Configuring Port Mirroring for Remote Destinations
Layer 2 Port Mirroring to Remote Destination by Using Destination as VLAN
You configure port mirroring on an EX9200 switch to send copies of traffic to an output destination, such as an interface, a routing-instance, or a VLAN; and for the input traffic, you can configure a firewall filter term with various match conditions and actions.
When you configure VLAN as the output destination in a port-mirroring configuration, the traffic for each port-mirroring session is carried over a user-specified VLAN that is dedicated for that mirroring session in all participating switches. The mirrored traffic is copied onto that VLAN (also called as mirror VLAN) and forwarded to interfaces, which are members of the mirror VLAN. The destination interfaces, which are members of the mirror VLAN, can span across multiple switches in the network provided that the same remote mirroring VLAN is used for a mirroring session in all the switches.
You can use the port-mirror or port-mirror-instance action in the firewall filter
configuration when you mirror traffic to remote destinations by configuring
a VLAN as a port-mirroring output destination.
Configuration Layer 2 Port Mirroring to a Remote VLAN
EX9200 switches enable you to configure mirroring to send copies of packets to either a local interface for local monitoring or to a VLAN for remote monitoring. You can use mirroring to copy the following packets:
Packets entering or exiting a port
Packets entering or exiting a VLAN
Mirror only necessary packets to reduce potential performance impact. We recommend that you:
Disable port mirroring that you have configured when you are not using them.
Specify individual interfaces as input rather than specifying all interfaces as input in a port mirroring configuration.
Limit the amount of mirrored traffic by:
Using statistical sampling.
Setting ratios to select statistical samples.
Using firewall filters.
Configuring Port Mirroring to a Remote VLAN
To filter packets to be mirrored to a port-mirroring instance, create the instance and then use it as the action in the firewall filter. You can use firewall filters in both local and remote mirroring configurations.
If the same port-mirroring instance is used in multiple filters or terms, the packets are copied to the port-mirroring output port or port-mirroring VLAN only once.
To filter mirrored traffic, create a port-mirroring instance
under the [edit forwarding-options] hierarchy level, and
then create a firewall filter. The filter can use any of the available
match conditions and must have port-mirror-instance instance-name as an action. This action in the firewall
filter configuration provides the input to the port-mirroring instance.
To configure a port-mirroring instance with firewall filters:
Example: Configuring Layer 2 Port Mirroring to Remote VLAN
EX9200 switches enable you to configure mirroring to send copies of packets to either a local interface for local monitoring or to a VLAN for remote monitoring. You can use mirroring to copy these packets:
-
Packets entering or exiting a port
-
Packets entering or existing a VLAN
You can analyze the mirrored traffic by using a protocol analyzer application running on a remote monitoring station if you are sending mirrored traffic to an analyzer VLAN.
This topic includes two related examples that describe how to
mirror traffic entering ports on the switch to the remote-analyzer VLAN so that you can perform analysis from a remote monitoring station.
The first example shows how to mirror all traffic entering the ports
connected to employee computers. The second example shows the same
scenario but includes a filter to mirror only the employee traffic
going to the Web.
Mirror only necessary packets to reduce potential performance impact. We recommend that you:
-
Disable your configured mirroring sessions when you are not using them.
-
Specify individual interfaces as input to analyzers rather than specifying all interfaces as input.
-
Limit the amount of mirrored traffic by using firewall filters.
This example describes how to configure remote mirroring:
- Requirements
- Overview and Topology
- Mirroring Employee-to-Web Traffic for Remote Analysis
- Verification
Requirements
Before you configure remote mirroring, be sure that:
-
You have an understanding of mirroring concepts.
-
The interfaces that port-mirroring will use as output interfaces have been configured on the switch.
Overview and Topology
This topic includes two related examples that describe how to
configure mirroring to the remote-analyzer VLAN so that
analysis can be performed from a remote monitoring station. The first
example shows how to configure a switch to mirror all traffic from
employee computers. The second example shows the same scenario, but
the setup includes a filter to mirror only the employee traffic going
to the Web.
Figure 1 shows the network topology for both these example scenarios.
Topology
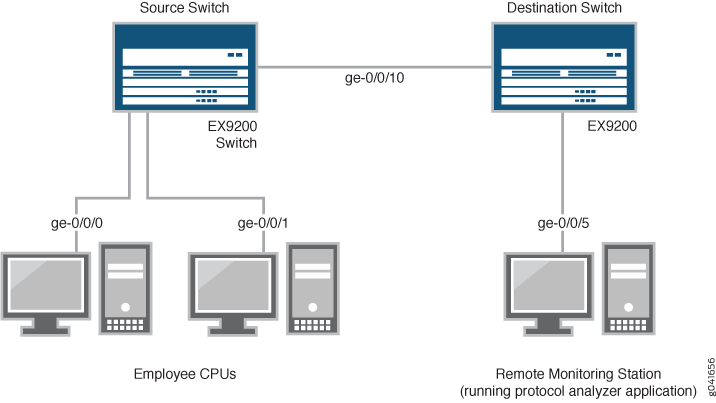
In this example:
-
Interface ge-0/0/0 is a Layer 2 interface, and interface ge-0/0/1 is a Layer 2 interface (both interfaces on the source switch) that serve as connections for employee computers.
-
Interface ge-0/0/10 is a Layer 2 interface that connects the source switch to the destination switch.
-
Interface ge-0/0/5 is a Layer 2 interface that connects the destination switch to the remote monitoring station.
-
VLAN
remote-analyzeris configured on all switches in the topology to carry the mirrored traffic.
Mirroring Employee-to-Web Traffic for Remote Analysis
To configure port mirroring for remote traffic analysis of employee-to-Web traffic, perform these tasks:
Procedure
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure port-mirroring to mirror employee traffic to the external Web, copy the following commands and paste them into the switch terminal window:
-
Copy and paste the following commands in the source switch terminal window:
[edit] set forwarding-options port-mirroring instance employee-web-monitor output vlan 999 set vlans remote-analyzer vlan-id 999 set interfaces ge-0/0/10 unit 0 family ethernet-switching interface-mode access set interfaces ge-0/0/10 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members 999 set firewall family ethernet-switching filter watch-employee term employee-to-corp from destination-address 192.0.2.16/28 set firewall family ethernet-switching filter watch-employee term employee-to-corp from source-address 192.0.2.16/28 set firewall family ethernet-switching filter watch-employee term employee-to-corp then accept set firewall family ethernet-switching filter watch-employee term employee-to-web from destination-port 80 set firewall family ethernet-switching filter watch-employee term employee-to-web then port-mirror-instance employee-web-monitor set interfaces ge-0/0/0 unit 0 family ethernet-switching filter input watch-employee set interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 0 family ethernet-switching filter input watch-employee
-
Copy and paste the following commands in the destination switch terminal window:
[edit] set vlans remote-analyzer vlan-id 999 set interfaces ge-0/0/10 unit 0 family ethernet-switching interface-mode access set interfaces ge-0/0/10 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members 999 set interfaces ge-0/0/5 unit 0 family ethernet-switching interface-mode access set interfaces ge-0/0/5 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members 999
Step-by-Step Procedure
To configure port mirroring of all traffic from the two
ports connected to employee computers to the remote-analyzer VLAN for use from a remote monitoring station:
-
On the source switch:
-
Configure the
employee-web-monitorport-mirroring instance:[edit ] user@switch# set interfaces ge-0/0/10 unit 0 family ethernet-switching port mode access user@switch# set forwarding-options port-mirroring instance employee-web-monitor output vlan 999
-
Configure the VLAN ID for the
remote-analyzerVLAN:[edit vlans] user@switch# set remote-analyzer vlan-id 999
-
Configure the interface to associate it with the
remote-analyzerVLAN:[edit interfaces] user@switch# set ge-0/0/10 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members 999
-
Configure the firewall filter called
watch-employee:[edit firewall family ethernet-switching] user@switch# set filter watch-employee term employee-to-corp from destination-address 192.0.2.16/28 user@switch# set filter watch-employee term employee-to-corp from source-address 192.0.2.16/28 user@switch# set filter watch-employee term employee-to-corp then accept user@switch# set filter watch-employee term employee-to-web from destination-port 80 user@switch# set filter watch-employee term employee-to-web then port-mirror-instance employee-web-monitor
In this configuration, the
employee-to-corpterm defines that traffic from destination-address192.0.2.16/28and source address192.0.2.16/28can be accepted to pass through the switch, and theemployee-to-webterm defines that traffic from port80must be sent to the port-mirroring instanceemployee-web-monitor. -
Apply the firewall filter to the employee interfaces:
[edit interfaces] user@switch# set ge-0/0/0 unit 0 family ethernet-switching filter input watch-employee user@switch# set ge-0/0/1 unit 0 family ethernet-switching filter input watch-employee
-
-
On the destination switch:
-
Configure the VLAN ID for the
remote-analyzerVLAN:[edit vlans] user@switch# set remote-analyzer vlan-id 999
-
Configure the interface on the destination switch for access mode and associate it with the
remote-analyzerVLAN:[edit interfaces] user@switch# set ge-0/0/10 unit 0 family ethernet-switching interface-mode access user@switch# set ge-0/0/10 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members 999
-
Configure the interface connected to the destination switch for access mode and associate it with the
remote-analyzerVLAN:[edit interfaces] user@switch# set ge-0/0/5 unit 0 family ethernet-switching interface-mode access user@switch# set ge-0/0/5 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members 999
-
Results
Check the results of the configuration on the source switch:
[edit]
user@switch> show
interfaces {
ge-0/0/10 {
unit 0 {
family ethernet-switching {
interface-mode access;
vlan {
members remote-analyzer;
}
}
}
}
ge-0/0/0 {
unit 0 {
family ethernet-switching {
filter {
input watch-employee;
}
}
}
}
ge-0/0/1 {
unit 0 {
family ethernet-switching {
filter {
input watch-employee;
}
}
}
}
}
firewall {
family ethernet-switching {
filter watch-employee {
term employee-to-corp {
from {
source-address {
192.0.2.16/28;
}
destination-address {
192.0.2.16/28;
}
}
then accept;
}
term employee-to-web {
from {
destination-port 80;
}
then port-mirror-instance employee-web-monitor;
}
}
}
}
forwarding-options {
analyzer employee-web-monitor {
output {
vlan {
999;
}
}
}
vlans {
remote-analyzer {
vlan-id 999;
}
}
Check the results of the configuration on the destination switch:
[edit]
user@switch> show
vlans {
remote-analyzer {
vlan-id 999;
}
}
interfaces {
ge-0/0/10 {
unit 0 {
family ethernet-switching {
interface-mode access;
vlan {
members remote-analyzer;
}
}
}
}
ge-0/0/5 {
unit 0 {
family ethernet-switching {
interface-mode access;
vlan {
members remote-analyzer;
}
}
}
}
}
Verification
To confirm that the configuration is working properly, perform these tasks:
Verifying That the Port-Mirroring Instance Has Been Correctly Created
Purpose
Verify that the port-mirror instance employee-web-monitor has been created on the switch with the appropriate output VLAN.
Action
You can verify that the port-mirror is configured as
expected by using the show forwarding-options port-mirror command. To view previously created analyzers that are disabled,
go to the J-Web interface.
To verify that the port-mirror is configured as expected while
monitoring employee traffic on the source switch, run the show
forwarding-options port-miror command on the source switch.
The following output is displayed for this configuration example:
user@switch> show forwarding-options port-mirror
Instance Name: employee-web-monitor
Instance Id: 3
Input parameters:
Rate : 1
Run-length : 0
Maximum-packet-length : 0
Output parameters:
Family State Destination Next-hop
ethernet-switching up default-switch/remote-analyzer
Meaning
This output shows that the employee-web-monitor instance
has a ratio of 1 (mirroring every packet, which is the default), the
maximum size of the original packet that was mirrored (0 indicates
the entire packet), the state of the configuration is up (which indicates
the proper state and that the analyzer is programmed, is mirroring
the traffic entering ge-0/0/0 and ge-0/0/1, and is sending the mirrored
traffic to the VLAN called remote-analyzer).
