SCU with Layer 3 VPNs Configuration
Configuring SCU in a Layer 3 VPN
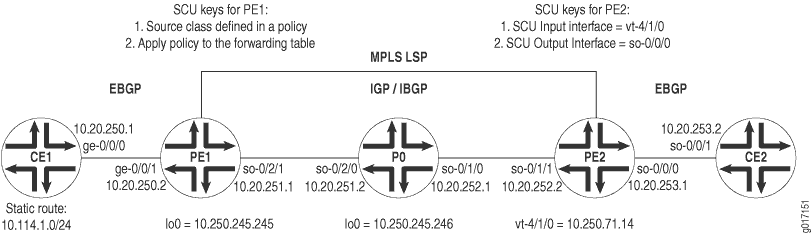
Figure 1 displays a Layer 3 VPN topology. CE1 and CE2 are customer edge (CE) routers connected by a VPN through provider routers PE1, P0, and PE2. EBGP is established between routers CE1 and PE1, IBGP connects routers PE1 and PE2 over an IS-IS/MPLS/LDP core, and a second EBGP connection flows between routers PE2 and CE2.
On Router CE1, begin your VPN by setting up an
EBGP connection to PE1. Install a static route of 10.114.1.0/24 and advertise this route to your EBGP neighbor.
Router CE1
[edit]
interfaces {
ge-0/0/0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.20.250.1/30;
}
}
}
}
routing-options {
static {
route 10.114.1.0/24 reject;
}
autonomous-system 100;
}
protocols {
bgp {
group to-pe1 {
local-address 10.20.250.1;
export inject-direct;
peer-as 300;
neighbor 10.20.250.2;
}
}
}
policy-options {
policy-statement inject-direct {
term 1 {
from {
protocol static;
route-filter 10.114.1.0/24 exact;
}
then accept;
}
term 2 {
from protocol direct;
then accept;
}
}
}
On PE1, complete the EBGP connection to CE1 through a VRF routing instance. Set an export policy for your VRF instance that puts BGP traffic into a community, and an import policy that accepts like community traffic from your VPN neighbor. Lastly, configure an IBGP relationship to Router PE2 that runs over an IS-IS, MPLS, and LDP core.
Router PE1
[edit]
interfaces {
ge-0/0/1 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.20.250.2/30;
}
}
}
so-0/2/1 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.20.251.1/30;
}
family iso;
family mpls;
}
}
lo0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.250.245.245/32;
}
family iso;
family mpls;
}
}
}
routing-options {
autonomous-system 300;
}
protocols {
mpls {
interface so-0/2/1;
}
bgp {
group ibgp {
type internal;
local-address 10.250.245.245;
family inet-vpn {
unicast;
}
neighbor 10.250.71.14;
}
}
isis {
interface so-0/2/1;
}
ldp {
interface so-0/2/1;
}
}
policy-options {
policy-statement red-import {
from {
protocol bgp;
community red-com;
}
then accept;
}
policy-statement red-export {
from protocol bgp;
then {
community add red-com;
accept;
}
}
community red-com members target:20:20;
}
routing-instances {
red {
instance-type vrf;
interface ge-0/0/1.0;
route-distinguisher 10.250.245.245:100;
vrf-import red-import;
vrf-export red-export;
protocols {
bgp {
group to-ce1 {
local-address 10.20.250.2;
peer-as 100;
neighbor 10.20.250.1;
}
}
}
}
}
On P0, connect the IBGP neighbors located at PE1 and PE2. Remember to include VPN-related protocols (MPLS, LDP, and IGP) on all interfaces.
Router P0
[edit]
interfaces {
so-0/1/0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.20.252.1/30;
}
family iso;
family mpls;
}
}
so-0/2/0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.20.251.2/30;
}
family iso;
family mpls;
}
}
lo0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.250.245.246/32;
}
family iso;
family mpls;
}
}
}
routing-options {
autonomous-system 300;
}
protocols {
mpls {
interface so-0/1/0;
interface so-0/2/0;
}
isis {
interface all;
}
ldp {
interface all;
}
}
On PE2, complete the IBGP relationship to Router PE1. Establish
an EBGP connection to CE2 through a VRF routing instance. Set an export
policy for the VRF instance that places BGP traffic into a community,
and an import policy that accepts like community traffic from the
VPN neighbor. Next, establish a policy that adds the static route
from CE1 to a source class called GOLD1. Also, export this
SCU policy into the forwarding table. Finally, set your vt interface as the SCU input interface and establish the CE-facing
interface so-0/0/0 as the SCU output interface.
Router PE2
[edit]
interfaces {
so-0/1/1 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.20.252.2/30;
}
family iso;
family mpls;
}
}
so-0/0/0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
accounting {
source-class-usage {
output;
}
}
address 10.20.253.1/30;
}
}
}
vt-4/1/0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
accounting {
source-class-usage {
input;
}
}
address 10.250.71.14/32;
}
family iso;
family mpls;
}
}
}
routing-options {
autonomous-system 300;
forwarding-table {
export inject-customer2-dest-class;
}
}
protocols {
mpls {
interface so-0/1/1;
interface vt-4/1/0;
}
bgp {
group ibgp {
type internal;
local-address 10.250.71.14;
family inet-vpn {
unicast;
}
neighbor 10.250.245.245;
}
}
isis {
interface so-0/1/1;
}
ldp {
interface so-0/1/1;
}
}
routing-instances {
red {
instance-type vrf;
interface so-0/0/0.0;
interface vt-4/1/0.0;
route-distinguisher 10.250.71.14:100;
vrf-import red-import;
vrf-export red-export;
protocols {
bgp {
group to-ce2 {
local-address 10.20.253.1;
peer-as 400;
neighbor 10.20.253.2;
}
}
}
}
}
policy-options {
policy-statement red-import {
from {
protocol bgp;
community red-com;
}
then accept;
}
policy-statement red-export {
from protocol bgp;
then {
community add red-com;
accept;
}
}
policy-statement inject-customer2-dest-class {
term term-gold1-traffic {
from {
route-filter 10.114.1.0/24 exact;
}
then source-class GOLD1;
}
}
community red-com members target:20:20;
}
On Router CE2, complete the VPN path by finishing the EBGP connection to PE2.
Router CE2
[edit]
interfaces {
so-0/0/1 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.20.253.2/30;
}
}
}
}
routing-options {
autonomous-system 400;
}
protocols {
bgp {
group to-pe2 {
local-address 10.20.253.2;
export inject-direct;
peer-as 300;
neighbor 10.20.253.1;
}
}
}
policy-options {
policy-statement inject-direct {
from {
protocol direct;
}
then accept;
}
}
Verifying Your Work
To verify that SCU is functioning properly in the Layer 3 VPN, use the following commands:
show interfaces interface-name statisticsshow interfaces source-class source-class-name interface-nameshow interfaces interface-name(extensive|detail)show route(extensive|detail)clear interface interface-name statistics
You should always verify SCU statistics at the
outbound SCU interface on which you configured the output statement. To check SCU functionality, follow these steps:
Clear all counters on your SCU-enabled router and verify they are empty.
Send a ping from the ingress CE router to the second CE router to generate SCU traffic across the SCU-enabled VPN route.
Verify that the counters are incrementing correctly on the outbound interface.
The following section shows the output of these commands used with the configuration example.
user@pe2> clear interfaces statistics all
user@pe2> show interfaces so-0/0/0.0 statistics
Logical interface so-0/0/0.0 (Index 6) (SNMP ifIndex 113)
Flags: Point-To-Point SNMP-Traps Encapsulation: PPP
Protocol inet, MTU: 4470
Source class Packets Bytes
GOLD1 0 0
Addresses, Flags: Is-Preferred Is-Primary
user@pe2> show interfaces source-class GOLD1 so-0/0/0.0
Protocol inet
Source class Packets Bytes
GOLD1 0 0
user@ce1> ping 10.20.253.2 source 10.114.1.1 rapid count 10000
user@scu> show interfaces source-class GOLD1 so-0/0/0.0
Protocol inet
Source class Packets Bytes
GOLD1 20000 1680000
user@scu> show interfaces so-0/0/0.0 statistics
Logical interface so-0/0/0.0 (Index 6) (SNMP ifIndex 113)
Flags: Point-To-Point SNMP-Traps Encapsulation: PPP
Protocol inet, MTU: 4470
Source class Packets Bytes
GOLD1 20000 1680000
Addresses, Flags: Is-Preferred Is-Primary
Destination: 10.20.253/24, Local: 10.20.253.1
