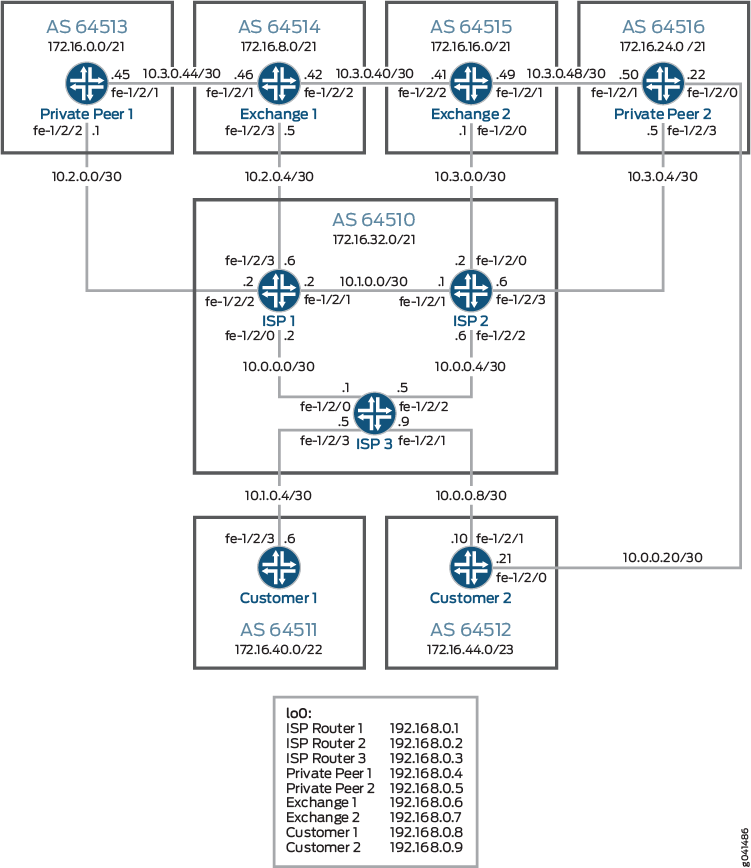
Ejemplo: Uso de la política de enrutamiento en una red de ISP
Este ejemplo es un caso práctico de cómo se pueden usar las directivas de enrutamiento en una red típica de proveedor de servicios Internet (ISP).
Requisitos
No se necesita ninguna configuración especial más allá de la inicialización del dispositivo antes de configurar este ejemplo.
Descripción general
En este ejemplo de red, el número de AS del ISP es 64510. El ISP tiene dos pares de tránsito (AS 64514 y AS 64515) a los que se conecta en un punto de intercambio. El ISP también está conectado a dos pares privados (AS 64513 y AS 64516) con los que intercambia rutas específicas de clientes. El ISP tiene dos clientes (AS 64511 y AS 64512).
Las directivas de ISP se configuran en dirección saliente. Es decir, el ejemplo se centra en las rutas que el ISP anuncia a sus pares y clientes, e incluye lo siguiente:
Al ISP se le ha asignado el AS 64510 y el espacio de enrutamiento es 172.16.32.0/21. Con la excepción de las dos redes de clientes, todas las demás rutas de clientes se simulan con rutas estáticas.
Los pares de intercambio se utilizan para el servicio de tránsito a otras partes de Internet. Esto significa que el ISP está aceptando todas las rutas (la tabla de enrutamiento de Internet completa) de esos pares BGP. Para ayudar a mantener una tabla de enrutamiento de Internet optimizada, el ISP está configurado para anunciar solo dos rutas agregadas a los pares de tránsito.
Los administradores del ISP quieren que todos los datos de los pares privados utilicen los enlaces directos. Como resultado, todas las rutas de clientes del ISP se anuncian a esos pares privados. Estos pares luego anuncian todas las rutas de sus clientes al ISP.
Finalmente, cada cliente tiene un conjunto diferente de requisitos. El cliente-1 requiere una ruta predeterminada única. El cliente-2 requiere rutas específicas.
Establecer comandos para todos los dispositivos de la topología
Configuración rápida de CLI
Para configurar rápidamente este ejemplo, copie los siguientes comandos, péguelos en un archivo de texto, elimine los saltos de línea, cambie los detalles necesarios para que coincidan con su configuración de red y, a continuación, copie y pegue los comandos en la CLI en el nivel de [edit] jerarquía.
Cliente del dispositivo-1
set interfaces fe-1/2/3 unit 0 description to_ISP-3 set interfaces fe-1/2/3 unit 0 family inet address 10.1.0.6/30 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.0.8/32 set protocols bgp group ext type external set protocols bgp group ext export send-statics set protocols bgp group ext peer-as 64510 set protocols bgp group ext neighbor 10.1.0.5 set policy-options policy-statement send-statics term static-routes from protocol static set policy-options policy-statement send-statics term static-routes then accept set routing-options static route 172.16.40.0/25 reject set routing-options static route 172.16.40.128/25 reject set routing-options static route 172.16.41.0/25 reject set routing-options static route 172.16.41.128/25 reject set routing-options autonomous-system 64511
Cliente del dispositivo-2
set interfaces fe-1/2/1 unit 0 description to_ISP-3 set interfaces fe-1/2/1 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.10/30 set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 description to-Private-Peer-2 set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.21/30 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.0.9/32 set protocols bgp group ext type external set protocols bgp group ext import inbound-routes set protocols bgp group ext export outbound-routes set protocols bgp group ext neighbor 10.0.0.9 peer-as 64510 set protocols bgp group ext neighbor 10.0.0.22 peer-as 64516 set policy-options policy-statement inbound-routes term AS64510-primary from protocol bgp set policy-options policy-statement inbound-routes term AS64510-primary from as-path AS64510-routes set policy-options policy-statement inbound-routes term AS64510-primary then local-preference 200 set policy-options policy-statement inbound-routes term AS64510-primary then accept set policy-options policy-statement inbound-routes term AS64516-backup from protocol bgp set policy-options policy-statement inbound-routes term AS64516-backup from as-path AS64516-routes set policy-options policy-statement inbound-routes term AS64516-backup then local-preference 50 set policy-options policy-statement inbound-routes term AS64516-backup then accept set policy-options policy-statement outbound-routes term statics from protocol static set policy-options policy-statement outbound-routes term statics then accept set policy-options policy-statement outbound-routes term internal-bgp-routes from protocol bgp set policy-options policy-statement outbound-routes term internal-bgp-routes from as-path my-own-routes set policy-options policy-statement outbound-routes term internal-bgp-routes then accept set policy-options policy-statement outbound-routes term no-transit then reject set policy-options as-path my-own-routes "()" set policy-options as-path AS64510-routes "64510 .*" set policy-options as-path AS64516-routes "64516 .*" set routing-options static route 172.16.44.0/26 reject set routing-options static route 172.16.44.64/26 reject set routing-options static route 172.16.44.128/26 reject set routing-options static route 172.16.44.192/26 reject set routing-options autonomous-system 64512
Dispositivo ISP-1
set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 description to_ISP-3 set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.2/30 set interfaces fe-1/2/1 unit 0 description to_ISP-2 set interfaces fe-1/2/1 unit 0 family inet address 10.1.0.2/30 set interfaces fe-1/2/2 unit 0 description to_Private-Peer-1 set interfaces fe-1/2/2 unit 0 family inet address 10.2.0.2/30 set interfaces fe-1/2/3 unit 0 description to_Exchange-1 set interfaces fe-1/2/3 unit 0 family inet address 10.2.0.6/30 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.0.1/32 set protocols bgp group int type internal set protocols bgp group int local-address 192.168.0.1 set protocols bgp group int export internal-peers set protocols bgp group int neighbor 192.168.0.2 set protocols bgp group int neighbor 192.168.0.3 set protocols bgp group to_64513 type external set protocols bgp group to_64513 export private-peer set protocols bgp group to_64513 peer-as 64513 set protocols bgp group to_64513 neighbor 10.2.0.1 set protocols bgp group to_64514 type external set protocols bgp group to_64514 export exchange-peer set protocols bgp group to_64514 peer-as 64514 set protocols bgp group to_64514 neighbor 10.2.0.5 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface fe-1/2/0.0 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface fe-1/2/1.0 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.0 passive set policy-options policy-statement exchange-peer term AS64510-Aggregate from protocol aggregate set policy-options policy-statement exchange-peer term AS64510-Aggregate from route-filter 172.16.32.0/21 exact set policy-options policy-statement exchange-peer term AS64510-Aggregate then accept set policy-options policy-statement exchange-peer term Customer-2-Aggregate from protocol aggregate set policy-options policy-statement exchange-peer term Customer-2-Aggregate from route-filter 172.16.40.0/22 exact set policy-options policy-statement exchange-peer term Customer-2-Aggregate then accept set policy-options policy-statement exchange-peer term reject-all-other-routes then reject set policy-options policy-statement internal-peers term statics from protocol static set policy-options policy-statement internal-peers term statics then accept set policy-options policy-statement internal-peers term next-hop-self then next-hop self set policy-options policy-statement private-peer term statics from protocol static set policy-options policy-statement private-peer term statics then accept set policy-options policy-statement private-peer term isp-and-customer-routes from protocol bgp set policy-options policy-statement private-peer term isp-and-customer-routes from route-filter 172.16.32.0/21 orlonger set policy-options policy-statement private-peer term isp-and-customer-routes then accept set policy-options policy-statement private-peer term reject-all then reject set routing-options static route 172.16.32.0/24 reject set routing-options static route 172.16.33.0/24 reject set routing-options aggregate route 172.16.32.0/21 set routing-options aggregate route 172.16.40.0/22 set routing-options router-id 192.168.0.1 set routing-options autonomous-system 64510
Dispositivo ISP-2
set interfaces fe-1/2/1 unit 0 description to_ISP-1 set interfaces fe-1/2/1 unit 0 family inet address 10.1.0.1/30 set interfaces fe-1/2/2 unit 0 description to_ISP-3 set interfaces fe-1/2/2 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.6/30 set interfaces fe-1/2/3 unit 0 description to_Private-Peer-2 set interfaces fe-1/2/3 unit 0 family inet address 10.3.0.6/30 set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 description to_Exchange-2 set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.3.0.2/30 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.0.2/32 set protocols bgp group int type internal set protocols bgp group int local-address 192.168.0.2 set protocols bgp group int export internal-peers set protocols bgp group int neighbor 192.168.0.1 set protocols bgp group int neighbor 192.168.0.3 set protocols bgp group AS-64516 type external set protocols bgp group AS-64516 export private-peer set protocols bgp group AS-64516 peer-as 64516 set protocols bgp group AS-64516 neighbor 10.3.0.5 set protocols bgp group AS-64515 type external set protocols bgp group AS-64515 export exchange-peer set protocols bgp group AS-64515 peer-as 64515 set protocols bgp group AS-64515 neighbor 10.3.0.1 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface fe-1/2/2.0 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface fe-1/2/1.0 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.0 passive set policy-options policy-statement exchange-peer term AS64510-Aggregate from protocol aggregate set policy-options policy-statement exchange-peer term AS64510-Aggregate from route-filter 172.16.32.0/21 exact set policy-options policy-statement exchange-peer term AS64510-Aggregate then accept set policy-options policy-statement exchange-peer term Customer-2-Aggregate from protocol aggregate set policy-options policy-statement exchange-peer term Customer-2-Aggregate from route-filter 172.16.44.0/23 exact set policy-options policy-statement exchange-peer term Customer-2-Aggregate then accept set policy-options policy-statement exchange-peer term reject-all-other-routes then reject set policy-options policy-statement internal-peers term statics from protocol static set policy-options policy-statement internal-peers term statics then accept set policy-options policy-statement internal-peers term next-hop-self then next-hop self set policy-options policy-statement private-peer term statics from protocol static set policy-options policy-statement private-peer term statics then accept set policy-options policy-statement private-peer term isp-and-customer-routes from protocol bgp set policy-options policy-statement private-peer term isp-and-customer-routes from route-filter 172.16.32.0/21 orlonger set policy-options policy-statement private-peer term isp-and-customer-routes then accept set policy-options policy-statement private-peer term reject-all then reject set routing-options static route 172.16.34.0/24 reject set routing-options static route 172.16.35.0/24 reject set routing-options aggregate route 172.16.44.0/23 set routing-options aggregate route 172.16.32.0/21 set routing-options router-id 192.168.0.2 set routing-options autonomous-system 64510
Dispositivo ISP-3
set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 description to_ISP-1 set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.1/30 set interfaces fe-1/2/2 unit 0 description to_ISP-2 set interfaces fe-1/2/2 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.5/30 set interfaces fe-1/2/3 unit 0 description to_Customer-1 set interfaces fe-1/2/3 unit 0 family inet address 10.1.0.5/30 set interfaces fe-1/2/1 unit 0 description to_Customer-2 set interfaces fe-1/2/1 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.9/30 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.0.3/32 set protocols bgp group int type internal set protocols bgp group int local-address 192.168.0.3 set protocols bgp group int export internal-peers set protocols bgp group int neighbor 192.168.0.1 set protocols bgp group int neighbor 192.168.0.2 set protocols bgp group to_64511 type external set protocols bgp group to_64511 export customer-1-peer set protocols bgp group to_64511 neighbor 10.1.0.6 peer-as 64511 set protocols bgp group to_64512 type external set protocols bgp group to_64512 export customer-2-peer set protocols bgp group to_64512 neighbor 10.0.0.10 peer-as 64512 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface fe-1/2/0.0 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface fe-1/2/2.0 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.0 passive set policy-options policy-statement customer-1-peer term defaut-route from route-filter 0.0.0.0/0 exact set policy-options policy-statement customer-1-peer term defaut-route then accept set policy-options policy-statement customer-1-peer term reject-all-other-routes then reject set policy-options policy-statement customer-2-peer term statics from protocol static set policy-options policy-statement customer-2-peer term statics then accept set policy-options policy-statement customer-2-peer term isp-and-customer-routes from protocol bgp set policy-options policy-statement customer-2-peer term isp-and-customer-routes from route-filter 172.16.32.0/21 orlonger set policy-options policy-statement customer-2-peer term isp-and-customer-routes then accept set policy-options policy-statement customer-2-peer term default-route from route-filter 0.0.0.0/0 exact set policy-options policy-statement customer-2-peer term default-route then accept set policy-options policy-statement customer-2-peer term reject-all-other-routes then reject set policy-options policy-statement if-upstream-routes-exist term only-certain-contributing-routes from route-filter 172.16.8.0/21 exact set policy-options policy-statement if-upstream-routes-exist term only-certain-contributing-routes then accept set policy-options policy-statement if-upstream-routes-exist term reject-all-other-routes then reject set policy-options policy-statement internal-peers term statics from protocol static set policy-options policy-statement internal-peers term statics then accept set policy-options policy-statement internal-peers term next then next-hop self set routing-options static route 172.16.36.0/24 reject set routing-options static route 172.16.37.0/24 reject set routing-options static route 172.16.38.0/24 reject set routing-options static route 172.16.39.0/24 reject set routing-options generate route 0.0.0.0/0 policy if-upstream-routes-exist set routing-options router-id 192.168.0.3 set routing-options autonomous-system 64510
Intercambio de dispositivos-1
set interfaces fe-1/2/3 unit 0 description to_ISP-1 set interfaces fe-1/2/3 unit 0 family inet address 10.2.0.5/30 set interfaces fe-1/2/2 unit 0 description to_Exchange-2 set interfaces fe-1/2/2 unit 0 family inet address 10.3.0.42/30 set interfaces fe-1/2/1 unit 0 description to_Private-Peer-1 set interfaces fe-1/2/1 unit 0 family inet address 10.3.0.45/30 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.0.6/32 set protocols bgp group ext type external set protocols bgp group ext export send-static set protocols bgp group ext peer-as 64510 set protocols bgp group ext neighbor 10.2.0.6 set protocols bgp group ext neighbor 10.3.0.41 peer-as 64515 set policy-options policy-statement send-static from protocol static set policy-options policy-statement send-static then accept set routing-options static route 172.16.8.0/21 reject set routing-options autonomous-system 64514
Intercambio de dispositivos-2
set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 description to_ISP-2 set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.3.0.1/30 set interfaces fe-1/2/2 unit 0 description to_Exchange-1 set interfaces fe-1/2/2 unit 0 family inet address 10.3.0.41/30 set interfaces fe-1/2/1 unit 0 description to_Private-Peer-2 set interfaces fe-1/2/1 unit 0 family inet address 10.3.0.49/30 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.0.7/32 set protocols bgp group ext type external set protocols bgp group ext export outbound-routes set protocols bgp group ext neighbor 10.3.0.2 peer-as 64510 set protocols bgp group ext neighbor 10.3.0.50 peer-as 64516 set protocols bgp group ext neighbor 10.3.0.42 peer-as 64514 set policy-options policy-statement outbound-routes term statics from protocol static set policy-options policy-statement outbound-routes term statics then accept set routing-options autonomous-system 64515 set routing-options static route 172.16.16.0/21 reject
Dispositivo Private-Peer-1
set interfaces fe-1/2/2 unit 0 description to_ISP-1 set interfaces fe-1/2/2 unit 0 family inet address 10.2.0.1/30 set interfaces fe-1/2/1 unit 0 description to_Exchange-1 set interfaces fe-1/2/1 unit 0 family inet address 10.3.0.46/30 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.0.4/32 set protocols bgp group ext type external set protocols bgp group ext peer-as 64510 set protocols bgp group ext neighbor 10.2.0.2 set routing-options autonomous-system 64513
Dispositivo Private-Peer-2
set interfaces fe-1/2/3 unit 0 description to_ISP-2 set interfaces fe-1/2/3 unit 0 family inet address 10.3.0.5/30 set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 description to_Customer-1 set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.22/30 set interfaces fe-1/2/1 unit 0 description to_Exchange-2 set interfaces fe-1/2/1 unit 0 family inet address 10.3.0.50/30 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.0.5/32 set protocols bgp group ext type external set protocols bgp group ext export outbound-routes set protocols bgp group ext peer-as 64510 set protocols bgp group ext neighbor 10.3.0.6 set protocols bgp group to-64512 type external set protocols bgp group to-64512 peer-as 64512 set protocols bgp group to-64512 neighbor 10.0.0.21 set protocols bgp group to-64512 export internal-routes set protocols bgp group to-64515 type external set protocols bgp group to-64515 export outbound-routes set protocols bgp group to-64515 peer-as 64515 set protocols bgp group to-64515 neighbor 10.3.0.49 set policy-options policy-statement if-upstream-routes-exist term as-64515-routes from route-filter 172.16.16.0/21 exact set policy-options policy-statement if-upstream-routes-exist term as-64515-routes then accept set policy-options policy-statement if-upstream-routes-exist term reject-all-other-routes then reject set policy-options policy-statement internal-routes term statics from protocol static set policy-options policy-statement internal-routes term statics then accept set policy-options policy-statement internal-routes term default-route from route-filter 0.0.0.0/0 exact set policy-options policy-statement internal-routes term default-route then accept set policy-options policy-statement internal-routes term reject-all-other-routes then reject set policy-options policy-statement outbound-routes term statics from protocol static set policy-options policy-statement outbound-routes term statics then accept set policy-options policy-statement outbound-routes term allowed-bgp-routes from as-path my-own-routes set policy-options policy-statement outbound-routes term allowed-bgp-routes from as-path AS64512-routes set policy-options policy-statement outbound-routes term allowed-bgp-routes then accept set policy-options policy-statement outbound-routes term no-transit then reject set policy-options as-path my-own-routes "()" set policy-options as-path AS64512-routes 64512 set routing-options static route 172.16.24.0/25 reject set routing-options static route 172.16.24.128/25 reject set routing-options static route 172.16.25.0/26 reject set routing-options static route 172.16.25.64/26 reject set routing-options generate route 0.0.0.0/0 policy if-upstream-routes-exist set routing-options autonomous-system 64516
Configuración del dispositivo cliente-1
Procedimiento
Procedimiento paso a paso
El ejemplo siguiente requiere que navegue por varios niveles en la jerarquía de configuración. Para obtener información acerca de cómo navegar por la CLI, consulte Usar el editor de CLI en el modo de configuración el Manual del usuario de la CLI de Junos OS.
El dispositivo Cliente-1 tiene varias rutas estáticas configuradas para simular rutas del cliente. Estas rutas se envían al ISP.
Para configurar Device Customer-1:
Configure las interfaces del dispositivo.
[edit interfaces] user@Customer-1# set fe-1/2/3 unit 0 description to_ISP-3 user@Customer-1# set fe-1/2/3 unit 0 family inet address 10.1.0.6/30 user@Customer-1# set lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.0.8/32
Configure las rutas estáticas.
[edit routing-options static] user@Customer-1# set route 172.16.40.0/25 reject user@Customer-1# set route 172.16.40.128/25 reject user@Customer-1# set route 172.16.41.0/25 reject user@Customer-1# set route 172.16.41.128/25 reject
Configure la directiva para enviar rutas estáticas.
[edit policy-options policy-statement send-statics term static-routes] user@Customer-1# set from protocol static user@Customer-1# set then accept
Configure la conexión BGP externa (EBGP) con el ISP.
[edit protocols bgp group ext] user@Customer-1# set type external user@Customer-1# set export send-statics user@Customer-1# set peer-as 64510 user@Customer-1# set neighbor 10.1.0.5
Configure el número de sistema autónomo (AS).
[edit routing-options] user@Customer-1# set autonomous-system 64511
Resultados
Desde el modo de configuración, ingrese los comandos show interfaces, show protocols, show policy-options y show routing-options para confirmar la configuración. Si el resultado no muestra la configuración deseada, repita las instrucciones en este ejemplo para corregir la configuración.
user@Customer-1# show interfaces
fe-1/2/1 {
unit 0 {
description to_ISP-3;
family inet {
address 10.1.0.6/30;
}
}
}
lo0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 192.168.0.8/32;
}
}
}
user@Customer-1# show protocols
bgp {
group ext {
type external;
export send-statics;
peer-as 64510;
neighbor 10.1.0.5;
}
}
user@Customer-1# show policy-options
policy-statement send-statics {
term static-routes {
from protocol static;
then accept;
}
}
user@Customer-1# show routing-options
static {
route 172.16.40.0/25 reject;
route 172.16.40.128/25 reject;
route 172.16.41.0/25 reject;
route 172.16.41.128/25 reject;
}
autonomous-system 64511;
Cuando termine de configurar el dispositivo, ingrese commit en el modo de configuración.
Configuración del dispositivo Cliente-2
Procedimiento
Procedimiento paso a paso
El ejemplo siguiente requiere que navegue por varios niveles en la jerarquía de configuración. Para obtener información acerca de cómo navegar por la CLI, consulte Usar el editor de CLI en el modo de configuración el Manual del usuario de la CLI de Junos OS.
El dispositivo Customer-2 tiene dos rutas estáticas configuradas para simular las rutas del cliente. Estas rutas se envían al ISP. El cliente 2 tiene un vínculo con el ISP, así como un vínculo con el AS 8000. Este cliente ha solicitado al ISP rutas del cliente específicas, así como del AS 64516. El cliente 2 desea usar el ISP para el servicio de tránsito a Internet y ha solicitado una ruta predeterminada al ISP.
Para configurar Device Customer-2:
Configure las interfaces del dispositivo.
[edit interfaces] user@Customer-2# set fe-1/2/1 unit 0 description to_ISP-3 user@Customer-2# set fe-1/2/1 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.10/30 user@Customer-2# set fe-1/2/0 unit 0 description to-Private-Peer-2 user@Customer-2# set fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.21/30 user@Customer-2# set lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.0.9/32
Configure las rutas estáticas.
[edit routing-options static] user@Customer-2# set route 172.16.44.0/26 reject user@Customer-2# set route 172.16.44.64/26 reject user@Customer-2# set route 172.16.44.128/26 reject user@Customer-2# set route 172.16.44.192/26 reject
Configure la directiva de enrutamiento de importación.
Se prefiere la ruta con el valor de preferencia local más alto. Las rutas del ISP son preferibles a las mismas rutas desde Device Private-Peer-2
[edit policy-options policy-statement inbound-routes] user@Customer-2# set term AS64510-primary from protocol bgp user@Customer-2# set term AS64510-primary from as-path AS64510-routes user@Customer-2# set term AS64510-primary then local-preference 200 user@Customer-2# set term AS64510-primary then accept [edit policy-options policy-statement inbound-routes] user@Customer-2# set term AS64516-backup from protocol bgp user@Customer-2# set term AS64516-backup from as-path AS64516-routes user@Customer-2# set term AS64516-backup then local-preference 50 user@Customer-2# set term AS64516-backup then accept [edit policy-options] user@Customer-2# set as-path AS64510-routes "64510 .*" user@Customer-2# set as-path AS64516-routes "64516 .*"
Configure la directiva de enrutamiento de exportación.
[edit policy-options policy-statement outbound-routes] user@Customer-2# set term statics from protocol static user@Customer-2# set term statics then accept user@Customer-2# set term internal-bgp-routes from protocol bgp user@Customer-2# set term internal-bgp-routes from as-path my-own-routes user@Customer-2# set term internal-bgp-routes then accept user@Customer-2# set term no-transit then reject [edit policy-options] user@Customer-2# set as-path my-own-routes "()"
Configure la conexión BGP externa (EBGP) al ISP y al dispositivo Private-Peer-2.
[edit protocols bgp group ext] user@Customer-2# set type external user@Customer-2# set import inbound-routes user@Customer-2# set export outbound-routes user@Customer-2# set neighbor 10.0.0.9 peer-as 64510 user@Customer-2# set neighbor 10.0.0.22 peer-as 64516
Configure el número de sistema autónomo (AS).
[edit routing-options] user@Customer-2# set autonomous-system 64512
Resultados
Desde el modo de configuración, ingrese los comandos show interfaces, show protocols, show policy-options y show routing-options para confirmar la configuración. Si el resultado no muestra la configuración deseada, repita las instrucciones en este ejemplo para corregir la configuración.
user@Customer-2# show interfaces
fe-1/2/1 {
unit 0 {
description to_ISP-3;
family inet {
address 10.0.0.10/30;
}
}
}
fe-1/2/0 {
unit 0 {
description to-Private-Peer-2;
family inet {
address 10.0.0.21/30;
}
}
}
lo0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 192.168.0.9/32;
}
}
}
user@Customer-2# show protocols
bgp {
group ext {
type external;
import inbound-routes;
export outbound-routes;
neighbor 10.0.0.9 {
peer-as 64510;
}
neighbor 10.0.0.22 {
peer-as 64516;
}
}
}
user@Customer-2# show policy-options
policy-statement inbound-routes {
term AS64510-primary {
from {
protocol bgp;
as-path AS64510-routes;
}
then {
local-preference 200;
accept;
}
}
term AS64516-backup {
from {
protocol bgp;
as-path AS64516-routes;
}
then {
local-preference 50;
accept;
}
}
}
policy-statement outbound-routes {
term statics {
from protocol static;
then accept;
}
term internal-bgp-routes {
from {
protocol bgp;
as-path my-own-routes;
}
then accept;
}
term no-transit {
then reject;
}
}
as-path my-own-routes "()";
as-path AS64510-routes "64510 .*";
as-path AS64516-routes "64516 .*";
user@Customer-2# show routing-options
static {
route 172.16.44.0/26 reject;
route 172.16.44.64/26 reject;
route 172.16.44.128/26 reject;
route 172.16.44.192/26 reject;
}
autonomous-system 64512;
Cuando termine de configurar el dispositivo, ingrese commit en el modo de configuración.
Configuración de los dispositivos ISP-1 e ISP-2
Procedimiento
Procedimiento paso a paso
El ejemplo siguiente requiere que navegue por varios niveles en la jerarquía de configuración. Para obtener información acerca de cómo navegar por la CLI, consulte Usar el editor de CLI en el modo de configuración el Manual del usuario de la CLI de Junos OS.
El dispositivo ISP-1 y el dispositivo ISP-2 tienen configuradas dos directivas: La private-peer política y la exchange-peer política. Debido a sus configuraciones similares, este ejemplo muestra la configuración paso a paso solo para el dispositivo ISP-2.
En el dispositivo ISP-2, la política del par privado envía las rutas del cliente del ISP al par privado del dispositivo 2. La política acepta todas las rutas estáticas locales (clientes ISP-2 de dispositivos locales) y todas las rutas BGP en el rango 172.16.32.0/21 (anunciadas por otros enrutadores ISP). Estos dos términos de política representan las rutas del cliente del ISP. El término de directiva final rechaza todas las demás rutas, lo que incluye toda la tabla de enrutamiento de Internet enviada por los pares de intercambio. No es necesario enviar estas rutas al dispositivo Private-Peer-2 por dos motivos:
El par ya mantiene una conexión con Device Exchange-2 en nuestro ejemplo, por lo que las rutas son redundantes.
El par privado solo quiere rutas de clientes. La
private-peerpolítica logra este objetivo. Laexchange-peerpolítica envía rutas a Device Exchange-2.
En el ejemplo, solo se deben enviar dos rutas a Device Exchange-2:
Ruta de agregado que representa el espacio de enrutamiento del AS 64510 de 172.16.32.0/21. Esta ruta se configura como una ruta agregada localmente y la política la anuncia.
exchange-peerEl espacio de direcciones asignado a Cliente-2, 172.16.44.0/23. Esta ruta agregada más pequeña debe enviarse al dispositivo de intercambio -2 porque el cliente también está conectado al par del AS 64516 (Par privado del dispositivo 2).
El envío de estas dos rutas a Device Exchange-2 permite que otras redes en Internet lleguen al cliente a través del ISP o del par privado. Si solo el par privado anunciase en la red /23 mientras el ISP mantuvo solo su agregado /21, todo el tráfico destinado al cliente solo podría transitar por el AS 64516. Debido a que el cliente también quiere rutas del ISP, la ruta 172.16.44.0/23 es anunciada por el dispositivo ISP-2. Al igual que la ruta agregada más grande, la ruta 172.16.44.0/23 se configura localmente y se anuncia mediante la directiva de pares de intercambio. El término final de esa política rechaza todas las rutas, incluidas las redes de clientes específicas del ISP, las rutas del cliente desde Device Private-Peer-1, las rutas del cliente desde Device Private-Peer-2 y la tabla de enrutamiento desde Device Exchange-1. En esencia, este último término impide que el ISP realice servicios de tránsito para Internet en general.
Para configurar el dispositivo ISP-2:
Configure las interfaces del dispositivo.
[edit interfaces] user@ISP-2# set fe-1/2/1 unit 0 description to_ISP-1 user@ISP-2# set fe-1/2/1 unit 0 family inet address 10.1.0.1/30 user@ISP-2# set fe-1/2/2 unit 0 description to_ISP-3 user@ISP-2# set fe-1/2/2 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.6/30 user@ISP-2# set fe-1/2/3 unit 0 description to_Private-Peer-2 user@ISP-2# set fe-1/2/3 unit 0 family inet address 10.3.0.6/30 user@ISP-2# set fe-1/2/0 unit 0 description to_Exchange-2 user@ISP-2# set fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.3.0.2/30 user@ISP-2# set lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.0.2/32
Configure el protocolo de puerta de enlace interior (IGP).
[edit protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0] user@ISP-2# set interface fe-1/2/2.0 user@ISP-2# set interface fe-1/2/1.0 user@ISP-2# set interface lo0.0 passive
Configure las rutas estáticas y agregadas.
[edit routing-options static] user@ISP-2# set route 172.16.34.0/24 reject user@ISP-2# set route 172.16.35.0/24 reject [edit routing-options aggregate] user@ISP-2# set route 172.16.44.0/23 user@ISP-2# set route 172.16.32.0/21
Configure las directivas de enrutamiento para los pares de intercambio.
[edit policy-options policy-statement exchange-peer] user@ISP-2# set term AS64510-Aggregate from protocol aggregate user@ISP-2# set term AS64510-Aggregate from route-filter 172.16.32.0/21 exact user@ISP-2# set term AS64510-Aggregate then accept user@ISP-2# set term Customer-2-Aggregate from protocol aggregate user@ISP-2# set term Customer-2-Aggregate from route-filter 172.16.44.0/23 exact user@ISP-2# set term Customer-2-Aggregate then accept user@ISP-2# set term reject-all-other-routes then reject
Configure las directivas de enrutamiento para los pares internos.
[edit policy-options policy-statement internal-peers] user@ISP-2# set term statics from protocol static user@ISP-2# set term statics then accept user@ISP-2# set term next-hop-self then next-hop self
Configure las directivas de enrutamiento para el par privado.
[edit policy-options policy-statement private-peer] user@ISP-2# set term statics from protocol static user@ISP-2# set term statics then accept user@ISP-2# set term isp-and-customer-routes from protocol bgp user@ISP-2# set term isp-and-customer-routes from route-filter 172.16.32.0/21 orlonger user@ISP-2# set term isp-and-customer-routes then accept user@ISP-2# set term reject-all then reject
Configure las conexiones BGP internas (IBGP) con los demás dispositivos ISP.
[edit protocols bgp group int] user@ISP-2# set type internal user@ISP-2# set local-address 192.168.0.2 user@ISP-2# set export internal-peers user@ISP-2# set neighbor 192.168.0.1 user@ISP-2# set neighbor 192.168.0.3
Configure las conexiones EBGP con el par de intercambio y el par privado.
[edit protocols bgp group AS-64516] user@ISP-2# set type external user@ISP-2# set export private-peer user@ISP-2# set peer-as 64516 user@ISP-2# set neighbor 10.3.0.5 [edit protocols bgp group AS-64515] user@ISP-2# set type external user@ISP-2# set export exchange-peer user@ISP-2# set peer-as 64515 user@ISP-2# set neighbor 10.3.0.1
Configure el número de sistema autónomo (AS) y el ID del enrutador.
[edit routing-options] user@ISP-2# set router-id 192.168.0.2 user@ISP-2# set autonomous-system 64510
Resultados
Desde el modo de configuración, ingrese los comandos show interfaces, show protocols, show policy-options y show routing-options para confirmar la configuración. Si el resultado no muestra la configuración deseada, repita las instrucciones en este ejemplo para corregir la configuración.
user@ISP-2# show interfaces
fe-1/2/0 {
unit 0{
description to_Exchange-2;
family inet {
address 10.3.0.2/30;
}
}
}
fe-1/2/1 {
unit 0{
description to_ISP-1;
family inet {
address 10.1.0.1/30;
}
}
}
fe-1/2/2 {
unit 0 {
description to_ISP-3;
family inet {
address 10.0.0.6/30;
}
}
}
fe-1/2/3 {
unit 0 {
description to_Private-Peer-2;
family inet {
address 10.3.0.6/30;
}
}
}
lo0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 192.168.0.2/32;
}
}
}
user@ISP-2# show protocols
bgp {
group int {
type internal;
local-address 192.168.0.2;
export internal-peers;
neighbor 192.168.0.1;
neighbor 192.168.0.3;
}
group AS-64516 {
type external;
export private-peer;
peer-as 64516;
neighbor 10.3.0.5;
}
group AS-64515 {
type external;
export exchange-peer;
peer-as 64515;
neighbor 10.3.0.1;
}
}
ospf {
area 0.0.0.0 {
interface fe-1/2/2.0;
interface fe-1/2/1.0;
interface lo0.0 {
passive;
}
}
}
user@ISP-2# show policy-options
policy-statement exchange-peer {
term AS64510-Aggregate {
from {
protocol aggregate;
route-filter 172.16.32.0/21 exact;
}
then accept;
}
term Customer-2-Aggregate {
from {
protocol aggregate;
route-filter 172.16.44.0/23 exact;
}
then accept;
}
term reject-all-other-routes {
then reject;
}
}
policy-statement internal-peers {
term statics {
from protocol static;
then accept;
}
term next-hop-self {
then {
next-hop self;
}
}
}
policy-statement private-peer {
term statics {
from protocol static;
then accept;
}
term isp-and-customer-routes {
from {
protocol bgp;
route-filter 172.16.32.0/21 orlonger;
}
then accept;
}
term reject-all {
then reject;
}
}
user@ISP-2# show routing-options
static {
route 172.16.34.0/24 reject;
route 172.16.35.0/24 reject;
}
aggregate {
route 172.16.44.0/23;
route 172.16.32.0/21;
}
router-id 192.168.0.2;
autonomous-system 64510;
Cuando termine de configurar el dispositivo, ingrese commit en el modo de configuración.
Configuración del dispositivo ISP-3
Procedimiento
Procedimiento paso a paso
El ejemplo siguiente requiere que navegue por varios niveles en la jerarquía de configuración. Para obtener información acerca de cómo navegar por la CLI, consulte Usar el editor de CLI en el modo de configuración el Manual del usuario de la CLI de Junos OS.
En el dispositivo ISP-3, existe una política independiente para cada cliente. La directiva envía la ruta predeterminada para Cliente-1 customer-1-peer . Esta política encuentra la ruta predeterminada 0.0.0.0/0 en inet.0 y la acepta. La política también rechaza todas las demás rutas, por lo que no envía todas las rutas BGP en el enrutador ISP. La customer-2-peer política es para el cliente-2 y contiene los mismos términos de la política, que también envían la ruta predeterminada y ninguna otra ruta BGP de tránsito. Los términos adicionales de la customer-2-peer política envían las rutas del cliente ISP al Cliente 2. Debido a que hay rutas estáticas locales en el dispositivo ISP-3 que representan a clientes locales, estas rutas se envían, así como todas las demás rutas internas anunciadas al enrutador local por los otros enrutadores ISP.
Si la ruta ascendente de Device Exchange-1 (172.16.8.0/21) está presente, Device ISP-3 genera una ruta predeterminada.
Para configurar el dispositivo ISP-3:
Configure las interfaces del dispositivo.
[edit interfaces] user@ISP-3# set fe-1/2/0 unit 0 description to_ISP-1 user@ISP-3# set fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.1/30 user@ISP-3# set fe-1/2/2 unit 0 description to_ISP-2 user@ISP-3# set fe-1/2/2 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.5/30 user@ISP-3# set fe-1/2/3 unit 0 description to_Customer-1 user@ISP-3# set fe-1/2/3 unit 0 family inet address 10.1.0.5/30 user@ISP-3# set fe-1/2/1 unit 0 description to_Customer-2 user@ISP-3# set fe-1/2/1 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.9/30 user@ISP-3# set lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.0.3/32
Configure el protocolo de puerta de enlace interior (IGP).
[edit protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0] user@ISP-3# set interface fe-1/2/0.0 user@ISP-3# set interface fe-1/2/2.0 user@ISP-3# set interface lo0.0 passive
Configure las rutas estáticas.
[edit routing-options static] user@ISP-3# set route 172.16.36.0/24 reject user@ISP-3# set route 172.16.37.0/24 reject user@ISP-3# set route 172.16.38.0/24 reject user@ISP-3# set route 172.16.39.0/24 reject
Configure una directiva de enrutamiento que genere una ruta estática predeterminada solo si existe una determinada ruta ascendente.
[edit policy-options policy-statement if-upstream-routes-exist term only-certain-contributing-routes] user@ISP-3# set from route-filter 172.16.8.0/21 exact user@ISP-3# set then accept [edit policy-options policy-statement if-upstream-routes-exist] user@ISP-3# set term reject-all-other-routes then reject [edit routing-options generate route 0.0.0.0/0] user@ISP-3# set policy if-upstream-routes-exist
Configure la directiva de enrutamiento para Cliente-1.
[edit policy-options policy-statement customer-1-peer] user@ISP-3# set term defaut-route from route-filter 0.0.0.0/0 exact user@ISP-3# set term defaut-route then accept user@ISP-3# set term reject-all-other-routes then reject
Configure la directiva de enrutamiento para Cliente-2.
[edit policy-options policy-statement customer-2-peer] user@ISP-3# set term statics from protocol static user@ISP-3# set term statics then accept user@ISP-3# set term isp-and-customer-routes from protocol bgp user@ISP-3# set term isp-and-customer-routes from route-filter 172.16.32.0/21 orlonger user@ISP-3# set term isp-and-customer-routes then accept user@ISP-3# set term default-route from route-filter 0.0.0.0/0 exact user@ISP-3# set term default-route then accept user@ISP-3# set term reject-all-other-routes then reject
Configure las directivas de enrutamiento para los pares internos.
[edit policy-options policy-statement internal-peers] user@ISP-3# set term statics from protocol static user@ISP-3# set term statics then accept user@ISP-3# set term next then next-hop self
Configure las conexiones BGP internas (IBGP) con los demás dispositivos ISP.
[edit protocols bgp group int] user@ISP-3# set type internal user@ISP-3# set local-address 192.168.0.3 user@ISP-3# set export internal-peers user@ISP-3# set neighbor 192.168.0.1 user@ISP-3# set neighbor 192.168.0.2
Configure las conexiones del EBGP con los pares del cliente.
[edit protocols bgp group to_64511] user@ISP-3# set type external user@ISP-3# set export customer-1-peer user@ISP-3# set neighbor 10.1.0.6 peer-as 64511 [edit protocols bgp group to_64512] user@ISP-3# set type external user@ISP-3# set export customer-2-peer user@ISP-3# set neighbor 10.0.0.10 peer-as 64512
Configure el número de sistema autónomo (AS) y el ID del enrutador.
[edit routing-options] user@ISP-3# set router-id 192.168.0.3 user@ISP-3# set autonomous-system 64510
Resultados
Desde el modo de configuración, ingrese los comandos show interfaces, show protocols, show policy-options y show routing-options para confirmar la configuración. Si el resultado no muestra la configuración deseada, repita las instrucciones en este ejemplo para corregir la configuración.
user@ISP-3# show interfaces
fe-1/2/0 {
unit 0 {
description to_ISP-1;
family inet {
address 10.0.0.1/30;
}
}
}
fe-1/2/1 {
unit 0 {
description to_Customer-2;
family inet {
address 10.0.0.9/30;
}
}
}
fe-1/2/2 {
unit 0 {
description to_ISP-2;
family inet {
address 10.0.0.5/30;
}
}
}
fe-1/2/3 {
unit 0 {
description to_Customer-1;
family inet {
address 10.1.0.5/30;
}
}
}
lo0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 192.168.0.3/32;
}
}
}
user@ISP-3# show protocols
bgp {
group int {
type internal;
local-address 192.168.0.3;
export internal-peers;
neighbor 192.168.0.1;
neighbor 192.168.0.2;
}
group to_64511 {
type external;
export customer-1-peer;
neighbor 10.1.0.6 {
peer-as 64511;
}
}
group to_64512 {
type external;
export customer-2-peer;
neighbor 10.0.0.10 {
peer-as 64512;
}
}
}
ospf {
area 0.0.0.0 {
interface fe-1/2/0.0;
interface fe-1/2/2.0;
interface lo0.0 {
passive;
}
}
}
user@ISP-3# show policy-options
policy-statement customer-1-peer {
term defaut-route {
from {
route-filter 0.0.0.0/0 exact;
}
then accept;
}
term reject-all-other-routes {
then reject;
}
}
policy-statement customer-2-peer {
term statics {
from protocol static;
then accept;
}
term isp-and-customer-routes {
from {
protocol bgp;
route-filter 172.16.32.0/21 orlonger;
}
then accept;
}
term default-route {
from {
route-filter 0.0.0.0/0 exact;
}
then accept;
}
term reject-all-other-routes {
then reject;
}
}
policy-statement if-upstream-routes-exist {
term only-certain-contributing-routes {
from {
route-filter 172.16.8.0/21 exact;
}
then accept;
}
term reject-all-other-routes {
then reject;
}
}
policy-statement internal-peers {
term statics {
from protocol static;
then accept;
}
term next {
then {
next-hop self;
}
}
}
user@ISP-3# show routing-options
static {
route 172.16.36.0/24 reject;
route 172.16.37.0/24 reject;
route 172.16.38.0/24 reject;
route 172.16.39.0/24 reject;
}
generate {
route 0.0.0.0/0 policy if-upstream-routes-exist;
}
router-id 192.168.0.3;
autonomous-system 64510;
Cuando termine de configurar el dispositivo, ingrese commit en el modo de configuración.
Configuración del dispositivo Exchange-2
Procedimiento
Procedimiento paso a paso
El ejemplo siguiente requiere que navegue por varios niveles en la jerarquía de configuración. Para obtener información acerca de cómo navegar por la CLI, consulte Usar el editor de CLI en el modo de configuración el Manual del usuario de la CLI de Junos OS.
Device Exchange-2 intercambia todas las rutas BGP con todos los pares BGP. La directiva de rutas salientes para Device Exchange-2 anuncia rutas estáticas definidas localmente mediante BGP. La exclusión de un término final then reject hace que surta efecto la política de exportación de BGP predeterminada, que consiste en enviar todas las rutas de BGP a todos los pares de BGP externos.
Para configurar Device Exchange-2:
Configure las interfaces del dispositivo.
[edit interfaces] user@Exchange-2# set fe-1/2/0 unit 0 description to_ISP-2 user@Exchange-2# set fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.3.0.1/30 user@Exchange-2# set fe-1/2/2 unit 0 description to_Exchange-1 user@Exchange-2# set fe-1/2/2 unit 0 family inet address 10.3.0.41/30 user@Exchange-2# set fe-1/2/1 unit 0 description to_Private-Peer-2 user@Exchange-2# set fe-1/2/1 unit 0 family inet address 10.3.0.49/30 user@Exchange-2# set lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.0.7/32
Configure las rutas estáticas.
[edit routing-options static] set route 172.16.16.0/21 reject
Configure una directiva de enrutamiento que genere una ruta estática predeterminada solo si existen determinadas rutas internas.
[edit policy-options policy-statement outbound-routes term statics] user@Exchange-2# set from protocol static user@Exchange-2# set then accept
Configure las conexiones del EBGP con los pares del cliente.
[edit protocols bgp group ext] user@Exchange-2# set type external user@Exchange-2# set export outbound-routes user@Exchange-2# set neighbor 10.3.0.2 peer-as 64510 user@Exchange-2# set neighbor 10.3.0.50 peer-as 64516 user@Exchange-2# set neighbor 10.3.0.42 peer-as 64514
Configure el número de sistema autónomo (AS).
[edit routing-options] user@Exchange-2# set autonomous-system 64515
Resultados
Desde el modo de configuración, ingrese los comandos show interfaces, show protocols, show policy-options y show routing-options para confirmar la configuración. Si el resultado no muestra la configuración deseada, repita las instrucciones en este ejemplo para corregir la configuración.
user@Exchange-2 show interfaces
fe-1/2/0 {
unit 0 {
description to_ISP-2;
family inet {
address 10.3.0.1/30;
}
}
}
fe-1/2/1 {
unit 0 {
description to_Private-Peer-2;
family inet {
address 10.3.0.49/30;
}
}
}
fe-1/2/2 {
unit 0 {
description to_Exchange-1;
family inet {
address 10.3.0.41/30;
}
}
}
lo0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 192.168.0.7/32;
}
}
}
user@Exchange-2# show protocols
bgp {
group ext {
type external;
export outbound-routes;
neighbor 10.3.0.2 {
peer-as 64510;
}
neighbor 10.3.0.50 {
peer-as 64516;
}
neighbor 10.3.0.42 {
peer-as 64514;
}
}
}
user@Exchange-2# show policy-options
policy-statement outbound-routes {
term statics {
from protocol static;
then accept;
}
}
user@Exchange-2# show routing-options
static {
route 172.16.16.0/21 reject;
}
autonomous-system 64515;
Cuando termine de configurar el dispositivo, ingrese commit en el modo de configuración.
Configuración del dispositivo private-peer-2
Procedimiento
Procedimiento paso a paso
El ejemplo siguiente requiere que navegue por varios niveles en la jerarquía de configuración. Para obtener información acerca de cómo navegar por la CLI, consulte Usar el editor de CLI en el modo de configuración el Manual del usuario de la CLI de Junos OS.
Device Private-Peer-2 realiza dos funciones principales:
Anuncia rutas locales al AS 64516 tanto a los pares de intercambio como a los enrutadores ISP. La
outbound-routesdirectiva anuncia las rutas estáticas locales (es decir, los clientes) del enrutador y también anuncia todas las rutas aprendidas por BGP que se originaron en el AS 64516 o en el AS 64512. Estas rutas incluyen otras rutas de clientes de AS 64516 además del cliente del AS 64512. Las rutas del AS se identifican mediante criterios de coincidencia de expresión regular de ruta de AS de la política.Anuncia la ruta predeterminada 0.0.0.0/0 al enrutador del cliente del AS 64512. Para lograr esto, el par privado crea una ruta generada para 0.0.0.0/0 localmente en el enrutador. A esta ruta generada se le asigna además una política denominada
if-upstream-routes-exist, que permite que solo ciertas rutas contribuyan a la ruta generada, lo que la convierte en una ruta activa en la tabla de enrutamiento. Una vez que la ruta está activa, puede enviarse al enrutador del AS 64512 mediante el BGP y las políticas configuradas. Laif-upstream-routes-existpolítica solo acepta la ruta 172.16.32.0/21 de Device Exchange-2 y rechaza todas las demás rutas. Si el par de intercambio retira la ruta 172.16.32.0/21, el par privado pierde la ruta predeterminada 0.0.0.0/0 y retira la ruta predeterminada del enrutador del cliente 64512.
Para configurar Device Private-Peer-2:
Configure las interfaces del dispositivo.
[edit interfaces] user@Private-Peer-2# set fe-1/2/3 unit 0 description to_ISP-2 user@Private-Peer-2# set fe-1/2/3 unit 0 family inet address 10.3.0.5/30 user@Private-Peer-2# set fe-1/2/0 unit 0 description to_Customer-1 user@Private-Peer-2# set fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.22/30 user@Private-Peer-2# set fe-1/2/1 unit 0 description to_Exchange-2 user@Private-Peer-2# set fe-1/2/1 unit 0 family inet address 10.3.0.50/30 user@Private-Peer-2# set lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.0.5/32
Configure las rutas estáticas.
[edit routing-options static] user@Private-Peer-2# set route 172.16.24.0/25 reject user@Private-Peer-2# set route 172.16.24.128/25 reject user@Private-Peer-2# set route 172.16.25.0/26 reject user@Private-Peer-2# set route 172.16.25.64/26 reject
Configure una directiva de enrutamiento que genere una ruta estática predeterminada solo si existen determinadas rutas internas.
[edit policy-options policy-statement if-upstream-routes-exist] user@Private-Peer-2# set term as-64515-routes from route-filter 172.16.16.0/21 exact user@Private-Peer-2# set term as-64515-routes then accept user@Private-Peer-2# set term reject-all-other-routes then reject [edit routing-options generate route 0.0.0.0/0] user@Private-Peer-2# set policy if-upstream-routes-exist
Configure la directiva de enrutamiento que anuncia rutas estáticas locales y la ruta predeterminada.
[edit policy-options policy-statement internal-routes] user@Private-Peer-2# set term statics from protocol static user@Private-Peer-2# set term statics then accept user@Private-Peer-2# set term default-route from route-filter 0.0.0.0/0 exact user@Private-Peer-2# set term default-route then accept user@Private-Peer-2# set term reject-all-other-routes then reject
Configure la directiva de enrutamiento que anuncia las rutas de los clientes locales.
[edit policy-options policy-statement outbound-routes] user@Private-Peer-2# set term statics from protocol static user@Private-Peer-2# set term statics then accept user@Private-Peer-2# set term allowed-bgp-routes from as-path my-own-routes user@Private-Peer-2# set term allowed-bgp-routes from as-path AS64512-routes user@Private-Peer-2# set term allowed-bgp-routes then accept user@Private-Peer-2# set term no-transit then reject [edit policy-options] user@Private-Peer-2# set as-path my-own-routes "()" user@Private-Peer-2# set as-path AS64512-routes 64512
Configure la conexión EBGP para el cliente-2.
[edit protocols bgp group to-64512] user@Private-Peer-2# set type external user@Private-Peer-2# set export internal-routes user@Private-Peer-2# set peer-as 64512 user@Private-Peer-2# set neighbor 10.0.0.21
Configure la conexión EBGP a Device Exchange-2.
[edit protocols bgp group to-64515] user@Private-Peer-2# set type external user@Private-Peer-2# set export outbound-routes user@Private-Peer-2# set peer-as 64515 user@Private-Peer-2# set neighbor 10.3.0.49
Configure las conexiones EBGP con el ISP.
[edit protocols bgp group ext] user@Private-Peer-2# set type external user@Private-Peer-2# set export outbound-routes user@Private-Peer-2# set peer-as 64510 user@Private-Peer-2# set neighbor 10.3.0.6
Configure el número de sistema autónomo (AS).
[edit routing-options] user@Private-Peer-2# set autonomous-system 64516
Resultados
Desde el modo de configuración, ingrese los comandos show interfaces, show protocols, show policy-options y show routing-options para confirmar la configuración. Si el resultado no muestra la configuración deseada, repita las instrucciones en este ejemplo para corregir la configuración.
user@Private-Peer-2# show interfaces
fe-1/2/0 {
unit 0 {
description to_Customer-1;
family inet {
address 10.0.0.22/30;
}
}
}
fe-1/2/1 {
unit 0 {
description to_Exchange-2;
family inet {
address 10.3.0.50/30;
}
}
}
fe-1/2/3 {
unit 0 {
description to_ISP-2;
family inet {
address 10.3.0.5/30;
}
}
}
lo0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 192.168.0.5/32;
}
}
}
user@Private-Peer-2# show protocols
bgp {
group ext {
type external;
export outbound-routes;
peer-as 64510;
neighbor 10.3.0.6;
}
group to-64512 {
type external;
export internal-routes;
peer-as 64512;
neighbor 10.0.0.21;
}
group to-64515 {
type external;
export outbound-routes;
peer-as 64515;
neighbor 10.3.0.49;
}
}
user@Private-Peer-2# show policy-options
policy-statement if-upstream-routes-exist {
term as-64515-routes {
from {
route-filter 172.16.16.0/21 exact;
}
then accept;
}
term reject-all-other-routes {
then reject;
}
}
policy-statement internal-routes {
term statics {
from protocol static;
then accept;
}
term default-route {
from {
route-filter 0.0.0.0/0 exact;
}
then accept;
}
term reject-all-other-routes {
then reject;
}
}
policy-statement outbound-routes {
term statics {
from protocol static;
then accept;
}
term allowed-bgp-routes {
from as-path [ my-own-routes AS64512-routes ];
then accept;
}
term no-transit {
then reject;
}
}
as-path my-own-routes "()";
as-path AS64512-routes 64512;
user@Private-Peer-2# show routing-options
static {
route 172.16.24.0/25 reject;
route 172.16.24.128/25 reject;
route 172.16.25.0/26 reject;
route 172.16.25.64/26 reject;
}
generate {
route 0.0.0.0/0 policy if-upstream-routes-exist;
}
autonomous-system 64516;
Cuando termine de configurar el dispositivo, ingrese commit en el modo de configuración.
Verificación
Confirme que la configuración funcione correctamente.
- Verificación de las rutas en el dispositivo Cliente-1
- Verificación de las rutas en el dispositivo cliente-2
- Verificación de las rutas en el dispositivo ISP-1
- Verificación de las rutas en el dispositivo ISP-2
- Verificación de las rutas en el dispositivo ISP-3
- Verificación de las rutas en Device Exchange-1
- Verificación de las rutas en Device Exchange-2
- Verificación de las rutas en el dispositivo private-peer-1
- Verificación de las rutas en el dispositivo private-peer-2
Verificación de las rutas en el dispositivo Cliente-1
Propósito
En Device Customer-1, compruebe las rutas en la tabla de enrutamiento.
Acción
user@Customer-1> show route
inet.0: 8 destinations, 8 routes (8 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
+ = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both
0.0.0.0/0 *[BGP/170] 00:09:25, localpref 100
AS path: 64510 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.1.0.5 via fe-1/2/3.0
10.1.0.4/30 *[Direct/0] 23:50:20
> via fe-1/2/3.0
10.1.0.6/32 *[Local/0] 5d 21:56:47
Local via fe-1/2/3.0
172.16.40.0/25 *[Static/5] 22:59:04
Reject
172.16.40.128/25 *[Static/5] 22:59:04
Reject
172.16.41.0/25 *[Static/5] 22:59:04
Reject
172.16.41.128/25 *[Static/5] 22:59:04
Reject
192.168.0.8/32 *[Direct/0] 5d 21:25:45
> via lo0.0Significado
El dispositivo Customer-1 tiene sus cuatro rutas estáticas y ha aprendido la ruta predeterminada a través de BGP.
Verificación de las rutas en el dispositivo cliente-2
Propósito
En Device Customer-2, compruebe las rutas en la tabla de enrutamiento.
Acción
user@Customer-2> show route
inet.0: 22 destinations, 23 routes (22 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
+ = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both
0.0.0.0/0 *[BGP/170] 00:10:35, localpref 200
AS path: 64510 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.9 via fe-1/2/0.10
[BGP/170] 04:58:09, localpref 50
AS path: 64516 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.22 via fe-1/2/0.0
10.0.0.8/30 *[Direct/0] 23:51:29
> via fe-1/2/0.10
10.0.0.10/32 *[Local/0] 23:52:49
Local via fe-1/2/0.10
10.0.0.20/30 *[Direct/0] 23:52:49
> via fe-1/2/0.0
10.0.0.21/32 *[Local/0] 23:52:49
Local via fe-1/2/0.0
172.16.24.0/25 *[BGP/170] 04:58:09, localpref 50
AS path: 64516 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.22 via fe-1/2/0.0
172.16.24.128/25 *[BGP/170] 04:58:09, localpref 50
AS path: 64516 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.22 via fe-1/2/0.0
172.16.25.0/26 *[BGP/170] 04:58:09, localpref 50
AS path: 64516 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.22 via fe-1/2/0.0
172.16.25.64/26 *[BGP/170] 04:58:09, localpref 50
AS path: 64516 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.22 via fe-1/2/0.0
172.16.32.0/24 *[BGP/170] 22:38:47, localpref 200
AS path: 64510 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.9 via fe-1/2/0.10
172.16.33.0/24 *[BGP/170] 22:38:47, localpref 200
AS path: 64510 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.9 via fe-1/2/0.10
172.16.34.0/24 *[BGP/170] 22:38:47, localpref 200
AS path: 64510 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.9 via fe-1/2/0.10
172.16.35.0/24 *[BGP/170] 22:38:47, localpref 200
AS path: 64510 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.9 via fe-1/2/0.10
172.16.36.0/24 *[BGP/170] 22:38:47, localpref 200
AS path: 64510 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.9 via fe-1/2/0.10
172.16.37.0/24 *[BGP/170] 22:38:47, localpref 200
AS path: 64510 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.9 via fe-1/2/0.10
172.16.38.0/24 *[BGP/170] 22:38:47, localpref 200
AS path: 64510 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.9 via fe-1/2/0.10
172.16.39.0/24 *[BGP/170] 22:38:47, localpref 200
AS path: 64510 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.9 via fe-1/2/0.10
172.16.44.0/26 *[Static/5] 22:57:28
Reject
172.16.44.64/26 *[Static/5] 22:57:28
Reject
172.16.44.128/26 *[Static/5] 22:57:28
Reject
172.16.44.192/26 *[Static/5] 22:57:28
Reject
192.168.0.9/32 *[Direct/0] 23:52:49
> via lo0.0Significado
Device Customer-2 ha aprendido la ruta predeterminada a través de su sesión con el ISP y también a través de su sesión con el par privado. Se prefiere la ruta aprendida del ISP porque tiene una preferencia local más alta.
Verificación de las rutas en el dispositivo ISP-1
Propósito
En el dispositivo ISP-1, compruebe las rutas en la tabla de enrutamiento.
Acción
user@ISP-1> show route
inet.0: 42 destinations, 53 routes (42 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
+ = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both
0.0.0.0/0 *[BGP/170] 22:44:26, localpref 100, from 192.168.0.2
AS path: 64516 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.1.0.1 via fe-1/2/1.0
10.0.0.0/30 *[Direct/0] 23:52:01
> via fe-1/2/0.0
10.0.0.2/32 *[Local/0] 23:52:01
Local via fe-1/2/0.0
10.0.0.4/30 *[OSPF/10] 23:51:06, metric 2
to 10.1.0.1 via fe-1/2/1.0
> to 10.0.0.1 via fe-1/2/0.0
10.0.0.20/30 *[BGP/170] 23:50:55, localpref 100, from 192.168.0.2
AS path: 64516 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.1.0.1 via fe-1/2/1.0
[BGP/170] 23:51:28, localpref 100
AS path: 64514 64515 64516 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.2.0.5 via fe-1/2/3.0
10.1.0.0/30 *[Direct/0] 23:52:01
> via fe-1/2/1.0
10.1.0.2/32 *[Local/0] 23:52:01
Local via fe-1/2/1.0
10.2.0.0/30 *[Direct/0] 23:52:01
> via fe-1/2/2.0
10.2.0.2/32 *[Local/0] 23:52:01
Local via fe-1/2/2.0
10.2.0.4/30 *[Direct/0] 23:52:00
> via fe-1/2/3.0
10.2.0.6/32 *[Local/0] 23:52:00
Local via fe-1/2/3.0
10.3.0.4/30 *[BGP/170] 23:51:28, localpref 100
AS path: 64514 64515 64516 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.2.0.5 via fe-1/2/3.0
10.3.0.48/30 *[BGP/170] 23:50:55, localpref 100, from 192.168.0.2
AS path: 64516 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.1.0.1 via fe-1/2/1.0
172.16.8.0/21 *[BGP/170] 00:11:08, localpref 100
AS path: 64514 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.2.0.5 via fe-1/2/3.0
172.16.16.0/21 *[BGP/170] 02:02:10, localpref 100, from 192.168.0.2
AS path: 64515 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.1.0.1 via fe-1/2/1.0
[BGP/170] 02:02:10, localpref 100
AS path: 64514 64515 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.2.0.5 via fe-1/2/3.0
172.16.24.0/25 *[BGP/170] 23:06:33, localpref 100, from 192.168.0.2
AS path: 64516 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.1.0.1 via fe-1/2/1.0
[BGP/170] 23:06:33, localpref 100
AS path: 64514 64515 64516 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.2.0.5 via fe-1/2/3.0
172.16.24.128/25 *[BGP/170] 23:06:33, localpref 100, from 192.168.0.2
AS path: 64516 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.1.0.1 via fe-1/2/1.0
[BGP/170] 23:06:33, localpref 100
AS path: 64514 64515 64516 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.2.0.5 via fe-1/2/3.0
172.16.25.0/26 *[BGP/170] 23:06:33, localpref 100, from 192.168.0.2
AS path: 64516 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.1.0.1 via fe-1/2/1.0
[BGP/170] 23:06:33, localpref 100
AS path: 64514 64515 64516 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.2.0.5 via fe-1/2/3.0
172.16.25.64/26 *[BGP/170] 23:06:33, localpref 100, from 192.168.0.2
AS path: 64516 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.1.0.1 via fe-1/2/1.0
[BGP/170] 23:06:33, localpref 100
AS path: 64514 64515 64516 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.2.0.5 via fe-1/2/3.0
172.16.32.0/21 *[Aggregate/130] 22:44:27
Reject
172.16.32.0/24 *[Static/5] 22:44:27
Reject
172.16.33.0/24 *[Static/5] 22:44:27
Reject
172.16.34.0/24 *[BGP/170] 22:39:20, localpref 100, from 192.168.0.2
AS path: I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.1.0.1 via fe-1/2/1.0
172.16.35.0/24 *[BGP/170] 22:39:20, localpref 100, from 192.168.0.2
AS path: I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.1.0.1 via fe-1/2/1.0
172.16.36.0/24 *[BGP/170] 22:39:20, localpref 100, from 192.168.0.3
AS path: I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.1 via fe-1/2/0.0
172.16.37.0/24 *[BGP/170] 22:39:20, localpref 100, from 192.168.0.3
AS path: I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.1 via fe-1/2/0.0
172.16.38.0/24 *[BGP/170] 22:39:20, localpref 100, from 192.168.0.3
AS path: I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.1 via fe-1/2/0.0
172.16.39.0/24 *[BGP/170] 22:39:20, localpref 100, from 192.168.0.3
AS path: I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.1 via fe-1/2/0.0
172.16.40.0/22 *[Aggregate/130] 22:44:27
Reject
172.16.40.0/25 *[BGP/170] 23:00:47, localpref 100, from 192.168.0.3
AS path: 64511 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.1 via fe-1/2/0.0
172.16.40.128/25 *[BGP/170] 23:00:47, localpref 100, from 192.168.0.3
AS path: 64511 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.1 via fe-1/2/0.0
172.16.41.0/25 *[BGP/170] 23:00:47, localpref 100, from 192.168.0.3
AS path: 64511 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.1 via fe-1/2/0.0
172.16.41.128/25 *[BGP/170] 23:00:47, localpref 100, from 192.168.0.3
AS path: 64511 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.1 via fe-1/2/0.0
172.16.44.0/26 *[BGP/170] 22:58:01, localpref 100, from 192.168.0.3
AS path: 64512 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.1 via fe-1/2/0.0
[BGP/170] 22:58:01, localpref 100
AS path: 64514 64515 64516 64512 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.2.0.5 via fe-1/2/3.0
172.16.44.64/26 *[BGP/170] 22:58:01, localpref 100, from 192.168.0.3
AS path: 64512 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.1 via fe-1/2/0.0
[BGP/170] 22:58:01, localpref 100
AS path: 64514 64515 64516 64512 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.2.0.5 via fe-1/2/3.0
172.16.44.128/26 *[BGP/170] 22:58:01, localpref 100, from 192.168.0.3
AS path: 64512 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.1 via fe-1/2/0.0
[BGP/170] 22:58:01, localpref 100
AS path: 64514 64515 64516 64512 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.2.0.5 via fe-1/2/3.0
172.16.44.192/26 *[BGP/170] 22:58:01, localpref 100, from 192.168.0.3
AS path: 64512 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.1 via fe-1/2/0.0
[BGP/170] 22:58:01, localpref 100
AS path: 64514 64515 64516 64512 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.2.0.5 via fe-1/2/3.0
192.168.0.1/32 *[Direct/0] 23:52:01
> via lo0.0
192.168.0.2/32 *[OSPF/10] 23:51:06, metric 1
> to 10.1.0.1 via fe-1/2/1.0
192.168.0.3/32 *[OSPF/10] 23:51:06, metric 1
> to 10.0.0.1 via fe-1/2/0.0
192.168.0.5/32 *[BGP/170] 23:50:55, localpref 100, from 192.168.0.2
AS path: 64516 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.1.0.1 via fe-1/2/1.0
[BGP/170] 23:51:28, localpref 100
AS path: 64514 64515 64516 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.2.0.5 via fe-1/2/3.0
172.16.233.5/32 *[OSPF/10] 23:52:07, metric 1
MultiRecvVerificación de las rutas en el dispositivo ISP-2
Propósito
En el dispositivo ISP-2, compruebe las rutas en la tabla de enrutamiento.
Acción
user@ISP-2> show route
inet.0: 41 destinations, 59 routes (41 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
+ = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both
0.0.0.0/0 *[BGP/170] 22:45:44, localpref 100
AS path: 64516 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.5 via fe-1/2/3.0
10.0.0.0/30 *[OSPF/10] 23:52:25, metric 2
to 10.0.0.5 via fe-1/2/2.0
> to 10.1.0.2 via fe-1/2/1.0
10.0.0.4/30 *[Direct/0] 23:53:21
> via fe-1/2/2.0
10.0.0.6/32 *[Local/0] 23:53:23
Local via fe-1/2/2.0
10.0.0.20/30 *[BGP/170] 23:53:11, localpref 100
AS path: 64516 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.5 via fe-1/2/3.0
[BGP/170] 23:53:09, localpref 100
AS path: 64515 64516 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.1 via fe-1/2/0.0
10.1.0.0/30 *[Direct/0] 23:53:19
> via fe-1/2/1.0
10.1.0.1/32 *[Local/0] 23:53:23
Local via fe-1/2/1.0
10.3.0.0/30 *[Direct/0] 23:53:22
> via fe-1/2/0.0
10.3.0.2/32 *[Local/0] 23:53:23
Local via fe-1/2/0.0
10.3.0.4/30 *[Direct/0] 23:53:23
> via fe-1/2/3.0
[BGP/170] 23:53:11, localpref 100
AS path: 64516 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.5 via fe-1/2/3.0
[BGP/170] 23:53:09, localpref 100
AS path: 64515 64516 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.1 via fe-1/2/0.0
[BGP/170] 23:52:13, localpref 100, from 192.168.0.1
AS path: 64514 64515 64516 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.1.0.2 via fe-1/2/1.0
10.3.0.6/32 *[Local/0] 23:53:23
Local via fe-1/2/3.0
10.3.0.48/30 *[BGP/170] 23:53:11, localpref 100
AS path: 64516 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.5 via fe-1/2/3.0
172.16.8.0/21 *[BGP/170] 00:12:26, localpref 100, from 192.168.0.1
AS path: 64514 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.1.0.2 via fe-1/2/1.0
[BGP/170] 00:12:26, localpref 100
AS path: 64515 64514 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.1 via fe-1/2/0.0
172.16.16.0/21 *[BGP/170] 02:03:28, localpref 100
AS path: 64515 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.1 via fe-1/2/0.0
172.16.24.0/25 *[BGP/170] 23:07:51, localpref 100
AS path: 64516 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.5 via fe-1/2/3.0
[BGP/170] 23:07:51, localpref 100
AS path: 64515 64516 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.1 via fe-1/2/0.0
172.16.24.128/25 *[BGP/170] 23:07:51, localpref 100
AS path: 64516 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.5 via fe-1/2/3.0
[BGP/170] 23:07:51, localpref 100
AS path: 64515 64516 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.1 via fe-1/2/0.0
172.16.25.0/26 *[BGP/170] 23:07:51, localpref 100
AS path: 64516 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.5 via fe-1/2/3.0
[BGP/170] 23:07:51, localpref 100
AS path: 64515 64516 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.1 via fe-1/2/0.0
172.16.25.64/26 *[BGP/170] 23:07:51, localpref 100
AS path: 64516 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.5 via fe-1/2/3.0
[BGP/170] 23:07:51, localpref 100
AS path: 64515 64516 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.1 via fe-1/2/0.0
172.16.32.0/21 *[Aggregate/130] 22:40:38
Reject
172.16.32.0/24 *[BGP/170] 22:45:44, localpref 100, from 192.168.0.1
AS path: I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.1.0.2 via fe-1/2/1.0
172.16.33.0/24 *[BGP/170] 22:45:44, localpref 100, from 192.168.0.1
AS path: I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.1.0.2 via fe-1/2/1.0
172.16.34.0/24 *[Static/5] 22:40:38
Reject
172.16.35.0/24 *[Static/5] 22:40:38
Reject
172.16.36.0/24 *[BGP/170] 22:40:38, localpref 100, from 192.168.0.3
AS path: I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.5 via fe-1/2/2.0
172.16.37.0/24 *[BGP/170] 22:40:38, localpref 100, from 192.168.0.3
AS path: I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.5 via fe-1/2/2.0
172.16.38.0/24 *[BGP/170] 22:40:38, localpref 100, from 192.168.0.3
AS path: I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.5 via fe-1/2/2.0
172.16.39.0/24 *[BGP/170] 22:40:38, localpref 100, from 192.168.0.3
AS path: I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.5 via fe-1/2/2.0
172.16.40.0/25 *[BGP/170] 23:02:05, localpref 100, from 192.168.0.3
AS path: 64511 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.5 via fe-1/2/2.0
172.16.40.128/25 *[BGP/170] 23:02:05, localpref 100, from 192.168.0.3
AS path: 64511 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.5 via fe-1/2/2.0
172.16.41.0/25 *[BGP/170] 23:02:05, localpref 100, from 192.168.0.3
AS path: 64511 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.5 via fe-1/2/2.0
172.16.41.128/25 *[BGP/170] 23:02:05, localpref 100, from 192.168.0.3
AS path: 64511 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.5 via fe-1/2/2.0
172.16.44.0/23 *[Aggregate/130] 22:40:38
Reject
172.16.44.0/26 *[BGP/170] 22:59:19, localpref 100, from 192.168.0.3
AS path: 64512 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.5 via fe-1/2/2.0
[BGP/170] 22:59:19, localpref 100
AS path: 64516 64512 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.5 via fe-1/2/3.0
[BGP/170] 22:59:19, localpref 100
AS path: 64515 64516 64512 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.1 via fe-1/2/0.0
172.16.44.64/26 *[BGP/170] 22:59:19, localpref 100, from 192.168.0.3
AS path: 64512 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.5 via fe-1/2/2.0
[BGP/170] 22:59:19, localpref 100
AS path: 64516 64512 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.5 via fe-1/2/3.0
[BGP/170] 22:59:19, localpref 100
AS path: 64515 64516 64512 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.1 via fe-1/2/0.0
172.16.44.128/26 *[BGP/170] 22:59:19, localpref 100, from 192.168.0.3
AS path: 64512 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.5 via fe-1/2/2.0
[BGP/170] 22:59:19, localpref 100
AS path: 64516 64512 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.5 via fe-1/2/3.0
[BGP/170] 22:59:19, localpref 100
AS path: 64515 64516 64512 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.1 via fe-1/2/0.0
172.16.44.192/26 *[BGP/170] 22:59:19, localpref 100, from 192.168.0.3
AS path: 64512 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.5 via fe-1/2/2.0
[BGP/170] 22:59:19, localpref 100
AS path: 64516 64512 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.5 via fe-1/2/3.0
[BGP/170] 22:59:19, localpref 100
AS path: 64515 64516 64512 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.1 via fe-1/2/0.0
192.168.0.1/32 *[OSPF/10] 23:52:25, metric 1
> to 10.1.0.2 via fe-1/2/1.0
192.168.0.2/32 *[Direct/0] 23:53:23
> via lo0.0
192.168.0.3/32 *[OSPF/10] 23:52:30, metric 1
> to 10.0.0.5 via fe-1/2/2.0
192.168.0.5/32 *[BGP/170] 23:53:11, localpref 100
AS path: 64516 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.5 via fe-1/2/3.0
[BGP/170] 23:53:09, localpref 100
AS path: 64515 64516 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.1 via fe-1/2/0.0
172.16.233.5/32 *[OSPF/10] 23:53:25, metric 1
MultiRecvVerificación de las rutas en el dispositivo ISP-3
Propósito
En el dispositivo ISP-3, compruebe las rutas en la tabla de enrutamiento.
Acción
user@ISP-3> show route
inet.0: 40 destinations, 41 routes (40 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
+ = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both
0.0.0.0/0 *[Aggregate/130] 23:53:57, metric2 1
> to 10.0.0.2 via fe-1/2/0.0
[BGP/170] 22:46:17, localpref 100, from 192.168.0.2
AS path: 64516 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.6 via fe-1/2/2.0
10.0.0.0/30 *[Direct/0] 23:53:52
> via fe-1/2/0.0
10.0.0.1/32 *[Local/0] 23:53:53
Local via fe-1/2/0.0
10.0.0.4/30 *[Direct/0] 23:53:54
> via fe-1/2/2.0
10.0.0.5/32 *[Local/0] 23:53:54
Local via fe-1/2/2.0
10.0.0.8/30 *[Direct/0] 23:53:53
> via fe-1/2/1.0
10.0.0.9/32 *[Local/0] 23:53:53
Local via fe-1/2/1.0
10.0.0.20/30 *[BGP/170] 23:53:02, localpref 100, from 192.168.0.2
AS path: 64516 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.6 via fe-1/2/2.0
10.1.0.0/30 *[OSPF/10] 23:53:03, metric 2
> to 10.0.0.6 via fe-1/2/2.0
to 10.0.0.2 via fe-1/2/0.0
10.1.0.4/30 *[Direct/0] 23:53:54
> via fe-1/2/3.0
10.1.0.5/32 *[Local/0] 23:53:54
Local via fe-1/2/3.0
10.3.0.4/30 *[BGP/170] 23:52:46, localpref 100, from 192.168.0.1
AS path: 64514 64515 64516 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.2 via fe-1/2/0.0
10.3.0.48/30 *[BGP/170] 23:53:02, localpref 100, from 192.168.0.2
AS path: 64516 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.6 via fe-1/2/2.0
172.16.8.0/21 *[BGP/170] 00:12:59, localpref 100, from 192.168.0.1
AS path: 64514 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.2 via fe-1/2/0.0
172.16.16.0/21 *[BGP/170] 02:04:01, localpref 100, from 192.168.0.2
AS path: 64515 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.6 via fe-1/2/2.0
172.16.24.0/25 *[BGP/170] 23:08:24, localpref 100, from 192.168.0.2
AS path: 64516 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.6 via fe-1/2/2.0
172.16.24.128/25 *[BGP/170] 23:08:24, localpref 100, from 192.168.0.2
AS path: 64516 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.6 via fe-1/2/2.0
172.16.25.0/26 *[BGP/170] 23:08:24, localpref 100, from 192.168.0.2
AS path: 64516 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.6 via fe-1/2/2.0
172.16.25.64/26 *[BGP/170] 23:08:24, localpref 100, from 192.168.0.2
AS path: 64516 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.6 via fe-1/2/2.0
172.16.32.0/24 *[BGP/170] 22:46:17, localpref 100, from 192.168.0.1
AS path: I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.2 via fe-1/2/0.0
172.16.33.0/24 *[BGP/170] 22:46:17, localpref 100, from 192.168.0.1
AS path: I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.2 via fe-1/2/0.0
172.16.34.0/24 *[BGP/170] 22:41:11, localpref 100, from 192.168.0.2
AS path: I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.6 via fe-1/2/2.0
172.16.35.0/24 *[BGP/170] 22:41:11, localpref 100, from 192.168.0.2
AS path: I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.6 via fe-1/2/2.0
172.16.36.0/24 *[Static/5] 22:41:11
Reject
172.16.37.0/24 *[Static/5] 22:41:11
Reject
172.16.38.0/24 *[Static/5] 22:41:11
Reject
172.16.39.0/24 *[Static/5] 22:41:11
Reject
172.16.40.0/25 *[BGP/170] 23:02:38, localpref 100
AS path: 64511 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.1.0.6 via fe-1/2/3.0
172.16.40.128/25 *[BGP/170] 23:02:38, localpref 100
AS path: 64511 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.1.0.6 via fe-1/2/3.0
172.16.41.0/25 *[BGP/170] 23:02:38, localpref 100
AS path: 64511 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.1.0.6 via fe-1/2/3.0
172.16.41.128/25 *[BGP/170] 23:02:38, localpref 100
AS path: 64511 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.1.0.6 via fe-1/2/3.0
172.16.44.0/26 *[BGP/170] 22:59:52, localpref 100
AS path: 64512 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.10 via fe-1/2/1.0
172.16.44.64/26 *[BGP/170] 22:59:52, localpref 100
AS path: 64512 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.10 via fe-1/2/1.0
172.16.44.128/26 *[BGP/170] 22:59:52, localpref 100
AS path: 64512 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.10 via fe-1/2/1.0
172.16.44.192/26 *[BGP/170] 22:59:52, localpref 100
AS path: 64512 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.10 via fe-1/2/1.0
192.168.0.1/32 *[OSPF/10] 23:53:03, metric 1
> to 10.0.0.2 via fe-1/2/0.0
192.168.0.2/32 *[OSPF/10] 23:53:03, metric 1
> to 10.0.0.6 via fe-1/2/2.0
192.168.0.3/32 *[Direct/0] 23:53:54
> via lo0.0
192.168.0.5/32 *[BGP/170] 23:53:02, localpref 100, from 192.168.0.2
AS path: 64516 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.6 via fe-1/2/2.0
172.16.233.5/32 *[OSPF/10] 23:53:58, metric 1
MultiRecvVerificación de las rutas en Device Exchange-1
Propósito
En Device Exchange-1, compruebe las rutas en la tabla de enrutamiento.
Acción
user@Exchange-1> show route
inet.0: 23 destinations, 24 routes (23 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
+ = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both
10.0.0.20/30 *[BGP/170] 23:53:51, localpref 100
AS path: 64515 64516 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.41 via fe-1/2/2.0
10.2.0.4/30 *[Direct/0] 23:54:23
> via fe-1/2/3.0
10.2.0.5/32 *[Local/0] 23:54:29
Local via fe-1/2/3.0
10.3.0.4/30 *[BGP/170] 23:53:51, localpref 100
AS path: 64515 64516 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.41 via fe-1/2/2.0
10.3.0.40/30 *[Direct/0] 23:54:27
> via fe-1/2/2.0
10.3.0.42/32 *[Local/0] 23:54:29
Local via fe-1/2/2.0
10.3.0.44/30 *[Direct/0] 23:54:29
> via fe-1/2/1.0
10.3.0.45/32 *[Local/0] 23:54:29
Local via fe-1/2/1.0
172.16.8.0/21 *[Static/5] 00:13:31
Reject
172.16.16.0/21 *[BGP/170] 02:04:33, localpref 100
AS path: 64515 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.41 via fe-1/2/2.0
172.16.24.0/25 *[BGP/170] 23:08:56, localpref 100
AS path: 64515 64516 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.41 via fe-1/2/2.0
172.16.24.128/25 *[BGP/170] 23:08:56, localpref 100
AS path: 64515 64516 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.41 via fe-1/2/2.0
172.16.25.0/26 *[BGP/170] 23:08:56, localpref 100
AS path: 64515 64516 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.41 via fe-1/2/2.0
172.16.25.64/26 *[BGP/170] 23:08:56, localpref 100
AS path: 64515 64516 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.41 via fe-1/2/2.0
172.16.32.0/21 *[BGP/170] 22:46:49, localpref 100
AS path: 64510 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.2.0.6 via fe-1/2/3.0
[BGP/170] 22:41:43, localpref 100
AS path: 64515 64510 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.41 via fe-1/2/2.0
172.16.40.0/22 *[BGP/170] 22:46:49, localpref 100
AS path: 64510 64511 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.2.0.6 via fe-1/2/3.0
172.16.44.0/23 *[BGP/170] 22:41:43, localpref 100
AS path: 64515 64510 64512 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.41 via fe-1/2/2.0
172.16.44.0/26 *[BGP/170] 23:00:24, localpref 100
AS path: 64515 64516 64512 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.41 via fe-1/2/2.0
172.16.44.64/26 *[BGP/170] 23:00:24, localpref 100
AS path: 64515 64516 64512 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.41 via fe-1/2/2.0
172.16.44.128/26 *[BGP/170] 23:00:24, localpref 100
AS path: 64515 64516 64512 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.41 via fe-1/2/2.0
172.16.44.192/26 *[BGP/170] 23:00:24, localpref 100
AS path: 64515 64516 64512 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.41 via fe-1/2/2.0
192.168.0.5/32 *[BGP/170] 23:53:51, localpref 100
AS path: 64515 64516 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.41 via fe-1/2/2.0
192.168.0.6/32 *[Direct/0] 23:54:29
> via lo0.0Verificación de las rutas en Device Exchange-2
Propósito
En Device Exchange-2, compruebe las rutas en la tabla de enrutamiento.
Acción
user@Exchange-2> show route
inet.0: 24 destinations, 26 routes (23 active, 0 holddown, 1 hidden)
+ = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both
10.0.0.20/30 *[BGP/170] 23:54:44, localpref 100
AS path: 64516 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.50 via fe-1/2/1.0
10.3.0.0/30 *[Direct/0] 23:54:57
> via fe-1/2/0.0
10.3.0.1/32 *[Local/0] 23:54:57
Local via fe-1/2/0.0
10.3.0.4/30 *[BGP/170] 23:54:44, localpref 100
AS path: 64516 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.50 via fe-1/2/1.0
10.3.0.40/30 *[Direct/0] 23:54:57
> via fe-1/2/2.0
10.3.0.41/32 *[Local/0] 23:54:57
Local via fe-1/2/2.0
10.3.0.48/30 *[Direct/0] 23:54:57
> via fe-1/2/1.0
[BGP/170] 23:54:44, localpref 100
AS path: 64516 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.50 via fe-1/2/1.0
10.3.0.49/32 *[Local/0] 23:54:57
Local via fe-1/2/1.0
172.16.8.0/21 *[BGP/170] 00:14:01, localpref 100
AS path: 64514 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.42 via fe-1/2/2.0
172.16.16.0/21 *[Static/5] 02:05:03
Reject
172.16.24.0/25 *[BGP/170] 23:09:26, localpref 100
AS path: 64516 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.50 via fe-1/2/1.0
172.16.24.128/25 *[BGP/170] 23:09:26, localpref 100
AS path: 64516 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.50 via fe-1/2/1.0
172.16.25.0/26 *[BGP/170] 23:09:26, localpref 100
AS path: 64516 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.50 via fe-1/2/1.0
172.16.25.64/26 *[BGP/170] 23:09:26, localpref 100
AS path: 64516 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.50 via fe-1/2/1.0
172.16.32.0/21 *[BGP/170] 22:42:13, localpref 100
AS path: 64510 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.2 via fe-1/2/0.0
[BGP/170] 22:47:19, localpref 100
AS path: 64514 64510 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.42 via fe-1/2/2.0
172.16.40.0/22 *[BGP/170] 22:47:19, localpref 100
AS path: 64514 64510 64511 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.42 via fe-1/2/2.0
172.16.44.0/23 *[BGP/170] 22:42:13, localpref 100
AS path: 64510 64512 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.2 via fe-1/2/0.0
172.16.44.0/26 *[BGP/170] 23:00:54, localpref 100
AS path: 64516 64512 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.50 via fe-1/2/1.0
172.16.44.64/26 *[BGP/170] 23:00:54, localpref 100
AS path: 64516 64512 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.50 via fe-1/2/1.0
172.16.44.128/26 *[BGP/170] 23:00:54, localpref 100
AS path: 64516 64512 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.50 via fe-1/2/1.0
172.16.44.192/26 *[BGP/170] 23:00:54, localpref 100
AS path: 64516 64512 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.50 via fe-1/2/1.0
192.168.0.5/32 *[BGP/170] 23:54:44, localpref 100
AS path: 64516 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.50 via fe-1/2/1.0
192.168.0.7/32 *[Direct/0] 23:54:57
> via lo0.0Significado
En el dispositivo Exchange-2, la ruta predeterminada 0/0 está oculta porque el siguiente salto para la ruta es su propia interfaz para el dispositivo Private-Peer-2, de donde se recibió la ruta. La ruta está oculta para evitar un bucle.
Verificación de las rutas en el dispositivo private-peer-1
Propósito
En Device Private-Peer-1, compruebe las rutas en la tabla de enrutamiento.
Acción
user@Private-Peer-1> show route
inet.0: 13 destinations, 13 routes (13 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
+ = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both
10.2.0.0/30 *[Direct/0] 23:58:57
> via fe-1/2/2.0
10.2.0.1/32 *[Local/0] 5d 21:34:22
Local via fe-1/2/2.0
10.3.0.44/30 *[Direct/0] 23:59:02
> via fe-1/2/1.0
10.3.0.46/32 *[Local/0] 1d 03:19:52
Local via fe-1/2/1.0
172.16.32.0/24 *[BGP/170] 22:51:22, localpref 100
AS path: 64510 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.2.0.2 via fe-1/2/2.0
172.16.33.0/24 *[BGP/170] 22:51:22, localpref 100
AS path: 64510 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.2.0.2 via fe-1/2/2.0
172.16.34.0/24 *[BGP/170] 22:46:16, localpref 100
AS path: 64510 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.2.0.2 via fe-1/2/2.0
172.16.35.0/24 *[BGP/170] 22:46:16, localpref 100
AS path: 64510 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.2.0.2 via fe-1/2/2.0
172.16.36.0/24 *[BGP/170] 22:46:16, localpref 100
AS path: 64510 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.2.0.2 via fe-1/2/2.0
172.16.37.0/24 *[BGP/170] 22:46:16, localpref 100
AS path: 64510 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.2.0.2 via fe-1/2/2.0
172.16.38.0/24 *[BGP/170] 22:46:16, localpref 100
AS path: 64510 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.2.0.2 via fe-1/2/2.0
172.16.39.0/24 *[BGP/170] 22:46:16, localpref 100
AS path: 64510 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.2.0.2 via fe-1/2/2.0
192.168.0.4/32 *[Direct/0] 5d 21:34:22
> via lo0.0Verificación de las rutas en el dispositivo private-peer-2
Propósito
En Device Private-Peer-2, compruebe las rutas en la tabla de enrutamiento.
Acción
user@Private-Peer-2> show route
inet.0: 29 destinations, 29 routes (29 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
+ = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both
0.0.0.0/0 *[Aggregate/130] 1d 02:13:28
> to 10.3.0.49 via fe-1/2/1.0
10.0.0.20/30 *[Direct/0] 1d 00:00:53
> via fe-1/2/0.0
10.0.0.22/32 *[Local/0] 4d 23:51:14
Local via fe-1/2/0.0
10.3.0.4/30 *[Direct/0] 23:59:36
> via fe-1/2/3.0
10.3.0.5/32 *[Local/0] 5d 21:34:57
Local via fe-1/2/3.0
10.3.0.48/30 *[Direct/0] 23:59:35
> via fe-1/2/1.0
10.3.0.50/32 *[Local/0] 1d 03:20:27
Local via fe-1/2/1.0
172.16.8.0/21 *[BGP/170] 00:18:39, localpref 100
AS path: 64515 64514 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.49 via fe-1/2/1.0
172.16.16.0/21 *[BGP/170] 02:09:41, localpref 100
AS path: 64515 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.49 via fe-1/2/1.0
172.16.24.0/25 *[Static/5] 23:14:04
Reject
172.16.24.128/25 *[Static/5] 23:14:04
Reject
172.16.25.0/26 *[Static/5] 23:14:04
Reject
172.16.25.64/26 *[Static/5] 23:14:04
Reject
172.16.32.0/21 *[BGP/170] 22:46:51, localpref 100
AS path: 64515 64510 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.49 via fe-1/2/1.0
172.16.32.0/24 *[BGP/170] 22:46:51, localpref 100
AS path: 64510 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.6 via fe-1/2/3.0
172.16.33.0/24 *[BGP/170] 22:46:51, localpref 100
AS path: 64510 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.6 via fe-1/2/3.0
172.16.34.0/24 *[BGP/170] 22:46:51, localpref 100
AS path: 64510 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.6 via fe-1/2/3.0
172.16.35.0/24 *[BGP/170] 22:46:51, localpref 100
AS path: 64510 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.6 via fe-1/2/3.0
172.16.36.0/24 *[BGP/170] 22:46:51, localpref 100
AS path: 64510 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.6 via fe-1/2/3.0
172.16.37.0/24 *[BGP/170] 22:46:51, localpref 100
AS path: 64510 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.6 via fe-1/2/3.0
172.16.38.0/24 *[BGP/170] 22:46:51, localpref 100
AS path: 64510 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.6 via fe-1/2/3.0
172.16.39.0/24 *[BGP/170] 22:46:51, localpref 100
AS path: 64510 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.6 via fe-1/2/3.0
172.16.40.0/22 *[BGP/170] 22:51:57, localpref 100
AS path: 64515 64514 64510 64511 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.49 via fe-1/2/1.0
172.16.44.0/23 *[BGP/170] 22:46:51, localpref 100
AS path: 64515 64510 64512 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.3.0.49 via fe-1/2/1.0
172.16.44.0/26 *[BGP/170] 23:05:32, localpref 100
AS path: 64512 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.21 via fe-1/2/0.0
172.16.44.64/26 *[BGP/170] 23:05:32, localpref 100
AS path: 64512 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.21 via fe-1/2/0.0
172.16.44.128/26 *[BGP/170] 23:05:32, localpref 100
AS path: 64512 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.21 via fe-1/2/0.0
172.16.44.192/26 *[BGP/170] 23:05:32, localpref 100
AS path: 64512 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.0.0.21 via fe-1/2/0.0
192.168.0.5/32 *[Direct/0] 5d 21:34:57
> via lo0.0