示例:为 VPN 配置 BGP 路由目标过滤
BGP 路由目标过滤减少了接收 VPN 路由和路由更新的路由器数量,有助于限制与运行 VPN 相关的开销。在网络中有许多路由反射器或 AS 边界路由器不直接参与 VPN(不充当 CE 设备的 PE 路由器),BGP 路由目标过滤在减少 VPN 相关管理流量方面最为有效。
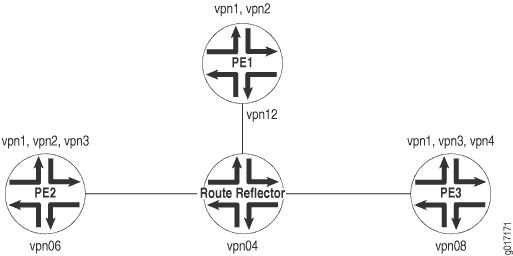
图 1 展示了一组 VPN 使用 BGP 路由目标过滤配置的网络的拓扑。
 启用 BGP 路由目标过滤
启用 BGP 路由目标过滤
以下部分介绍如何为一组 VPN 配置 BGP 路由目标过滤:
在路由器 PE1 上配置 BGP 路由目标过滤
本节介绍如何在此示例的路由器 PE1 上启用 BGP 路由目标过滤。
按如下配置路由器 PE1 上的路由选项:
[edit]
routing-options {
route-distinguisher-id 10.255.14.182;
autonomous-system 198;
}
在路由器 PE1 上配置 BGP 协议,如下所示:
[edit]
protocols {
bgp {
group to_VPN_D {
type internal;
local-address 10.255.14.182;
peer-as 198;
neighbor 10.255.14.174 {
family inet-vpn {
unicast;
}
family route-target;
}
}
}
}
按 vpn1 如下配置路由实例:
[edit]
routing-instances {
vpn1 {
instance-type vrf;
interface t1-0/1/2.0;
vrf-target target:198:101;
protocols {
ospf {
export bgp-routes;
area 0.0.0.0 {
interface t1-0/1/2.0;
}
}
}
}
}
在 vpn2 路由器 PE1 上配置路由实例,如下所示:
[edit]
routing-instances {
vpn2 {
instance-type vrf;
interface t1-0/1/2.1;
vrf-target target:198:102;
protocols {
ospf {
export bgp-routes;
area 0.0.0.0 {
interface t1-0/1/2.1;
}
}
}
}
}
实施此配置后,发出 show route table bgp.rtarget.0 命令时应看到以下内容:
user@host> show route table bgp.rtarget.0
bgp.rtarget.0: 4 destinations, 6 routes (4 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
+ = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both
198.198:101/96
*[RTarget/5] 00:27:42
Local
[BGP/170] 00:27:30, localpref 100, from
10.255.14.174
AS path: I
> via t3-0/0/0.0
198.198:102/96
*[RTarget/5] 00:27:42
Local
[BGP/170] 00:27:30, localpref 100, from
10.255.14.174
AS path: I
> via t3-0/0/0.0
198.198:103/96
*[BGP/170] 00:27:30, localpref 100, from
10.255.14.174
AS path: I
> via t3-0/0/0.0
198.198:104/96
*[BGP/170] 00:27:30, localpref 100, from
10.255.14.174
AS path: I
> via t3-0/0/0.0
在路由器 PE2 上配置 BGP 路由目标过滤
本节介绍如何在此示例的路由器 PE2 上启用 BGP 路由目标过滤。
按如下配置路由器 PE2 上的路由选项:
[edit]
routing-options {
route-distinguisher-id 10.255.14.176;
autonomous-system 198;
}
在路由器 PE2 上配置 BGP 协议,如下所示:
[edit]
protocols {
bgp {
group to_vpn04 {
type internal;
local-address 10.255.14.176;
peer-as 198;
neighbor 10.255.14.174 {
family inet-vpn {
unicast;
}
family route-target;
}
}
}
}
按如下在 vpn1 路由器 PE2 上配置路由实例:
[edit]
routing-instances {
vpn1 {
instance-type vrf;
interface t3-0/0/0.0;
vrf-target target:198:101;
protocols {
bgp {
group vpn1 {
type external;
peer-as 101;
as-override;
neighbor 10.49.11.2;
}
}
}
}
}
按如下在 vpn2 路由器 PE2 上配置路由实例:
[edit]
routing-instances {
vpn2 {
instance-type vrf;
interface t3-0/0/0.1;
vrf-target target:198:102;
protocols {
bgp {
group vpn2 {
type external;
peer-as 102;
as-override;
neighbor 10.49.21.2;
}
}
}
}
}
按如下在 vpn3 路由器 PE2 上配置路由实例:
[edit]
routing-instances {
vpn3 {
instance-type vrf;
interface t3-0/0/0.2;
vrf-import vpn3-import;
vrf-export vpn3-export;
protocols {
bgp {
group vpn3 {
type external;
peer-as 103;
as-override;
neighbor 10.49.31.2;
}
}
}
}
}
以这种方式配置路由器 PE2 后,发出 show route table bgp.rtarget.0 命令时应看到以下内容:
user@host> show route table bgp.rtarget.0
bgp.rtarget.0: 4 destinations, 7 routes (4 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
+ = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both
198.198:101/96
*[RTarget/5] 00:28:15
Local
[BGP/170] 00:28:03, localpref 100, from
10.255.14.174
AS path: I
> via t1-0/1/0.0
198.198:102/96
*[RTarget/5] 00:28:15
Local
[BGP/170] 00:28:03, localpref 100, from
10.255.14.174
AS path: I
> via t1-0/1/0.0
198.198:103/96
*[RTarget/5] 00:28:15
Local
[BGP/170] 00:28:03, localpref 100, from
10.255.14.174
AS path: I
> via t1-0/1/0.0
198.198:104/96
*[BGP/170] 00:28:03, localpref 100, from
10.255.14.174
AS path: I
> via t1-0/1/0.0
在路由反射器上配置 BGP 路由目标过滤
本节说明如何在此示例的路由反射器上启用 BGP 路由目标过滤。
在路由反射器上配置路由选项,如下所示:
[edit]
routing-options {
route-distinguisher-id 10.255.14.174;
autonomous-system 198;
}
在路由反射器上配置 BGP 协议,如下所示:
[edit]
protocols {
bgp {
group rr-group {
type internal;
local-address 10.255.14.174;
cluster 10.255.14.174;
peer-as 198;
neighbor 10.255.14.182 {
description to_PE1_vpn12;
family inet-vpn {
unicast;
}
family route-target;
}
neighbor 10.255.14.176 {
description to_PE2_vpn06;
family inet-vpn {
unicast;
}
family route-target;
}
neighbor 10.255.14.178 {
description to_PE3_vpn08;
family inet-vpn {
unicast;
}
family route-target;
}
}
}
}
以这种方式配置路由反射器后,发出 show route table bgp.rtarget.0 命令时应看到以下内容:
user@host> show route table bgp.rtarget.0
bgp.rtarget.0: 4 destinations, 8 routes (4 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
+ = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both
198.198:101/96
*[BGP/170] 00:29:03, localpref 100, from
10.255.14.176
AS path: I
> via t1-0/2/0.0
[BGP/170] 00:29:03, localpref 100, from
10.255.14.178
AS path: I
> via t3-0/1/1.0
[BGP/170] 00:29:03, localpref 100, from
10.255.14.182
AS path: I
> via t3-0/1/3.0
198.198:102/96
*[BGP/170] 00:29:03, localpref 100, from
10.255.14.176
AS path: I
> via t1-0/2/0.0
[BGP/170] 00:29:03, localpref 100, from
10.255.14.182
AS path: I
> via t3-0/1/3.0
198.198:103/96
*[BGP/170] 00:29:03, localpref 100, from
10.255.14.176
AS path: I
> via t1-0/2/0.0
[BGP/170] 00:29:03, localpref 100, from
10.255.14.178
AS path: I
> via t3-0/1/1.0
198.198:104/96
*[BGP/170] 00:29:03, localpref 100, from
10.255.14.178
AS path: I
> via t3-0/1/1.0
在路由器 PE3 上配置 BGP 路由目标过滤
下一节介绍如何在此示例的路由器 PE3 上启用 BGP 路由目标过滤。
按如下配置路由器 PE3 上的路由选项:
[edit]
routing-options {
route-distinguisher-id 10.255.14.178;
autonomous-system 198;
}
在路由器 PE3 上配置 BGP 协议,如下所示:
[edit]
protocols {
bgp {
group to_vpn04 {
type internal;
local-address 10.255.14.178;
peer-as 198;
neighbor 10.255.14.174 {
family inet-vpn {
unicast;
}
family route-target;
}
}
}
}
在 vpn1 路由器 PE3 上配置路由实例,如下所示:
[edit]
routing-instances {
vpn1 {
instance-type vrf;
interface t3-0/0/0.0;
vrf-target target:198:101;
protocols {
rip {
group vpn1 {
export bgp-routes;
neighbor t3-0/0/0.0;
}
}
}
}
}
在 vpn3 路由器 PE3 上配置路由实例,如下所示:
[edit]
routing-instances {
vpn3 {
instance-type vrf;
interface t3-0/0/0.1;
vrf-target target:198:103;
protocols {
rip {
group vpn3 {
export bgp-routes;
neighbor t3-0/0/0.1;
}
}
}
}
}
在 vpn4 路由器 PE3 上配置路由实例,如下所示:
[edit]
routing-instances {
vpn4 {
instance-type vrf;
interface t3-0/0/0.2;
vrf-target target:198:104;
protocols {
rip {
group vpn4 {
export bgp-routes;
neighbor t3-0/0/0.2;
}
}
}
}
}
以这种方式配置路由器 PE3 后,发出 show route table bgp.rtarget.0 命令时应看到以下内容:
user@host> show route table bgp.rtarget.0
bgp.rtarget.0: 4 destinations, 7 routes (4 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
+ = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both
198.198:101/96
*[RTarget/5] 00:29:42
Local
[BGP/170] 00:29:30, localpref 100, from
10.255.14.174
AS path: I
> via t3-0/0/1.0
198.198:102/96
*[BGP/170] 00:29:29, localpref 100, from
10.255.14.174
AS path: I
> via t3-0/0/1.0
198.198:103/96
*[RTarget/5] 00:29:42
Local
[BGP/170] 00:29:30, localpref 100, from
10.255.14.174
AS path: I
> via t3-0/0/1.0
198.198:104/96
*[RTarget/5] 00:29:42
Local
[BGP/170] 00:29:30, localpref 100, from
10.255.14.174
AS path: I
> via t3-0/0/1.0
