Troubleshooting Security Devices
Troubleshooting DNS Name Resolution in Logical System Security Policies (Primary Administrators Only)
Problem
Description
The address of a hostname in an address book entry that is used in a security policy might fail to resolve correctly.
Cause
Normally, address book entries that contain dynamic hostnames refresh automatically for SRX Series Firewalls. The TTL field associated with a DNS entry indicates the time after which the entry should be refreshed in the policy cache. Once the TTL value expires, the SRX Series Firewall automatically refreshes the DNS entry for an address book entry.
However, if the SRX Series Firewall is unable to obtain a response from the DNS server (for example, the DNS request or response packet is lost in the network or the DNS server cannot send a response), the address of a hostname in an address book entry might fail to resolve correctly. This can cause traffic to drop as no security policy or session match is found.
Solution
The primary administrator can use the show security dns-cache command to display
DNS cache information on the SRX Series Firewall. If the DNS cache information needs
to be refreshed, the primary administrator can use the clear security
dns-cache command.
These commands are only available to the primary administrator on devices that are configured for logical systems. This command is not available in user logical systems or on devices that are not configured for logical systems.
See Also
Troubleshooting the Link Services Interface
To solve configuration problems on a link services interface:
- Determine Which CoS Components Are Applied to the Constituent Links
- Determine What Causes Jitter and Latency on the Multilink Bundle
- Determine If LFI and Load Balancing Are Working Correctly
- Determine Why Packets Are Dropped on a PVC Between a Juniper Networks Device and a Third-Party Device
Determine Which CoS Components Are Applied to the Constituent Links
Problem
Description
You are configuring a multilink bundle, but you also have traffic without MLPPP encapsulation passing through constituent links of the multilink bundle. Do you apply all CoS components to the constituent links, or is applying them to the multilink bundle enough?
Solution
You can apply a scheduler map to the multilink bundle and its constituent links. Although you can apply several CoS components with the scheduler map, configure only the ones that are required. We recommend that you keep the configuration on the constituent links simple to avoid unnecessary delay in transmission.
Table 1 shows the CoS components to be applied on a multilink bundle and its constituent links.
Cos Component |
Multilink Bundle |
Constituent Links |
Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
Classifier |
Yes |
No |
CoS classification takes place on the incoming side of the interface, not on the transmitting side, so no classifiers are needed on constituent links. |
Forwarding class |
Yes |
No |
Forwarding class is associated with a queue, and the queue is applied to the interface by a scheduler map. The queue assignment is predetermined on the constituent links. All packets from Q2 of the multilink bundle are assigned to Q2 of the constituent link, and packets from all the other queues are queued to Q0 of the constituent link. |
Scheduler map |
Yes |
Yes |
Apply scheduler maps on the multilink bundle and the constituent link as follows:
|
Shaping rate for a per-unit scheduler or an interface-level scheduler |
No |
Yes |
Because per-unit scheduling is applied only at the end point, apply this shaping rate to the constituent links only. Any configuration applied earlier is overwritten by the constituent link configuration. |
Transmit-rate exact or queue-level shaping |
Yes |
No |
The interface-level shaping applied on the constituent links overrides any shaping on the queue. Thus apply transmit-rate exact shaping on the multilink bundle only. |
Rewrite rules |
Yes |
No |
Rewrite bits are copied from the packet into the fragments automatically during fragmentation. Thus what you configure on the multilink bundle is carried on the fragments to the constituent links. |
Virtual channel group |
Yes |
No |
Virtual channel groups are identified through firewall filter rules that are applied on packets only before the multilink bundle. Thus you do not need to apply the virtual channel group configuration to the constituent links. |
See Also
Determine What Causes Jitter and Latency on the Multilink Bundle
Problem
Description
To test jitter and latency, you send three streams of IP packets. All packets have the same IP precedence settings. After configuring LFI and CRTP, the latency increased even over a noncongested link. How can you reduce jitter and latency?
Solution
To reduce jitter and latency, do the following:
Make sure that you have configured a shaping rate on each constituent link.
Make sure that you have not configured a shaping rate on the link services interface.
Make sure that the configured shaping rate value is equal to the physical interface bandwidth.
If shaping rates are configured correctly, and jitter still persists, contact the Juniper Networks Technical Assistance Center (JTAC).
Determine If LFI and Load Balancing Are Working Correctly
Problem
Description
In this case, you have a single network that supports multiple services. The network transmits data and delay-sensitive voice traffic. After configuring MLPPP and LFI, make sure that voice packets are transmitted across the network with very little delay and jitter. How can you find out if voice packets are being treated as LFI packets and load balancing is performed correctly?
Solution
When LFI is enabled, data (non-LFI) packets are encapsulated with an MLPPP header and fragmented to packets of a specified size. The delay-sensitive, voice (LFI) packets are PPP-encapsulated and interleaved between data packet fragments. Queuing and load balancing are performed differently for LFI and non-LFI packets.
To verify that LFI is performed correctly, determine that packets are fragmented and encapsulated as configured. After you know whether a packet is treated as an LFI packet or a non-LFI packet, you can confirm whether the load balancing is performed correctly.
Solution Scenario—Suppose two Juniper Networks devices, R0 and R1, are connected by a multilink bundle lsq-0/0/0.0 that aggregates two serial links, se-1/0/0 and se-1/0/1. On R0 and R1, MLPPP and LFI are enabled on the link services interface and the fragmentation threshold is set to 128 bytes.
In this example, we used a packet generator to generate voice and data streams. You can use the packet capture feature to capture and analyze the packets on the incoming interface.
The following two data streams were sent on the multilink bundle:
100 data packets of 200 bytes (larger than the fragmentation threshold)
500 data packets of 60 bytes (smaller than the fragmentation threshold)
The following two voice streams were sent on the multilink bundle:
100 voice packets of 200 bytes from source port 100
300 voice packets of 200 bytes from source port 200
To confirm that LFI and load balancing are performed correctly:
Only the significant portions of command output are displayed and described in this example.
Verify packet fragmentation. From operational mode, enter the
show interfaces lsq-0/0/0command to check that large packets are fragmented correctly.user@R0#> show interfaces lsq-0/0/0 Physical interface: lsq-0/0/0, Enabled, Physical link is Up Interface index: 136, SNMP ifIndex: 29 Link-level type: LinkService, MTU: 1504 Device flags : Present Running Interface flags: Point-To-Point SNMP-Traps Last flapped : 2006-08-01 10:45:13 PDT (2w0d 06:06 ago) Input rate : 0 bps (0 pps) Output rate : 0 bps (0 pps) Logical interface lsq-0/0/0.0 (Index 69) (SNMP ifIndex 42) Flags: Point-To-Point SNMP-Traps 0x4000 Encapsulation: Multilink-PPP Bandwidth: 16mbps Statistics Frames fps Bytes bps Bundle: Fragments: Input : 0 0 0 0 Output: 1100 0 118800 0 Packets: Input : 0 0 0 0 Output: 1000 0 112000 0 ... Protocol inet, MTU: 1500 Flags: None Addresses, Flags: Is-Preferred Is-Primary Destination: 9.9.9/24, Local: 9.9.9.10Meaning—The output shows a summary of packets transiting the device on the multilink bundle. Verify the following information on the multilink bundle:The total number of transiting packets = 1000
The total number of transiting fragments=1100
The number of data packets that were fragmented =100
The total number of packets sent (600 + 400) on the multilink bundle match the number of transiting packets (1000), indicating that no packets were dropped.
The number of transiting fragments exceeds the number of transiting packets by 100, indicating that 100 large data packets were correctly fragmented.
Corrective Action—If the packets are not fragmented correctly, check your fragmentation threshold configuration. Packets smaller than the specified fragmentation threshold are not fragmented.Verify packet encapsulation. To find out whether a packet is treated as an LFI or non-LFI packet, determine its encapsulation type. LFI packets are PPP encapsulated, and non-LFI packets are encapsulated with both PPP and MLPPP. PPP and MLPPP encapsulations have different overheads resulting in different-sized packets. You can compare packet sizes to determine the encapsulation type.
A small unfragmented data packet contains a PPP header and a single MLPPP header. In a large fragmented data packet, the first fragment contains a PPP header and an MLPPP header, but the consecutive fragments contain only an MLPPP header.
PPP and MLPPP encapsulations add the following number of bytes to a packet:
PPP encapsulation adds 7 bytes:
4 bytes of header+2 bytes of frame check sequence (FCS)+1 byte that is idle or contains a flag
MLPPP encapsulation adds between 6 and 8 bytes:
4 bytes of PPP header+2 to 4 bytes of multilink header
Figure 1 shows the overhead added to PPP and MLPPP headers.
Figure 1: PPP and MLPPP Headers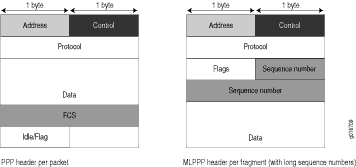
For CRTP packets, the encapsulation overhead and packet size are even smaller than for an LFI packet. For more information, see Example: Configuring the Compressed Real-Time Transport Protocol.
Table 2 shows the encapsulation overhead for a data packet and a voice packet of 70 bytes each. After encapsulation, the size of the data packet is larger than the size of the voice packet.
Table 2: PPP and MLPPP Encapsulation Overhead Packet Type
Encapsulation
Initial Packet Size
Encapsulation Overhead
Packet Size after Encapsulation
Voice packet (LFI)
PPP
70 bytes
4 + 2 + 1 = 7 bytes
77 bytes
Data fragment (non-LFI) with short sequence
MLPPP
70 bytes
4 + 2 + 1 + 4 + 2 = 13 bytes
83 bytes
Data fragment (non-LFI) with long sequence
MLPPP
70 bytes
4 + 2 + 1 + 4 + 4 = 15 bytes
85 bytes
From operational mode, enter the
show interfaces queuecommand to display the size of transmitted packet on each queue. Divide the number of bytes transmitted by the number of packets to obtain the size of the packets and determine the encapsulation type.Verify load balancing. From operational mode, enter the
show interfaces queuecommand on the multilink bundle and its constituent links to confirm whether load balancing is performed accordingly on the packets.user@R0> show interfaces queue lsq-0/0/0 Physical interface: lsq-0/0/0, Enabled, Physical link is Up Interface index: 136, SNMP ifIndex: 29 Forwarding classes: 8 supported, 8 in use Egress queues: 8 supported, 8 in use Queue: 0, Forwarding classes: DATA Queued: Packets : 600 0 pps Bytes : 44800 0 bps Transmitted: Packets : 600 0 pps Bytes : 44800 0 bps Tail-dropped packets : 0 0 pps RED-dropped packets : 0 0 pps … Queue: 1, Forwarding classes: expedited-forwarding Queued: Packets : 0 0 pps Bytes : 0 0 bps … Queue: 2, Forwarding classes: VOICE Queued: Packets : 400 0 pps Bytes : 61344 0 bps Transmitted: Packets : 400 0 pps Bytes : 61344 0 bps … Queue: 3, Forwarding classes: NC Queued: Packets : 0 0 pps Bytes : 0 0 bps …user@R0> show interfaces queue se-1/0/0 Physical interface: se-1/0/0, Enabled, Physical link is Up Interface index: 141, SNMP ifIndex: 35 Forwarding classes: 8 supported, 8 in use Egress queues: 8 supported, 8 in use Queue: 0, Forwarding classes: DATA Queued: Packets : 350 0 pps Bytes : 24350 0 bps Transmitted: Packets : 350 0 pps Bytes : 24350 0 bps ... Queue: 1, Forwarding classes: expedited-forwarding Queued: Packets : 0 0 pps Bytes : 0 0 bps … Queue: 2, Forwarding classes: VOICE Queued: Packets : 100 0 pps Bytes : 15272 0 bps Transmitted: Packets : 100 0 pps Bytes : 15272 0 bps … Queue: 3, Forwarding classes: NC Queued: Packets : 19 0 pps Bytes : 247 0 bps Transmitted: Packets : 19 0 pps Bytes : 247 0 bps …user@R0> show interfaces queue se-1/0/1 Physical interface: se-1/0/1, Enabled, Physical link is Up Interface index: 142, SNMP ifIndex: 38 Forwarding classes: 8 supported, 8 in use Egress queues: 8 supported, 8 in use Queue: 0, Forwarding classes: DATA Queued: Packets : 350 0 pps Bytes : 24350 0 bps Transmitted: Packets : 350 0 pps Bytes : 24350 0 bps … Queue: 1, Forwarding classes: expedited-forwarding Queued: Packets : 0 0 pps Bytes : 0 0 bps … Queue: 2, Forwarding classes: VOICE Queued: Packets : 300 0 pps Bytes : 45672 0 bps Transmitted: Packets : 300 0 pps Bytes : 45672 0 bps … Queue: 3, Forwarding classes: NC Queued: Packets : 18 0 pps Bytes : 234 0 bps Transmitted: Packets : 18 0 pps Bytes : 234 0 bpsMeaning—The output from these commands shows the packets transmitted and queued on each queue of the link services interface and its constituent links. Table 3 shows a summary of these values. (Because the number of transmitted packets equaled the number of queued packets on all the links, this table shows only the queued packets.)Table 3: Number of Packets Transmitted on a Queue Packets Queued
Bundle lsq-0/0/0.0
Constituent Link se-1/0/0
Constituent Link se-1/0/1
Explanation
Packets on Q0
600
350
350
The total number of packets transiting the constituent links (350+350 = 700) exceeded the number of packets queued (600) on the multilink bundle.
Packets on Q2
400
100
300
The total number of packets transiting the constituent links equaled the number of packets on the bundle.
Packets on Q3
0
19
18
The packets transiting Q3 of the constituent links are for keepalive messages exchanged between constituent links. Thus no packets were counted on Q3 of the bundle.
On the multilink bundle, verify the following:
The number of packets queued matches the number transmitted. If the numbers match, no packets were dropped. If more packets were queued than were transmitted, packets were dropped because the buffer was too small. The buffer size on the constituent links controls congestion at the output stage. To correct this problem, increase the buffer size on the constituent links.
The number of packets transiting Q0 (600) matches the number of large and small data packets received (100+500) on the multilink bundle. If the numbers match, all data packets correctly transited Q0.
The number of packets transiting Q2 on the multilink bundle (400) matches the number of voice packets received on the multilink bundle. If the numbers match, all voice LFI packets correctly transited Q2.
On the constituent links, verify the following:
The total number of packets transiting Q0 (350+350) matches the number of data packets and data fragments (500+200). If the numbers match, all the data packets after fragmentation correctly transited Q0 of the constituent links.
Packets transited both constituent links, indicating that load balancing was correctly performed on non-LFI packets.
The total number of packets transiting Q2 (300+100) on constituent links matches the number of voice packets received (400) on the multilink bundle. If the numbers match, all voice LFI packets correctly transited Q2.
LFI packets from source port
100transitedse-1/0/0, and LFI packets from source port200transitedse-1/0/1. Thus all LFI (Q2) packets were hashed based on the source port and correctly transited both constituent links.
Corrective Action—If the packets transited only one link, take the following steps to resolve the problem:Determine whether the physical link is
up(operational) ordown(unavailable). An unavailable link indicates a problem with the PIM, interface port, or physical connection (link-layer errors). If the link is operational, move to the next step.Verify that the classifiers are correctly defined for non-LFI packets. Make sure that non-LFI packets are not configured to be queued to Q2. All packets queued to Q2 are treated as LFI packets.
Verify that at least one of the following values is different in the LFI packets: source address, destination address, IP protocol, source port, or destination port. If the same values are configured for all LFI packets, the packets are all hashed to the same flow and transit the same link.
Use the results to verify load balancing.
Determine Why Packets Are Dropped on a PVC Between a Juniper Networks Device and a Third-Party Device
Problem
Description
You are configuring a permanent virtual circuit (PVC) between T1, E1, T3, or E3 interfaces on a Juniper Networks device and a third-party device, and packets are being dropped and ping fails.
Solution
If the third-party device does not have the same FRF.12 support as the Juniper Networks device or supports FRF.12 in a different way, the Juniper Networks device interface on the PVC might discard a fragmented packet containing FRF.12 headers and count it as a "Policed Discard."
As a workaround, configure multilink bundles on both peers, and configure fragmentation thresholds on the multilink bundles.
Troubleshooting Security Policies
- Synchronizing Policies Between Routing Engine and Packet Forwarding Engine
- Checking a Security Policy Commit Failure
- Verifying a Security Policy Commit
- Debugging Policy Lookup
Synchronizing Policies Between Routing Engine and Packet Forwarding Engine
Problem
Description
Security policies are stored in the routing engine and the packet forwarding engine. Security policies are pushed from the Routing Engine to the Packet Forwarding Engine when you commit configurations. If the security policies on the Routing Engine are out of sync with the Packet Forwarding Engine, the commit of a configuration fails. Core dump files may be generated if the commit is tried repeatedly. The out of sync can be due to:
A policy message from Routing Engine to the Packet Forwarding Engine is lost in transit.
An error with the routing engine, such as a reused policy UID.
Environment
The policies in the Routing Engine and Packet Forwarding Engine must be in sync for the configuration to be committed. However, under certain circumstances, policies in the Routing Engine and the Packet Forwarding Engine might be out of sync, which causes the commit to fail.
Symptoms
When the policy configurations are modified
and the policies are out of sync, the following error message displays
- error: Warning: policy might be out of sync between
RE and PFE <SPU-name(s)> Please request security
policies check/resync.
Solution
Use the show security policies checksum command to display the security policy checksum value and use the request security policies resync command to synchronize the
configuration of security policies in the Routing Engine and Packet
Forwarding Engine, if the security policies are out of sync.
See Also
Checking a Security Policy Commit Failure
Problem
Description
Most policy configuration failures occur during a commit or runtime.
Commit failures are reported directly on the CLI when you execute the CLI command commit-check in configuration mode. These errors are configuration errors, and you cannot commit the configuration without fixing these errors.
Solution
To fix these errors, do the following:
Review your configuration data.
Open the file /var/log/nsd_chk_only. This file is overwritten each time you perform a commit check and contains detailed failure information.
Verifying a Security Policy Commit
Problem
Description
Upon performing a policy configuration commit, if you notice that the system behavior is incorrect, use the following steps to troubleshoot this problem:
Solution
Operational show Commands—Execute the operational commands for security policies and verify that the information shown in the output is consistent with what you expected. If not, the configuration needs to be changed appropriately.
Traceoptions—Set the
traceoptionscommand in your policy configuration. The flags under this hierarchy can be selected as per user analysis of theshowcommand output. If you cannot determine what flag to use, the flag optionallcan be used to capture all trace logs.user@host#
set security policies traceoptions <flag all>
You can also configure an optional filename to capture the logs.
user@host# set security policies traceoptions <filename>
If you specified a filename in the trace options, you can look in the /var/log/<filename> for the log file to ascertain if any errors were reported in the file. (If you did not specify a filename, the default filename is eventd.) The error messages indicate the place of failure and the appropriate reason.
After configuring the trace options, you must recommit the configuration change that caused the incorrect system behavior.
Debugging Policy Lookup
Problem
Description
When you have the correct
configuration, but some traffic was incorrectly dropped or permitted,
you can enable the lookup flag in the security policies
traceoptions. The lookup flag logs the lookup related traces
in the trace file.
Solution
user@host# set security policies traceoptions <flag lookup>
