EN ESTA PÁGINA
Ejemplo: Publicidad de varias rutas en BGP
En este ejemplo, los enrutadores BGP están configurados para anunciar varias rutas en lugar de anunciar sólo la ruta activa. La publicidad de varias rutas en BGP se especifica en RFC 7911, Anuncio de varias rutas en BGP.
Requisitos
En este ejemplo, se utilizan los siguientes componentes de hardware y software:
Ocho dispositivos compatibles con BGP.
Cinco de los dispositivos habilitados para BGP no necesariamente tienen que ser enrutadores. Por ejemplo, pueden ser conmutadores Ethernet de la serie EX.
Tres de los dispositivos habilitados para BGP están configurados para enviar varias rutas o recibir varias rutas (o ambas envían y reciben varias rutas). Estos tres dispositivos habilitados para BGP deben ser enrutadores de borde multiservicio serie M, plataformas de enrutamiento universal 5G serie MX o enrutadores de núcleo serie T.
Los tres enrutadores deben ejecutar Junos OS versión 11.4 o posterior.
Descripción general
Las instrucciones siguientes se utilizan para configurar varias rutas de acceso a un destino:
[edit protocols bgp group group-name family family] add-path { receive; send { include-backup-path include-backup-path; multipath; path-count path-count; path-selection-mode { (all-paths | equal-cost-paths); } prefix-policy [ policy-names ... ]; } }
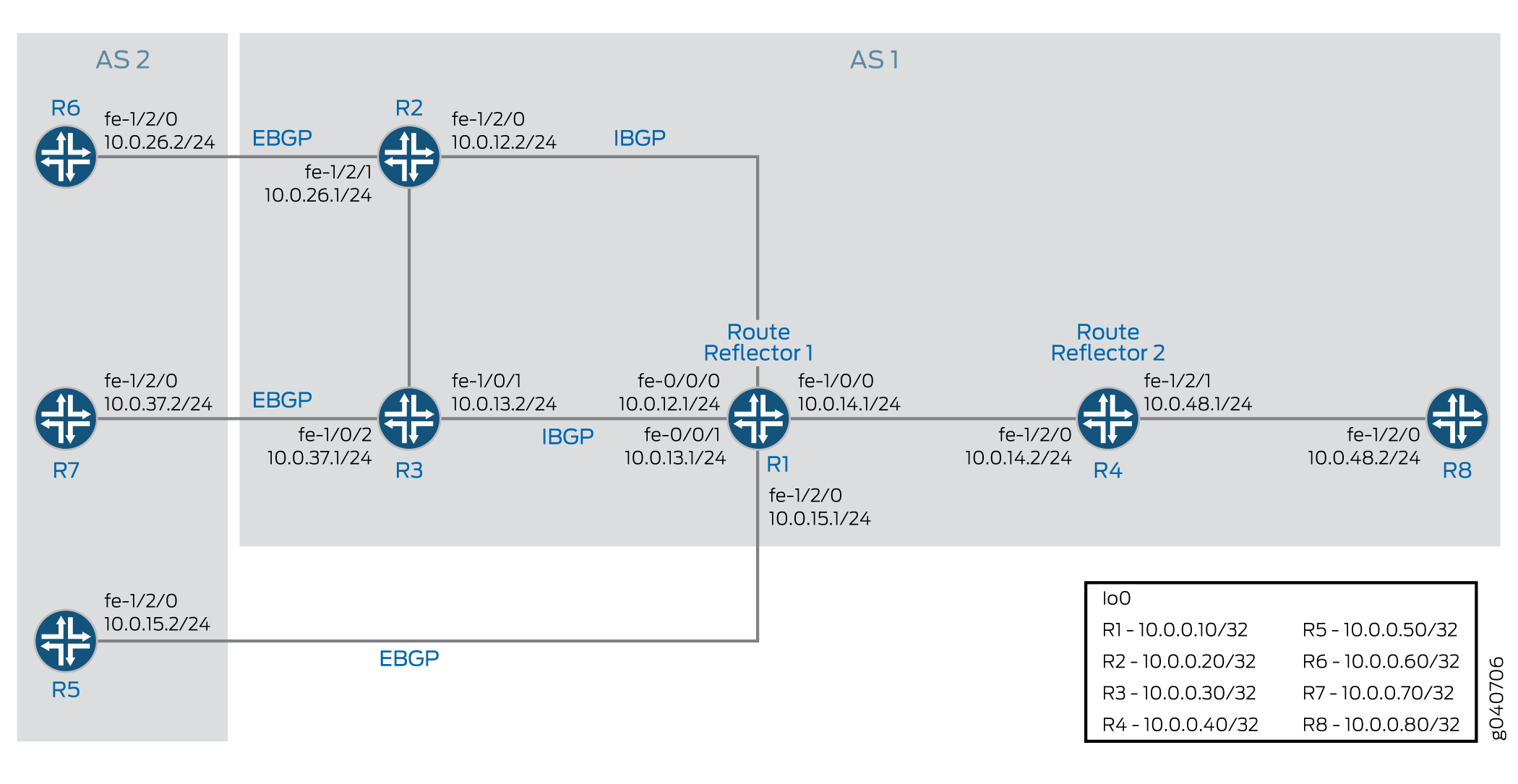
En este ejemplo, los enrutadores R5, R6 y R7 redistribuyen rutas estáticas en BGP. Los enrutadores R1 y R4 son reflectores de ruta. Los enrutadores R2 y R3 son clientes del reflector de ruta R1. El enrutador R8 es un cliente del Route Reflector R4.
La reflexión de ruta es opcional cuando el anuncio de varias rutas está habilitado en BGP.
Con esta configuración, el add-path send path-count 6 enrutador R1 está configurado para enviar hasta seis rutas (por destino) al enrutador R4.
Con esta configuración, el add-path receive enrutador R4 está configurado para recibir varias rutas del enrutador R1.
Con esta configuración, el add-path send path-count 6 enrutador R4 está configurado para enviar hasta seis rutas al enrutador R8.
Con esta configuración, el add-path receive enrutador R8 está configurado para recibir varias rutas del enrutador R4.
La add-path send prefix-policy allow_199 configuración de la política (junto con el filtro de ruta correspondiente) limita el enrutador R4 a enviar varias rutas solo para la ruta 172.16.199.1/32.
Diagrama de topología
Figura 1muestra la topología utilizada en este ejemplo.
Configuración
- Configuración rápida de CLI
- Configuración del enrutador R1
- Configuración del enrutador R2
- Configuración del enrutador R3
- Configuración del enrutador R4
- Configuración del enrutador R5
- Configuración del enrutador R6
- Configuración del enrutador R7
- Configuración del enrutador R8
- Resultados
Configuración rápida de CLI
Para configurar rápidamente este ejemplo, copie los siguientes comandos, péguelos en un archivo de texto, elimine los saltos de línea, cambie los detalles necesarios para que coincidan con su configuración de red y, a continuación, copie y pegue los comandos en la CLI en el nivel de [edit] jerarquía.
Enrutador R1
set interfaces fe-0/0/0 unit 12 family inet address 10.0.12.1/24 set interfaces fe-0/0/1 unit 13 family inet address 10.0.13.1/24 set interfaces fe-1/0/0 unit 14 family inet address 10.0.14.1/24 set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 15 family inet address 10.0.15.1/24 set interfaces lo0 unit 10 family inet address 10.0.0.10/32 set protocols bgp group rr type internal set protocols bgp group rr local-address 10.0.0.10 set protocols bgp group rr cluster 10.0.0.10 set protocols bgp group rr neighbor 10.0.0.20 set protocols bgp group rr neighbor 10.0.0.30 set protocols bgp group e1 type external set protocols bgp group e1 neighbor 10.0.15.2 local-address 10.0.15.1 set protocols bgp group e1 neighbor 10.0.15.2 peer-as 2 set protocols bgp group rr_rr type internal set protocols bgp group rr_rr local-address 10.0.0.10 set protocols bgp group rr_rr neighbor 10.0.0.40 family inet unicast add-path send path-count 6 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.10 passive set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface fe-0/0/0.12 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface fe-0/0/1.13 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface fe-1/0/0.14 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface fe-1/2/0.15 set routing-options router-id 10.0.0.10 set routing-options autonomous-system 1
Enrutador R2
set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 21 family inet address 10.0.12.2/24 set interfaces fe-1/2/1 unit 26 family inet address 10.0.26.1/24 set interfaces lo0 unit 20 family inet address 10.0.0.20/32 set protocols bgp group rr type internal set protocols bgp group rr local-address 10.0.0.20 set protocols bgp group rr neighbor 10.0.0.10 export set_nh_self set protocols bgp group e1 type external set protocols bgp group e1 neighbor 10.0.26.2 peer-as 2 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.20 passive set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface fe-1/2/0.21 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface fe-1/2/1.28 set policy-options policy-statement set_nh_self then next-hop self set routing-options autonomous-system 1
Enrutador R3
set interfaces fe-1/0/1 unit 31 family inet address 10.0.13.2/24 set interfaces fe-1/0/2 unit 37 family inet address 10.0.37.1/24 set interfaces lo0 unit 30 family inet address 10.0.0.30/32 set protocols bgp group rr type internal set protocols bgp group rr local-address 10.0.0.30 set protocols bgp group rr neighbor 10.0.0.10 export set_nh_self set protocols bgp group e1 type external set protocols bgp group e1 neighbor 10.0.37.2 peer-as 2 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.30 passive set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface fe-1/0/1.31 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface fe-1/0/2.37 set policy-options policy-statement set_nh_self then next-hop self set routing-options autonomous-system 1
Enrutador R4
set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 41 family inet address 10.0.14.2/24 set interfaces fe-1/2/1 unit 48 family inet address 10.0.48.1/24 set interfaces lo0 unit 40 family inet address 10.0.0.40/32 set protocols bgp group rr type internal set protocols bgp group rr local-address 10.0.0.40 set protocols bgp group rr family inet unicast add-path receive set protocols bgp group rr neighbor 10.0.0.10 set protocols bgp group rr_client type internal set protocols bgp group rr_client local-address 10.0.0.40 set protocols bgp group rr_client cluster 10.0.0.40 set protocols bgp group rr_client neighbor 10.0.0.80 family inet unicast add-path send path-count 6 set protocols bgp group rr_client neighbor 10.0.0.80 family inet unicast add-path send prefix-policy allow_199 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface fe-1/2/0.41 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.40 passive set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface fe-1/2/1.48 set policy-options policy-statement allow_199 from route-filter 172.16.199.1/32 exact set policy-options policy-statement allow_199 term match_199 from prefix-list match_199 set policy-options policy-statement allow_199 then add-path send-count 20 set policy-options policy-statement allow_199 then accept set routing-options autonomous-system 1
Enrutador R5
set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 51 family inet address 10.0.15.2/24 set interfaces lo0 unit 50 family inet address 10.0.0.50/32 set protocols bgp group e1 type external set protocols bgp group e1 neighbor 10.0.15.1 export s2b set protocols bgp group e1 neighbor 10.0.15.1 peer-as 1 set policy-options policy-statement s2b from protocol static set policy-options policy-statement s2b from protocol direct set policy-options policy-statement s2b then as-path-expand 2 set policy-options policy-statement s2b then accept set routing-options autonomous-system 2 set routing-options static route 172.16.199.1/32 reject set routing-options static route 172.16.198.1/32 reject
Enrutador R6
set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 62 family inet address 10.0.26.2/24 set interfaces lo0 unit 60 family inet address 10.0.0.60/32 set protocols bgp group e1 type external set protocols bgp group e1 neighbor 10.0.26.1 export s2b set protocols bgp group e1 neighbor 10.0.26.1 peer-as 1 set policy-options policy-statement s2b from protocol static set policy-options policy-statement s2b from protocol direct set policy-options policy-statement s2b then accept set routing-options autonomous-system 2 set routing-options static route 172.16.199.1/32 reject set routing-options static route 172.16.198.1/32 reject
Enrutador R7
set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 73 family inet address 10.0.37.2/24 set interfaces lo0 unit 70 family inet address 10.0.0.70/32 set protocols bgp group e1 type external set protocols bgp group e1 neighbor 10.0.37.1 export s2b set protocols bgp group e1 neighbor 10.0.37.1 peer-as 1 set policy-options policy-statement s2b from protocol static set policy-options policy-statement s2b from protocol direct set policy-options policy-statement s2b then accept set routing-options autonomous-system 2 set routing-options static route 172.16.199.1/32 reject
Enrutador R8
set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 84 family inet address 10.0.48.2/24 set interfaces lo0 unit 80 family inet address 10.0.0.80/32 set protocols bgp group rr type internal set protocols bgp group rr local-address 10.0.0.80 set protocols bgp group rr neighbor 10.0.0.40 family inet unicast add-path receive set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.80 passive set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface fe-1/2/0.84 set routing-options autonomous-system 1
Configuración del enrutador R1
Procedimiento paso a paso
En el ejemplo siguiente, debe explorar por varios niveles en la jerarquía de configuración. Para obtener información acerca de cómo navegar por la CLI, consulte Uso del editor de CLI en modo de configuración en la Guía del usuario de CLI de Junos OS.
Para configurar el enrutador R1:
Configure las interfaces con los enrutadores R2, R3, R4 y R5, y configure la interfaz de circuito cerrado (lo0).
[edit interfaces] user@R1# set fe-0/0/0 unit 12 family inet address 10.0.12.1/24 user@R1# set fe-0/0/1 unit 13 family inet address 10.0.13.1/24 user@R1# set fe-1/0/0 unit 14 family inet address 10.0.14.1/24 user@R1# set fe-1/2/0 unit 15 family inet address 10.0.15.1/24 user@R1#set lo0 unit 10 family inet address 10.0.0.10/32
Configure BGP en las interfaces y configure la reflexión de ruta del IBGP.
[edit protocols bgp] user@R1# set group rr type internal user@R1# set group rr local-address 10.0.0.10 user@R1# set group rr cluster 10.0.0.10 user@R1# set group rr neighbor 10.0.0.20 user@R1# set group rr neighbor 10.0.0.30 user@R1# set group rr_rr type internal user@R1# set group rr_rr local-address 10.0.0.10 user@R1# set group e1 type external user@R1# set group e1 neighbor 10.0.15.2 local-address 10.0.15.1 user@R1# set group e1 neighbor 10.0.15.2 peer-as 2
Configure el enrutador R1 para enviar hasta seis rutas a su vecino, el enrutador R4.
El destino de las rutas puede ser cualquier destino al que pueda llegar el enrutador R1 a través de varias rutas.
[edit protocols bgp] user@R1# set group rr_rr neighbor 10.0.0.40 family inet unicast add-path send path-count 6
Configure OSPF en las interfaces.
[edit protocols ospf] user@R1# set area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.10 passive user@R1# set area 0.0.0.0 interface fe-0/0/0.12 user@R1# set area 0.0.0.0 interface fe-0/0/1.13 user@R1# set area 0.0.0.0 interface fe-1/0/0.14 user@R1# set area 0.0.0.0 interface fe-1/2/0.15
Configure el ID del enrutador y el número de sistema autónomo.
[edit routing-options] user@R1# set router-id 10.0.0.10 user@R1# set autonomous-system 1
Cuando termine de configurar el dispositivo, confirme la configuración.
user@R1# commit
Resultados
Desde el modo de configuración, ingrese los comandos show interfaces, show protocols, show policy-options y show routing-options para confirmar la configuración. Si el resultado no muestra la configuración deseada, repita las instrucciones en este ejemplo para corregir la configuración.
user@R1# show interfaces
fe-0/0/0 {
unit 12 {
family inet {
address 10.0.12.1/24;
}
}
}
fe-0/0/1 {
unit 13 {
family inet {
address 10.0.13.1/24;
}
}
}
fe-1/0/0 {
unit 14 {
family inet {
address 10.0.14.1/24;
}
}
}
fe-1/2/0 {
unit 15 {
family inet {
address 10.0.15.1/24;
}
}
}
lo0 {
unit 10 {
family inet {
address 10.0.0.10/32;
}
}
}
user@R1# show protocols
bgp {
group rr {
type internal;
local-address 10.0.0.10;
cluster 10.0.0.10;
neighbor 10.0.0.20;
neighbor 10.0.0.30;
}
group e1 {
type external;
neighbor 10.0.15.2 {
local-address 10.0.15.1;
peer-as 2;
}
}
group rr_rr {
type internal;
local-address 10.0.0.10;
neighbor 10.0.0.40 {
family inet {
unicast {
add-path {
send {
path-count 6;
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
ospf {
area 0.0.0.0 {
interface lo0.10 {
passive;
}
interface fe-0/0/0.12;
interface fe-0/0/1.13;
interface fe-1/0/0.14;
interface fe-1/2/0.15;
}
}
user@R1# show routing-options router-id 10.0.0.10; autonomous-system 1;
Configuración del enrutador R2
Procedimiento paso a paso
Para configurar el enrutador R2:
Configure la interfaz de circuito cerrado (lo0) y las interfaces para los enrutadores R6 y R1.
[edit interfaces] user@R2# set fe-1/2/0 unit 21 family inet address 10.0.12.2/24 user@R2# set fe-1/2/1 unit 26 family inet address 10.0.26.1/24 user@R2# set lo0 unit 20 family inet address 10.0.0.20/32
Configure BGP y OSPF en las interfaces del enrutador R2.
[edit protocols] user@R2# set bgp group rr type internal user@R2# set bgp group rr local-address 10.0.0.20 user@R2# set bgp group e1 type external user@R2# set bgp group e1 neighbor 10.0.26.2 peer-as 2 user@R2# set ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.20 passive user@R2# set ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface fe-1/2/0.21 user@R2# set ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface fe-1/2/1.28
Para las rutas enviadas del enrutador R2 al enrutador R1, anuncie el enrutador R2 como el próximo salto, ya que el enrutador R1 no tiene una ruta a la dirección del enrutador R6 en la red 10.0.26.0/24.
[edit] user@R2# set policy-options policy-statement set_nh_self then next-hop self user@R2# set protocols bgp group rr neighbor 10.0.0.10 export set_nh_self
Configure el número de sistema autónomo.
[edit] user@R2# set routing-options autonomous-system 1
Cuando termine de configurar el dispositivo, confirme la configuración.
user@R2# commit
Resultados
Desde el modo de configuración, escriba los comandos , , y show routing-options para confirmar show interfacesla configuración. show protocolsshow policy-options Si el resultado no muestra la configuración deseada, repita las instrucciones en este ejemplo para corregir la configuración.
user@R2# show interfaces
fe-1/2/0 {
unit 21 {
family inet {
address 10.0.12.2/24;
}
}
}
fe-1/2/1 {
unit 26 {
family inet {
address 10.0.26.1/24;
}
}
}
lo0 {
unit 20 {
family inet {
address 10.0.0.20/32;
}
}
}
user@R2# show protocols
bgp {
group rr {
type internal;
local-address 10.0.0.20;
neighbor 10.0.0.10 {
export set_nh_self;
}
}
group e1 {
type external;
neighbor 10.0.26.2 {
peer-as 2;
}
}
}
ospf {
area 0.0.0.0 {
interface lo0.20 {
passive;
}
interface fe-1/2/0.21;
interface fe-1/2/1.28;
}
}
user@R2# show policy-options
policy-statement set_nh_self {
then {
next-hop self;
}
}
user@R2# show routing-options autonomous-system 1;
Configuración del enrutador R3
Procedimiento paso a paso
Para configurar el enrutador R3:
Configure la interfaz de circuito cerrado (lo0) y las interfaces para los enrutadores R7 y R1.
[edit interfaces] user@R3# set fe-1/0/1 unit 31 family inet address 10.0.13.2/24 user@R3# set fe-1/0/2 unit 37 family inet address 10.0.37.1/24 user@R3# set lo0 unit 30 family inet address 10.0.0.30/32
Configure BGP y OSPF en las interfaces del enrutador R3.
[edit protocols] user@R3# set bgp group rr type internal user@R3# set bgp group rr local-address 10.0.0.30 user@R3# set bgp group e1 type external user@R3# set bgp group e1 neighbor 10.0.37.2 peer-as 2 user@R3# set ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.30 passive user@R3# set ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface fe-1/0/1.31 user@R3# set ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface fe-1/0/2.37
Para las rutas enviadas del enrutador R3 al enrutador R1, anuncie el enrutador R3 como el próximo salto, ya que el enrutador R1 no tiene una ruta a la dirección del enrutador R7 en la red 10.0.37.0/24.
[edit] user@R3# set policy-options policy-statement set_nh_self then next-hop self user@R3# set protocols bgp group rr neighbor 10.0.0.10 export set_nh_self
Configure el número de sistema autónomo.
[edit] user@R3# set routing-options autonomous-system 1
Cuando termine de configurar el dispositivo, confirme la configuración.
user@R3# commit
Resultados
Desde el modo de configuración, ingrese los comandos show interfaces, show protocols, show policy-options y show routing-options para confirmar la configuración. Si el resultado no muestra la configuración deseada, repita las instrucciones en este ejemplo para corregir la configuración.
user@R3# show interfaces
fe-1/0/1 {
unit 31 {
family inet {
address 10.0.13.2/24;
}
}
}
fe-1/0/2 {
unit 37 {
family inet {
address 10.0.37.1/24;
}
}
}
lo0 {
unit 30 {
family inet {
address 10.0.0.30/32;
}
}
}
user@R3# show protocols
bgp {
group rr {
type internal;
local-address 10.0.0.30;
neighbor 10.0.0.10 {
export set_nh_self;
}
}
group e1 {
type external;
neighbor 10.0.37.2 {
peer-as 2;
}
}
}
ospf {
area 0.0.0.0 {
interface lo0.30 {
passive;
}
interface fe-1/0/1.31;
interface fe-1/0/2.37;
}
}
user@R3# show policy-options
policy-statement set_nh_self {
then {
next-hop self;
}
}
user@R3# show routing-options autonomous-system 1;
Configuración del enrutador R4
Procedimiento paso a paso
Para configurar el enrutador R4:
Configure las interfaces para los enrutadores R1 y R8, y configure la interfaz de circuito cerrado (lo0).
[edit interfaces] user@R4# set fe-1/2/0 unit 41 family inet address 10.0.14.2/24 user@R4# set fe-1/2/1 unit 48 family inet address 10.0.48.1/24 user@R4# set lo0 unit 40 family inet address 10.0.0.40/32
Configure BGP en las interfaces y configure la reflexión de ruta del IBGP.
[edit protocols bgp] user@R4# set group rr type internal user@R4# set group rr local-address 10.0.0.40 user@R4# set group rr neighbor 10.0.0.10 user@R4# set group rr_client type internal user@R4# set group rr_client local-address 10.0.0.40 user@R4# set group rr_client cluster 10.0.0.40
Configure el enrutador R4 para enviar hasta seis rutas a su vecino, el enrutador R8.
El destino de las rutas puede ser cualquier destino al que pueda llegar el enrutador R4 a través de varias rutas.
[edit protocols bgp] user@R4# set group rr_client neighbor 10.0.0.80 family inet unicast add-path send path-count 6
Configure el enrutador R4 para recibir varias rutas de su vecino, el enrutador R1.
El destino de las rutas puede ser cualquier destino al que pueda llegar el enrutador R1 a través de varias rutas.
[edit protocols bgp group rr family inet unicast] user@R4# set add-path receive
Configure OSPF en las interfaces.
[edit protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0] user@R4# set interface fe-1/2/0.41 user@R4# set interface lo0.40 passive user@R4# set interface fe-1/2/1.48
Configure una política que permita al enrutador R4 enviar varias rutas al enrutador R8 a la ruta 172.16.199.1/32.
El enrutador R4 recibe varias rutas para la ruta 172.16.198.1/32 y la ruta 172.16.199.1/32. Sin embargo, debido a esta política, el enrutador R4 solo envía varias rutas para la ruta 172.16.199.1/32.
[edit protocols bgp group rr_client neighbor 10.0.0.80 family inet unicast] user@R4# set add-path send prefix-policy allow_199 [edit policy-options policy-statement allow_199] user@R4# set from route-filter 172.16.199.1/32 exact user@R4# set then accept
El enrutador R4 también se puede configurar para enviar hasta 20 rutas BGP
add-pathpara un subconjunto de prefijos anunciados de ruta de adición.[edit policy-options policy-statement allow_199] user@R4# set term match_199 from prefix-list match_199 user@R4# set then add-path send-count 20
Configure el número de sistema autónomo.
[edit routing-options] user@R4# set autonomous-system 1
Cuando termine de configurar el dispositivo, confirme la configuración.
user@R4# commit
Resultados
Desde el modo de configuración, ingrese los comandos show interfaces, show protocols, show policy-options y show routing-options para confirmar la configuración. Si el resultado no muestra la configuración deseada, repita las instrucciones en este ejemplo para corregir la configuración.
user@R4# show interfaces
fe-1/2/0 {
unit 41 {
family inet {
address 10.0.14.2/24;
}
}
}
fe-1/2/1 {
unit 48 {
family inet {
address 10.0.48.1/24;
}
}
}
lo0 {
unit 40 {
family inet {
address 10.0.0.40/32;
}
}
}
user@R4# show protocols
bgp {
group rr {
type internal;
local-address 10.0.0.40;
family inet {
unicast {
add-path {
receive;
}
}
}
neighbor 10.0.0.10;
}
group rr_client {
type internal;
local-address 10.0.0.40;
cluster 10.0.0.40;
neighbor 10.0.0.80 {
family inet {
unicast {
add-path {
send {
path-count 6;
prefix-policy allow_199;
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
ospf {
area 0.0.0.0 {
interface lo0.40 {
passive;
}
interface fe-1/2/0.41;
interface fe-1/2/1.48;
}
}
user@R4# show policy-options
policy-statement allow_199 {
from {
route-filter 172.16.199.1/32 exact;
}
from term match_199 {
prefix-list match_199;
}
then add-path send-count 20;
then accept;
}
user@R4# show routing-options autonomous-system 1;
Configuración del enrutador R5
Procedimiento paso a paso
Para configurar el enrutador R5:
Configure la interfaz de circuito cerrado (lo0) y la interfaz para el enrutador R1.
[edit interfaces] user@R5# set fe-1/2/0 unit 51 family inet address 10.0.15.2/24 user@R5# set lo0 unit 50 family inet address 10.0.0.50/32
Configure BGP en la interfaz del enrutador R5.
[edit protocols bgp group e1] user@R5# set type external user@R5# set neighbor 10.0.15.1 peer-as 1
Cree rutas estáticas para redistribuirlas en BGP.
[edit routing-options] user@R5# set static route 172.16.199.1/32 reject user@R5# set static route 172.16.198.1/32 reject
Redistribuya rutas estáticas y directas en BGP.
[edit protocols bgp group e1 neighbor 10.0.15.1] user@R5# set export s2b [edit policy-options policy-statement s2b] user@R5# set from protocol static user@R5# set from protocol direct user@R5# set then as-path-expand 2 user@R5# set then accept
Configure el número de sistema autónomo.
[edit routing-options] user@R5# set autonomous-system 2
Cuando termine de configurar el dispositivo, confirme la configuración.
user@R5# commit
Resultados
Desde el modo de configuración, ingrese los comandos show interfaces, show protocols, show policy-options y show routing-options para confirmar la configuración. Si el resultado no muestra la configuración deseada, repita las instrucciones en este ejemplo para corregir la configuración.
user@R5# show interfaces
fe-1/2/0 {
unit 51 {
family inet {
address 10.0.15.2/24;
}
}
}
lo0 {
unit 50 {
family inet {
address 10.0.0.50/32;
}
}
}
user@R5# show protocols
bgp {
group e1 {
type external;
neighbor 10.0.15.1 {
export s2b;
peer-as 1;
}
}
}
user@R5# show policy-options
policy-statement s2b {
from protocol [ static direct ];
then {
as-path-expand 2;
accept;
}
}
user@R5# show routing-options
static {
route 172.16.198.1/32 reject;
route 172.16.199.1/32 reject;
}
autonomous-system 2;
Configuración del enrutador R6
Procedimiento paso a paso
Para configurar el enrutador R6:
Configure la interfaz de circuito cerrado (lo0) y la interfaz del enrutador R2.
[edit interfaces] user@R6# set fe-1/2/0 unit 62 family inet address 10.0.26.2/24 user@R6# set lo0 unit 60 family inet address 10.0.0.60/32
Configure BGP en la interfaz del enrutador R6.
[edit protocols] user@R6# set bgp group e1 type external user@R6# set bgp group e1 neighbor 10.0.26.1 peer-as 1
Cree rutas estáticas para redistribuirlas en BGP.
[edit] user@R6# set routing-options static route 172.16.199.1/32 reject user@R6# set routing-options static route 172.16.198.1/32 reject
Redistribuya rutas estáticas y directas de la tabla de enrutamiento del enrutador R6 a BGP.
[edit protocols bgp group e1 neighbor 10.0.26.1] user@R6# set export s2b [edit policy-options policy-statement s2b] user@R6# set from protocol static user@R6# set from protocol direct user@R6# set then accept
Configure el número de sistema autónomo.
[edit routing-options] user@R6# set autonomous-system 2
Cuando termine de configurar el dispositivo, confirme la configuración.
user@R6# commit
Resultados
Desde el modo de configuración, ingrese los comandos show interfaces, show protocols, show policy-options y show routing-options para confirmar la configuración. Si el resultado no muestra la configuración deseada, repita las instrucciones en este ejemplo para corregir la configuración.
user@R6# show interfaces
fe-1/2/0 {
unit 62 {
family inet {
address 10.0.26.2/24;
}
}
}
lo0 {
unit 60 {
family inet {
address 10.0.0.60/32;
}
}
}
user@R6# show protocols
bgp {
group e1 {
type external;
neighbor 10.0.26.1 {
export s2b;
peer-as 1;
}
}
}
user@R6# show policy-options
policy-statement s2b {
from protocol [ static direct ];
then accept;
}
user@R6# show routing-options
static {
route 172.16.198.1/32 reject;
route 172.16.199.1/32 reject;
}
autonomous-system 2;
Configuración del enrutador R7
Procedimiento paso a paso
Para configurar el enrutador R7:
Configure la interfaz de circuito cerrado (lo0) y la interfaz para el enrutador R3.
[edit interfaces] user@R7# set fe-1/2/0 unit 73 family inet address 10.0.37.2/24 user@R7# set lo0 unit 70 family inet address 10.0.0.70/32
Configure BGP en la interfaz del enrutador R7.
[edit protocols bgp group e1] user@R7# set type external user@R7# set neighbor 10.0.37.1 peer-as 1
Cree una ruta estática para redistribuirla en BGP.
[edit] user@R7# set routing-options static route 172.16.199.1/32 reject
Redistribuya rutas estáticas y directas de la tabla de enrutamiento del enrutador R7 a BGP.
[edit protocols bgp group e1 neighbor 10.0.37.1] user@R7# set export s2b [edit policy-options policy-statement s2b] user@R7# set from protocol static user@R7# set from protocol direct user@R7# set then accept
Configure el número de sistema autónomo.
[edit routing-options] user@R7# set autonomous-system 2
Cuando termine de configurar el dispositivo, confirme la configuración.
user@R7# commit
Resultados
Desde el modo de configuración, ingrese los comandos show interfaces, show protocols, show policy-options y show routing-options para confirmar la configuración. Si el resultado no muestra la configuración deseada, repita las instrucciones en este ejemplo para corregir la configuración.
user@R7# show interfaces
fe-1/2/0 {
unit 73 {
family inet {
address 10.0.37.2/24;
}
}
}
lo0 {
unit 70 {
family inet {
address 10.0.0.70/32;
}
}
}
user@R7# show protocols
bgp {
group e1 {
type external;
neighbor 10.0.37.1 {
export s2b;
peer-as 1;
}
}
}
user@R7# show policy-options
policy-statement s2b {
from protocol [ static direct ];
then accept;
}
user@R7# show routing-options
static {
route 172.16.199.1/32 reject;
}
autonomous-system 2;
Configuración del enrutador R8
Procedimiento paso a paso
Para configurar el enrutador R8:
Configure la interfaz de circuito cerrado (lo0) y la interfaz para el enrutador R4.
[edit interfaces] user@R8# set fe-1/2/0 unit 84 family inet address 10.0.48.2/24 user@R8# set lo0 unit 80 family inet address 10.0.0.80/32
Configure BGP y OSPF en la interfaz del enrutador R8.
[edit protocols] user@R8# set bgp group rr type internal user@R8# set bgp group rr local-address 10.0.0.80 user@R8# set ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.80 passive user@R8# set ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface fe-1/2/0.84
Configure el enrutador R8 para recibir varias rutas de su vecino, el enrutador R4.
El destino de las rutas puede ser cualquier destino al que pueda llegar el enrutador R4 a través de varias rutas.
[edit protocols] user@R8# set bgp group rr neighbor 10.0.0.40 family inet unicast add-path receive
Configure el número de sistema autónomo.
[edit] user@R8# set routing-options autonomous-system 1
Cuando termine de configurar el dispositivo, confirme la configuración.
user@R8# commit
Resultados
Desde el modo de configuración, ingrese los comandos show interfaces, show protocols, show policy-options y show routing-options para confirmar la configuración. Si el resultado no muestra la configuración deseada, repita las instrucciones en este ejemplo para corregir la configuración.
user@R8# show interfaces
fe-1/2/0 {
unit 84 {
family inet {
address 10.0.48.2/24;
}
}
}
lo0 {
unit 80 {
family inet {
address 10.0.0.80/32;
}
}
}
user@R8# show protocols
bgp {
group rr {
type internal;
local-address 10.0.0.80;
neighbor 10.0.0.40 {
family inet {
unicast {
add-path {
receive;
}
}
}
}
}
}
ospf {
area 0.0.0.0 {
interface lo0.80 {
passive;
}
interface fe-1/2/0.84;
}
}
user@R8# show routing-options autonomous-system 1;
Verificación
Confirme que la configuración funcione correctamente.
- Comprobación de que los pares BGP tienen la capacidad de enviar y recibir varias rutas
- Comprobación de que el enrutador R1 anuncia varias rutas
- Verificar que el enrutador R4 está recibiendo y anunciando múltiples rutas
- Comprobación de que el enrutador R8 recibe varias rutas
- Comprobación del ID de ruta
Comprobación de que los pares BGP tienen la capacidad de enviar y recibir varias rutas
Propósito
Asegúrese de que una o ambas de las siguientes cadenas aparecen en la salida del show bgp neighbor comando:
NLRI's for which peer can receive multiple paths: inet-unicastNLRI's for which peer can send multiple paths: inet-unicast
Acción
user@R1> show bgp neighbor 10.0.0.40 Peer: 10.0.0.40+179 AS 1 Local: 10.0.0.10+64227 AS 1 Type: Internal State: Established Flags: <Sync> ... NLRI's for which peer can receive multiple paths: inet-unicast ...
user@R4> show bgp neighbor 10.0.0.10 Peer: 10.0.0.10+64227 AS 1 Local: 10.0.0.40+179 AS 1 Type: Internal State: Established Flags: <Sync> ... NLRI's for which peer can send multiple paths: inet-unicast ...
user@R4> show bgp neighbor 10.0.0.80 Peer: 10.0.0.80+55416 AS 1 Local: 10.0.0.40+179 AS 1 Type: Internal State: Established (route reflector client)Flags: <Sync> ,,, NLRI's for which peer can receive multiple paths: inet-unicast ...
user@R8> show bgp neighbor 10.0.0.40 Peer: 10.0.0.40+179 AS 1 Local: 10.0.0.80+55416 AS 1 Type: Internal State: Established Flags: <Sync> ... NLRI's for which peer can send multiple paths: inet-unicast ...
Comprobación de que el enrutador R1 anuncia varias rutas
Propósito
Asegúrese de que se anuncien en el enrutador R4 varias rutas al destino 172.16.198.1/32 y varias rutas al destino 172.16.199.1/32.
Acción
user@R1> show route advertising-protocol bgp 10.0.0.40
inet.0: 21 destinations, 25 routes (21 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
Prefix Nexthop MED Lclpref AS path
* 10.0.0.50/32 10.0.15.2 100 2 2 I
* 10.0.0.60/32 10.0.0.20 100 2 I
* 10.0.0.70/32 10.0.0.30 100 2 I
* 172.16.198.1/32 10.0.0.20 100 2 I
10.0.15.2 100 2 2 I
* 172.16.199.1/32 10.0.0.20 100 2 I
10.0.0.30 100 2 I
10.0.15.2 100 2 2 I
* 172.16.200.0/30 10.0.0.20 100 2 I
Significado
Cuando vea un prefijo y más de un salto siguiente, significa que se anuncian múltiples rutas al enrutador R4.
Verificar que el enrutador R4 está recibiendo y anunciando múltiples rutas
Propósito
Asegúrese de que se reciben varias rutas al destino 172.16.199.1/32 desde el enrutador R1 y se anuncian en el enrutador R8. Asegúrese de que se reciben varias rutas al destino 172.16.198.1/32 desde el enrutador R1, pero solo se anuncia una ruta a este destino al enrutador R8.
Acción
user@R4> show route receive-protocol bgp 10.0.0.10
inet.0: 19 destinations, 22 routes (19 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
Prefix Nexthop MED Lclpref AS path
* 10.0.0.50/32 10.0.15.2 100 2 2 I
* 10.0.0.60/32 10.0.0.20 100 2 I
* 10.0.0.70/32 10.0.0.30 100 2 I
* 172.16.198.1/32 10.0.0.20 100 2 I
10.0.15.2 100 2 2 I
* 172.16.199.1/32 10.0.0.20 100 2 I
10.0.0.30 100 2 I
10.0.15.2 100 2 2 I
* 172.16.200.0/30 10.0.0.20 100 2 I
user@R4> show route advertising-protocol bgp 10.0.0.80
inet.0: 19 destinations, 22 routes (19 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
Prefix Nexthop MED Lclpref AS path
* 10.0.0.50/32 10.0.15.2 100 2 2 I
* 10.0.0.60/32 10.0.0.20 100 2 I
* 10.0.0.70/32 10.0.0.30 100 2 I
* 172.16.198.1/32 10.0.0.20 100 2 I
* 172.16.199.1/32 10.0.0.20 100 2 I
10.0.0.30 100 2 I
10.0.15.2 100 2 2 I
* 172.16.200.0/30 10.0.0.20 100 2 I
Significado
El show route receive-protocol comando muestra que el enrutador R4 recibe dos rutas al destino 172.16.198.1/32 y tres rutas al destino 172.16.199.1/32. El show route advertising-protocol comando muestra que el enrutador R4 anuncia solo una ruta al destino 172.16.198.1/32 y anuncia las tres rutas al destino 172.16.199.1/32.
Debido a la política de prefijos que se aplica al enrutador R4, el enrutador R4 no anuncia varias rutas al destino 172.16.198.1/32. El enrutador R4 anuncia solo una ruta al destino 172.16.198.1/32, aunque reciba varias rutas a este destino.
Comprobación de que el enrutador R8 recibe varias rutas
Propósito
Asegúrese de que el enrutador R8 reciba varias rutas al destino 172.16.199.1/32 a través del enrutador R4. Asegúrese de que el enrutador R8 reciba solo una ruta al destino 172.16.198.1/32 a través del enrutador R4.
Acción
user@R8> show route receive-protocol bgp 10.0.0.40
inet.0: 18 destinations, 20 routes (18 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
Prefix Nexthop MED Lclpref AS path
* 10.0.0.50/32 10.0.15.2 100 2 2 I
* 10.0.0.60/32 10.0.0.20 100 2 I
* 10.0.0.70/32 10.0.0.30 100 2 I
* 172.16.198.1/32 10.0.0.20 100 2 I
* 172.16.199.1/32 10.0.0.20 100 2 I
10.0.0.30 100 2 I
10.0.15.2 100 2 2 I
* 200.1.1.0/30 10.0.0.20 100 2 I
Comprobación del ID de ruta
Propósito
En los dispositivos descendentes, enrutadores R4 y R8, verifique que un ID de ruta identifique de forma exclusiva la ruta. Busque la Addpath Path ID: cuerda.
Acción
user@R4> show route 172.16.199.1/32 detail
inet.0: 18 destinations, 20 routes (18 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
172.16.199.1/32 (3 entries, 3 announced)
*BGP Preference: 170/-101
Next hop type: Indirect
Next-hop reference count: 9
Source: 10.0.0.10
Next hop type: Router, Next hop index: 676
Next hop: 10.0.14.1 via lt-1/2/0.41, selected
Protocol next hop: 10.0.0.20
Indirect next hop: 92041c8 262146
State: <Active Int Ext>
Local AS: 1 Peer AS: 1
Age: 1:44:37 Metric2: 2
Task: BGP_1.10.0.0.10+64227
Announcement bits (3): 2-KRT 3-BGP RT Background 4-Resolve tree 1
AS path: 2 I (Originator) Cluster list: 10.0.0.10
AS path: Originator ID: 10.0.0.20
Accepted
Localpref: 100
Router ID: 10.0.0.10
Addpath Path ID: 1
BGP Preference: 170/-101
Next hop type: Indirect
Next-hop reference count: 4
Source: 10.0.0.10
Next hop type: Router, Next hop index: 676
Next hop: 10.0.14.1 via lt-1/2/0.41, selected
Protocol next hop: 10.0.0.30
Indirect next hop: 92042ac 262151
State: <NotBest Int Ext>
Inactive reason: Not Best in its group - Router ID
Local AS: 1 Peer AS: 1
Age: 1:44:37 Metric2: 2
Task: BGP_1.10.0.0.10+64227
Announcement bits (1): 3-BGP RT Background
AS path: 2 I (Originator) Cluster list: 10.0.0.10
AS path: Originator ID: 10.0.0.30
Accepted
Localpref: 100
Router ID: 10.0.0.10
Addpath Path ID: 2
BGP Preference: 170/-101
Next hop type: Indirect
Next-hop reference count: 4
Source: 10.0.0.10
Next hop type: Router, Next hop index: 676
Next hop: 10.0.14.1 via lt-1/2/0.41, selected
Protocol next hop: 10.0.15.2
Indirect next hop: 92040e4 262150
State: <Int Ext>
Inactive reason: AS path
Local AS: 1 Peer AS: 1
Age: 1:44:37 Metric2: 2
Task: BGP_1.10.0.0.10+64227
Announcement bits (1): 3-BGP RT Background
AS path: 2 2 I
Accepted
Localpref: 100
Router ID: 10.0.0.10
Addpath Path ID: 3user@R8> show route 172.16.199.1/32 detail
inet.0: 17 destinations, 19 routes (17 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
172.16.199.1/32 (3 entries, 1 announced)
*BGP Preference: 170/-101
Next hop type: Indirect
Next-hop reference count: 9
Source: 10.0.0.40
Next hop type: Router, Next hop index: 1045
Next hop: 10.0.48.1 via lt-1/2/0.84, selected
Protocol next hop: 10.0.0.20
Indirect next hop: 91fc0e4 262148
State: <Active Int Ext>
Local AS: 1 Peer AS: 1
Age: 1:56:51 Metric2: 3
Task: BGP_1.10.0.0.40+179
Announcement bits (2): 2-KRT 4-Resolve tree 1
AS path: 2 I (Originator) Cluster list: 10.0.0.40 10.0.0.10
AS path: Originator ID: 10.0.0.20
Accepted
Localpref: 100
Router ID: 10.0.0.40
Addpath Path ID: 1
BGP Preference: 170/-101
Next hop type: Indirect
Next-hop reference count: 4
Source: 10.0.0.40
Next hop type: Router, Next hop index: 1045
Next hop: 10.0.48.1 via lt-1/2/0.84, selected
Protocol next hop: 10.0.0.30
Indirect next hop: 91fc1c8 262152
State: <NotBest Int Ext>
Inactive reason: Not Best in its group - Router ID
Local AS: 1 Peer AS: 1
Age: 1:56:51 Metric2: 3
Task: BGP_1.10.0.0.40+179
AS path: 2 I (Originator) Cluster list: 10.0.0.40 10.0.0.10
AS path: Originator ID: 10.0.0.30
Accepted
Localpref: 100
Router ID: 10.0.0.40
Addpath Path ID: 2
BGP Preference: 170/-101
Next hop type: Indirect
Next-hop reference count: 4
Source: 10.0.0.40
Next hop type: Router, Next hop index: 1045
Next hop: 10.0.48.1 via lt-1/2/0.84, selected
Protocol next hop: 10.0.15.2
Indirect next hop: 91fc2ac 262153
State: <Int Ext>
Inactive reason: AS path
Local AS: 1 Peer AS: 1
Age: 1:56:51 Metric2: 3
Task: BGP_1.10.0.0.40+179
AS path: 2 2 I (Originator) Cluster list: 10.0.0.40
AS path: Originator ID: 10.0.0.10
Accepted
Localpref: 100
Router ID: 10.0.0.40
Addpath Path ID: 3