Beispiel: Konfiguration der Sampling- und Verwerfungsabrechnung auf Routern der M-, MX- und T-Serie
Mit der Verwerfungsabrechnung können Sie Stichproben von Datenverkehr erstellen, ihn zur Analyse an einen Datenflussserver senden und alle Pakete verwerfen, ohne sie an ihr beabsichtigtes Ziel weiterzuleiten. Die Verwerfungsabrechnung wird mit der discard accounting group-name Anweisung in einem Firewallfilter auf Hierarchieebene [edit firewall family inet filter filter-name term term-name then] aktiviert. Anschließend wird der Filter auf eine Schnittstelle mit der filter Anweisung auf der [edit interfaces interface-name unit unit-number family inet] Hierarchieebene angewendet und mit der output Anweisung auf der [edit forwarding-options accounting group-name] Hierarchieebene verarbeitet.
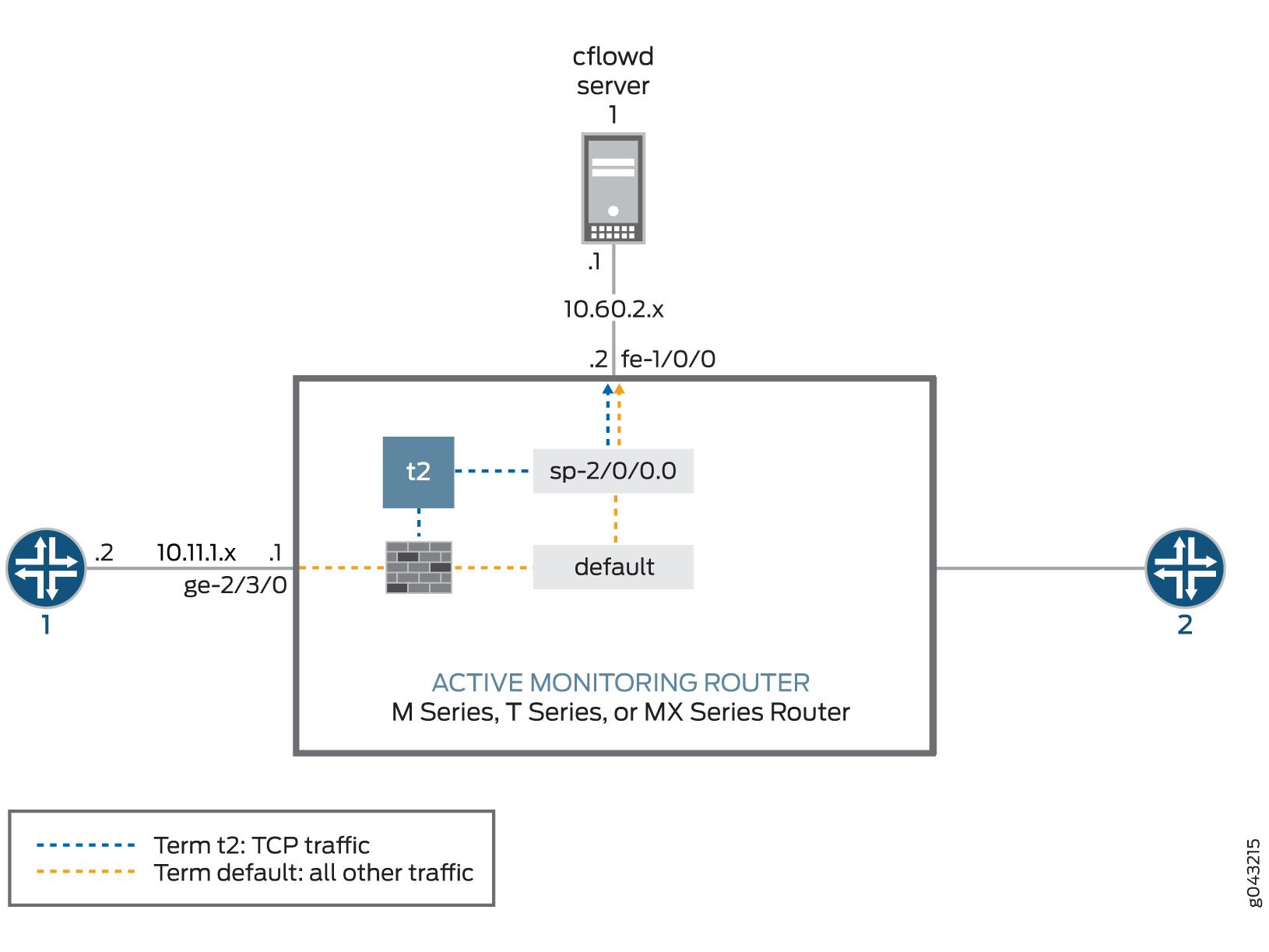
In Abbildung 1 gelangt der Datenverkehr von Router 1 über die Gigabit-Ethernet-Schnittstelle ge-2/3/0 des Überwachungsrouters. Die Exportschnittstelle, die zum Flow-Server führt, ist fe-1/0/0, und es gibt keine Beendigungsschnittstelle.
In diesem Beispiel wird TCP-Datenverkehr an eine Abrechnungsgruppe gesendet, und der gesamte andere Datenverkehr wird an eine zweite Gruppe umgeleitet. Nach der Stichprobenerhebung und Zählung werden die beiden Datenverkehrstypen von den Stichproben- und Abrechnungsprozessen bearbeitet. Diese Prozesse erstellen Flow-Datensätze und senden die Datensätze zur Analyse an den Flow-Server der Version 8. Da mehrere Datenverkehrstypen an denselben Server gesendet werden, empfiehlt es sich, die engine-id, den engine-type und source-address die Anweisungen manuell in Ihren Buchhaltungs- und Samplinghierarchien zu konfigurieren. Auf diese Weise können Sie zwischen Datenverkehrstypen unterscheiden, wenn sie beim Flow-Server eintreffen.
[edit]
interfaces {
sp-2/0/0 { # This adaptive services interface creates the flow records.
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.5.5.1/32 {
destination 10.5.5.2;
}
}
}
}
fe-1/0/0 { # This is the interface where records are sent to the flow server.
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.60.2.2/30;
}
}
}
ge-2/3/0 { # This is the input interface where traffic enters the router.
unit 0 {
family inet {
filter {
input catch_all;
}
address 10.11.1.1/30;
}
}
}
}
forwarding-options {
sampling { # The router samples the traffic.
input {
rate 100; # One out of every 100 packets is sampled.
}
}
family inet {
output { # The sampling process creates and exports flow records.
flow-server 10.60.2.1 { # You can configure a variety of settings.
port 2055;
version 8;
aggregation { # Aggregation is unique to flow version 8.
protocol-port;
source-destination-prefix;
}
}
aggregate-export-interval 90;
flow-inactive-timeout 60;
flow-active-timeout 60;
interface sp-2/0/0 { # This statement enables PIC-based sampling.
engine-id 5; # Engine statements are dynamic, but can be configured.
engine-type 55;
source-address 10.60.2.2; # You must configure this statement.
}
}
}
accounting counter1 { # This discard accounting process handles default traffic.
output { # This process creates and exports flow records.
flow-inactive-timeout 65;
flow-active-timeout 65;
flow-server 10.60.2.1 { # You can configure a variety of settings.
port 2055;
version 8;
aggregation { # Aggregation is unique to version 8.
protocol-port;
source-destination-prefix;
}
}
interface sp-2/0/0 { # This statement enables PIC-based discard accounting.
engine-id 1; # Engine statements are dynamic, but can be configured.
engine-type 11;
source-address 10.60.2.3; # You must configure this statement.
}
}
}
accounting t2 { # The second discard accounting process handles the TCP traffic.
output { # This process creates and exports flow records.
aggregate-export-interval 90;
flow-inactive-timeout 65;
flow-active-timeout 65;
flow-server 10.60.2.1 { # You can configure a variety of settings for the server.
port 2055;
version 8;
aggregation { # Aggregation is unique to version 8.
protocol-port;
source-destination-prefix;
}
}
interface sp-2/0/0 { # This statement enables PIC-based discard accounting.
engine-id 2; # Engine statements are dynamic, but can be configured.
engine-type 22;
source-address 10.60.2.4;# You must configure this statement.
}
}
}
}
firewall {
family inet {
filter catch_all { # Apply the firewall filter on the input interface.
term t2 { # This places TCP traffic into one group for sampling and
from { # discard accounting.
protocol tcp;
}
then {
count c2;# The count action counts traffic as it enters the router.
sample; # The sample action sends the traffic to the sampling process.
discard accounting t2; # The discard accounting discards traffic.
}
}
term default { # Performs sampling and discard accounting on all other traffic.
then {
count counter; # The count action counts traffic as it enters the router.
sample# The sample action sends the traffic to the sampling process.
discard accounting counter1; # This activates discard accounting.
}
}
}
}
}
Verifizierung Ihrer Arbeit
Um zu überprüfen, ob Ihre Konfiguration korrekt ist, verwenden Sie die folgenden Befehle auf der Überwachungsstation, die für die aktive Datenstromüberwachung konfiguriert ist:
-
show services accounting aggregation(nur für Flows der Version 8) -
show services accounting errors -
show services accounting (flow | flow-detail) -
show services accounting memory -
show services accounting packet-size-distribution -
show services accounting status -
show services accounting usage
Im Folgenden sehen Sie die Ausgabe der Befehle, die show mit dem Konfigurationsbeispiel verwendet werden:
user@host> show services accounting flow name t2
Service Accounting interface: sp-2/0/0, Local interface index: 468
Service name: t2
Flow information
Flow packets: 56130820, Flow bytes: 3592372480
Flow packets 10-second rate: 13024, Flow bytes 10-second rate: 833573
Active flows: 600, Total flows: 600
Flows exported: 28848, Flows packets exported: 960
Flows inactive timed out: 0, Flows active timed out: 35400
user@host> show services accounting
Service Name:
(default sampling)
counter1
t2
user@host> show services accounting aggregation protocol-port detail name t2
Service Accounting interface: sp-2/0/0, Local interface index: 468
Service name: t2
Protocol: 6, Source port: 20, Destination port: 20
Start time: 442794, End time: 6436260
Flow count: 1, Packet count: 4294693925, Byte count: 4277471552
user@host> show services accounting aggregation source-destination-prefix name
t2 limit 10 order packets
Service Accounting interface: sp-2/0/0, Local interface index: 542
Service name: t2
Source Destination Input SNMP Output SNMP Flow Packet Byte
Prefix Prefix Index Index count count count
10.1.1.2/20 10.225.0.1/0 24 26 0 13 9650
10.1.1.2/20 10.143.80.1/0 24 26 0 13 10061
10.1.1.2/20 10.59.176.1/0 24 26 0 13 10426
10.1.1.2/20 10.5.32.1/0 24 26 0 13 12225
10.1.1.2/20 10.36.16.1/0 24 26 0 13 9116
10.1.1.2/20 10.1.96.1/0 24 26 0 12 11050
10.1.1.2/20 10.14.48.1/0 24 26 0 13 10812
10.1.1.2/20 10.31.192.1/0 24 26 0 13 11473
10.1.1.2/20 10.129.144.1/0 24 26 0 13 7647
10.1.1.2/20 10.188.160.1/0 24 26 0 13 10056
user@host> show services accounting aggregation source-destination-prefix name
t2 extensive limit 3
Service Accounting interface: sp-2/0/0, Local interface index: 542
Service name: t2
Source address: 10.1.1.2, Source prefix length: 20
Destination address: 10.200.176.1, Destination prefix length: 0
Input SNMP interface index: 24, Output SNMP interface index: 26
Source-AS: 69, Destination-AS: 69
Start time: Fri Feb 21 14:16:57 2003, End time: Fri Feb 21 14:22:50 2003
Flow count: 0, Packet count: 6, Byte count: 5340
Source address: 10.1.1.2, Source prefix length: 20
Destination address: 10.243.160.1, Destination prefix length: 0
Input SNMP interface index: 24, Output SNMP interface index: 26
Source-AS: 69, Destination-AS: 69
Start time: Fri Feb 21 14:16:57 2003, End time: Fri Feb 21 14:22:50 2003
Flow count: 0, Packet count: 6, Byte count: 5490
Source address: 10.1.1.2, Source prefix length: 20
Destination address: 10.162.160.1, Destination prefix length: 0
Input SNMP interface index: 24, Output SNMP interface index: 26
Source-AS: 69, Destination-AS: 69
Start time: Fri Feb 21 14:16:57 2003, End time: Fri Feb 21 14:22:50 2003
Flow count: 0, Packet count: 6, Byte count: 4079
