unit 0 description to_CE2 user@PE1# set ge-2/1/1 unit 0 family bridge interface-mode trunk user@PE1# set ge-2/1/1 unit 0 family bridge vlan-id-list 1-100
Configure the routing instances.
[edit routing-instances] user@PE1# set vs1 instance-type virtual-switch user@PE1# set vs1 interface ge-2/0/1.1 user@PE1# set vs1 interface ge-2/0/4.0 user@PE1# set vs1 protocols vstp vlan 100 interface ge-2/0/1 user@PE1# set vs1 protocols vstp vlan 100 interface ge-2/0/4 access-trunk user@PE1# set vs1 bridge-domains bd vlan-id-list 1-100 user@PE1# set vs2 instance-type virtual-switch user@PE1# set vs2 interface ge-2/0/1.2 user@PE1# set vs2 interface ge-2/1/1.0 user@PE1# set vs2 protocols vstp vlan 200 interface ge-2/0/1 user@PE1# set vs2 protocols vstp vlan 200 interface ge-2/1/1 access-trunk user@PE1# set vs2 bridge-domains bd vlan-id-list 1-100
Step-by-Step Procedure
To configure Device PE2:
Configure the interfaces.
[edit interfaces] user@PE2# set ge-2/0/1 flexible-vlan-tagging user@PE2# set ge-2/0/1 encapsulation flexible-ethernet-services user@PE2# set ge-2/0/1 unit 1 vlan-id 100 user@PE2# set ge-2/0/1 unit 1 family bridge interface-mode trunk user@PE2# set ge-2/0/1 unit 1 family bridge inner-vlan-id-list 1-100 user@PE2# set ge-2/0/1 unit 2 vlan-id 200 user@PE2# set ge-2/0/1 unit 2 family bridge interface-mode trunk user@PE2# set ge-2/0/1 unit 2 family bridge inner-vlan-id-list 1-100 user@PE2# set ge-2/1/3 description to_CE1 user@PE2# set ge-2/1/3 unit 0 family bridge interface-mode trunk user@PE2# set ge-2/1/3 unit 0 family bridge vlan-id-list 1-100 user@PE2# set ge-2/0/5 description to_CE2 user@PE2# set ge-2/0/5 unit 0 family bridge interface-mode trunk user@PE2# set ge-2/0/5 unit 0 family bridge vlan-id-list 1-100
Configure the routing instances.
[edit routing-instances] user@PE2# set vs1 instance-type virtual-switch user@PE2# set vs1 interface ge-2/0/1.1 user@PE2# set vs1 interface ge-2/1/3.0 user@PE2# set vs1 protocols vstp vlan 100 interface ge-2/0/1 user@PE2# set vs1 protocols vstp vlan 100 interface ge-2/1/3 access-trunk user@PE2# set vs1 bridge-domains bd vlan-id-list 1-100 user@PE2# set vs2 instance-type virtual-switch user@PE2# set vs2 interface ge-2/0/1.2 user@PE2# set vs2 interface ge-2/0/5.0 user@PE2# set vs2 protocols vstp vlan 200 interface ge-2/0/1 user@PE2# set vs2 protocols vstp vlan 200 interface ge-2/0/5 access-trunk user@PE2# set vs2 bridge-domains bd vlan-id-list 1-100
Step-by-Step Procedure
To configure CE1:
Configure the interfaces.
[edit interfaces] user@CE1# set ge-2/0/7 unit 0 description to_PE1 user@CE1# set ge-2/0/7 unit 0 family bridge interface-mode trunk user@CE1# set ge-2/0/7 unit 0 family bridge vlan-id-list 1-100 user@CE1# set ge-2/1/4 unit 0 description to_PE2 user@CE1# set ge-2/1/4 unit 0 family bridge interface-mode trunk user@CE1# set ge-2/1/4 unit 0 family bridge vlan-id-list 1-100
Configure the protocols.
[edit protocols] user@CE1# set rstp interface ge-2/0/7 user@CE1# set rstp interface ge-2/1/4
Configure the bridge domain.
[edit bridge-domains] user@CE1# set bd vlan-id-list 1-100
Step-by-Step Procedure
To configure CE2:
Configure the interfaces.
[edit interfaces] user@CE2# set ge-2/0/8 unit 0 description to_PE2 user@CE2# set ge-2/0/8 unit 0 family bridge interface-mode trunk user@CE2# set ge-2/0/8 unit 0 family bridge vlan-id-list 1-100 user@CE2# set ge-2/1/1 unit 0 description to_PE1 user@CE2# set ge-2/1/1 unit 0 family bridge interface-mode trunk user@CE2# set ge-2/1/1 unit 0 family bridge vlan-id-list 1-100
Configure the protocols.
[edit protocols] user@CE2# set rstp interface ge-2/0/8 user@CE2# set rstp interface ge-2/1/1
Configure the bridge domain.
[edit bridge-domains] user@CE2# set bd vlan-id-list 1-100
Results
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration by entering the show interfaces, show routing-instances, show protocols, and show bridge-domains commands. If the output does not display the intended configuration, repeat the instructions in this example to correct the configuration.
Device PE1
user@PE1# show interfaces
ge-2/0/1 {
flexible-vlan-tagging;
encapsulation flexible-ethernet-services;
unit 1 {
vlan-id 100;
family bridge {
interface-mode trunk;
inner-vlan-id-list 1-100;
}
}
unit 2 {
vlan-id 200;
family bridge {
interface-mode trunk;
inner-vlan-id-list 1-100;
}
}
}
ge-2/0/4 {
encapsulation ethernet-vpls;
unit 0 {
description to_CE1;
family bridge {
interface-mode trunk;
vlan-id-list 1-100;
}
}
}
ge-2/1/1 {
unit 0 {
description to_CE2;
family bridge {
interface-mode trunk;
vlan-id-list 1-100;
}
}
}
user@PE1# show routing-instances
vs1 {
instance-type virtual-switch;
interface ge-2/0/1.1;
interface ge-2/0/4.0;
protocols {
vstp {
vlan 100 {
interface ge-2/0/1;
interface ge-2/0/4 {
access-trunk;
}
}
}
}
bridge-domains {
bd {
vlan-id-list 1-100;
}
}
}
vs2 {
instance-type virtual-switch;
interface ge-2/0/1.2;
interface ge-2/0/1.0;
protocols {
vstp {
vlan 200 {
interface ge-2/0/1;
interface ge-2/1/1 {
access-trunk;
}
}
}
}
bridge-domains {
bd {
vlan-id-list 1-100;
}
}
}
Device PE2
user@PE2# show interfaces
ge-2/0/1 {
flexible-vlan-tagging;
encapsulation flexible-ethernet-services;
unit 1 {
vlan-id 100;
family bridge {
interface-mode trunk;
inner-vlan-id-list 1-100;
}
}
unit 2 {
vlan-id 200;
family bridge {
interface-mode trunk;
inner-vlan-id-list 1-100;
}
}
}
ge-2/0/5 {
description to_CE2;
unit 0 {
family bridge {
interface-mode trunk;
vlan-id-list 1-100;
}
}
}
ge-2/1/3 {
description to_CE1;
unit 0 {
family bridge {
interface-mode trunk;
vlan-id-list 1-100;
}
}
}
user@PE2# show routing-instances
vs1 {
instance-type virtual-switch;
interface ge-2/0/1.1;
interface ge-2/1/3.0;
protocols {
vstp {
vlan 100 {
interface ge-2/0/1;
interface ge-2/1/3 {
access-trunk;
}
}
}
}
bridge-domains {
bd {
vlan-id-list 1-100;
}
}
}
vs2 {
instance-type virtual-switch;
interface ge-2/0/1.2;
interface ge-2/0/5.0;
protocols {
vstp {
vlan 200 {
interface ge-2/0/1;
interface ge-2/0/5 {
access-trunk;
}
}
}
}
bridge-domains {
bd {
vlan-id-list 1-100;
}
}
}
Device CE1
user@CE1# show interfaces
ge-2/0/7 {
unit 0 {
description to_PE1;
family bridge {
interface-mode trunk;
vlan-id-list 1-100;
}
}
}
ge-2/1/4 {
unit 0 {
description to_PE2;
family bridge {
interface-mode trunk;
vlan-id-list 1-100;
}
}
}
user@CE1# show protocols
rstp {
interface ge-2/0/7;
interface ge-2/1/4;
}
user@CE1# show bridge-domains
bd {
vlan-id-list 1-100;
}
Device CE2
user@CE2 show interfaces
ge-2/0/8 {
unit 0 {
description to_PE2;
family bridge {
interface-mode trunk;
vlan-id-list 1-100;
}
}
}
ge-2/1/1 {
unit 0 {
description to_PE1;
family bridge {
interface-mode trunk;
vlan-id-list 1-100;
}
}
}
user@CE2# show protocols
rstp {
interface ge-2/0/8;
interface ge-2/1/1;
}
user@CE2# show bridge-domains
bd {
vlan-id-list 1-100;
}
If you are done configuring the device, enter commit from configuration mode.
Verification
Confirm that the configuration is working properly.
- Verifying That the Interfaces Are Operational
- Verifying the STP Bridge Parameters of the Routing Instances
- Displaying STP Statistics for the Configured Bridge
Verifying That the Interfaces Are Operational
Purpose
Verify that the interfaces are operational.
Action
From operational mode, enter the show spanning-tree interface routing-instance command.
user@PE1> show spanning-tree interface routing-instance vs1
Spanning tree interface parameters for VLAN 100
Interface Port ID Designated Designated Port State Role
port ID bridge ID Cost
ge-2/0/1 128:82 128:82 32868.0021590f37d0 20000 FWD DESG
ge-2/0/4 128:85 128:85 32868.0021590f37d0 20000 FWD DESG
Meaning
The output shows the status of the interfaces configured for VLAN 100.
Verifying the STP Bridge Parameters of the Routing Instances
Purpose
Verify the STP bridge parameters configured for the routing instances.
Action
From operational mode, enter the show spanning-tree bridge routing-instance command.
user@PE1> show spanning-tree bridge routing-instance vs1
STP bridge parameters
Routing instance name : vs1
Enabled protocol : RSTP
STP bridge parameters for VLAN 100
Root ID : 32868.00:21:59:0f:37:d0
Hello time : 2 seconds
Maximum age : 20 seconds
Forward delay : 15 seconds
Message age : 0
Number of topology changes : 2
Time since last topology change : 687 seconds
Local parameters
Bridge ID : 32868.00:21:59:0f:37:d0
Extended system ID : 100Meaning
The output shows the status of the STP bridge parameters for routing instance vs1.
Displaying STP Statistics for the Configured Bridge
Purpose
Display spanning-tree statistics for the configured bridge.
Action
From operational mode, enter the show spanning-tree statistics bridge command.
user@PE1> show spanning-tree statistics bridge STP Context : default STP Instance : 0 Number of Root Bridge Changes: 0 Number of Root Port Changes: 0 STP Context : x/default STP Instance : 0 Number of Root Bridge Changes: 0 Number of Root Port Changes: 0 STP Context : vs1 STP Instance : 0 Number of Root Bridge Changes: 2 Last Changed: Thu Sep 20 15:12:18 2012 Number of Root Port Changes: 1 Last Changed: Thu Sep 20 15:01:13 2012 Recent TC Received: ge-2/0/1.1 Received : Thu Sep 20 15:01:17 2012 STP Context : vs2 STP Instance : 0 Number of Root Bridge Changes: 2 Last Changed: Thu Sep 20 15:10:25 2012 Number of Root Port Changes: 2 Last Changed: Thu Sep 20 15:10:25 2012 Recent TC Received: ge-2/1/1.0 Received : Thu Sep 20 15:10:47 2012 STP Context : CE1/default STP Instance : 0 Number of Root Bridge Changes: 0 Number of Root Port Changes: 0 Recent TC Received: ge-2/1/4.0 Received : Thu Sep 20 15:12:15 2012
Meaning
The command output shows spanning-tree statistics for the configured bridge.
Reverting to RSTP or VSTP from Forced IEEE 802.1D STP
On devices that support ELS on which Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) or VLAN Spanning Tree Protocol (VSTP) has been forced to run as the original IEEE 802.1D Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) version, you can revert back to RSTP or VSTP.
To revert from the forced instance of the original IEEE 802.1D STP version to the originally configured RSTP or VSTP version:
