聚合以太网接口上的负载平衡
聚合以太网接口上的负载平衡通过在多个接口之间划分流量来减少网络拥塞。
将多个物理聚合以太网接口捆绑在一起形成单个逻辑接口时,称为链路聚合。链路聚合可增加带宽,在发生故障时提供正常的降级,提高可用性并提供负载平衡功能。负载平衡使设备能够沿多个接口划分传入和传出流量,从而减少网络拥塞。本文介绍负载平衡以及如何在设备上配置负载平衡。
使用 功能资源管理器 确认平台和版本对特定功能的支持。
查看 特定于平台的聚合以太网负载平衡行为 部分,了解与平台相关的注意事项。
负载平衡和以太网链路聚合概述
您可以为一组以太网端口创建 LAG。L2 桥接流量在该组的成员链路上实现负载均衡,因此该配置在拥塞问题和冗余方面都很有吸引力。每个 LAG 束最多包含 16 个链路。平台支持取决于设备安装的 Junos OS 版本。
对于 LAG 捆绑包,散列算法确定进入 LAG 捆绑包的流量如何放置到捆绑包的成员链路上。散列算法尝试通过跨捆绑包中的成员链路平均均衡所有传入流量来管理带宽。默认情况下,散列算法的散列模式设置为 L2 有效负载。当散列模式设置为 L2 有效负载时,散列算法将使用 IPv4 和 IPv6 有效负载字段进行散列。您还可以使用 该 payload 语句为 L2 流量配置负载平衡哈希密钥,以使用 L3 和第 4 层标头中的字段。但是,请注意,负载平衡行为是特定于平台的,并且基于适当的哈希密钥配置。
有关更多信息,请参阅 在 LAG 链路上配置负载均衡。在 L2 交换机中,一个链路未得到充分利用,其他链路未得到充分利用。
了解聚合以太网负载平衡
链路聚合功能用于捆绑多个物理聚合以太网接口以形成一个逻辑接口。一个或多个链路被聚合形成虚拟链路或链路聚合组 (LAG)。MAC 客户端将此虚拟链路视为单个链路。链路聚合增加了带宽,在发生故障时提供了正常的降级,并提高了可用性。
除了这些优势之外,聚合以太网捆绑包还经过增强,可提供负载平衡功能,确保充分、高效地利用聚合以太网捆绑包的成员链路之间的链路利用率。
负载平衡功能允许设备沿多个路径或接口划分传入和传出流量,以减少网络中的拥塞。负载平衡提高了各种网络路径的利用率,并提供了更有效的网络带宽。
通常,使用负载平衡的应用程序包括:
聚合接口(第 2 层)
聚合接口(对于聚合以太网,也称为 AE;对于聚合 SONET,则称为 AS)是用于在两台设备之间的多个接口上进行负载平衡的第 2 层机制。由于这是第 2 层负载平衡机制,因此所有单独的组件链路都必须位于两端相同的两台设备之间。Junos OS 支持以太网和 SONET 的非信号(静态)配置,以及用于通过以太网链路进行协商的 802.3ad 标准化 LACP 协议。
等价多路径 (ECMP)(第 3 层)
默认情况下,当活动路由有多个到同一目标的等价路径时,Junos OS 会使用散列算法选择要安装在转发表中的下一跃点地址之一。每当目标的下一跃点集以任何方式发生变化时,就会使用散列算法重新选择下一跃点地址。还有一个选项允许在转发表中安装多个下一跃点地址,称为按数据包负载平衡。
ECMP 负载平衡可以是:
跨 BGP 路径(BGP 多路径)
在 BGP 路径中,跨多个 LSP
在复杂的以太网拓扑结构中,流量不平衡是由于流量增加而发生的,并且由于以下原因,负载平衡变得具有挑战性:
聚合下一跃点的负载平衡不正确
数据包散列计算不正确
数据包流中的方差不足
图案选择不正确
由于流量不平衡,负载分布不当,导致某些链路出现拥塞,而其他一些链路则得不到有效利用。
为了克服这些挑战,Junos OS 提供了以下解决方案来解决聚合以太网捆绑包 (IEEE 802.3ad) 上的真正流量不平衡问题。
自适应负载平衡
自适应负载平衡使用反馈机制来纠正真正的流量不平衡。为了纠正不平衡权重,需要调整链路的带宽和数据包流,以便在 AE 束中的链路之间实现高效的流量分配。
要配置自适应负载平衡,请在层次结构级别包含
adaptive[edit interfaces aex aggregated-ether-options load-balance]该语句。要将容差值配置为百分比,请在层次结构级别包含
tolerance[edit interfaces aex aggregated-ether-options load-balance adaptive]可选关键字。要基于每秒数据包数(而非默认的每秒位数设置)配置自适应负载平衡,请在层次结构级别添加
pps[edit interfaces aex aggregated-ether-options load-balance adaptive]optional 关键字。要根据最后两秒的采样率配置散列值的扫描间隔,请在层次结构级别添加
scan-intervaloptional 关键字[edit interfaces aex aggregated-ether-options load-balance adaptive]。每数据包随机喷洒负载均衡
当自适应负载平衡选项失败时,按数据包随机喷射负载平衡将作为最后的手段。它可确保 AE 捆绑包的成员负载相等,而无需考虑带宽。每个数据包会导致数据包重新排序,因此仅当应用程序吸收重新排序时才建议使用。每数据包随机喷洒可消除由软件错误引起的流量不平衡,数据包散列除外。
要配置每个数据包的随机喷负载平衡,请在层次结构级别包含
per-packet[edit interfaces aex aggregated-ether-options load-balance]该语句。
聚合以太网负载平衡解决方案是互斥的。配置多个负载平衡解决方案时,上次配置的解决方案将覆盖之前配置的解决方案。您可以通过发出 show interfaces aex aggregated-ether-options load-balance 命令来验证正在使用的负载均衡解决方案。
也可以看看
使用 5 元组数据的聚合以太网接口的有状态负载平衡
当多个流从聚合以太网 (ae) 接口传输出时,流量必须均匀分布在不同的成员链路之间,以实现有效且最佳的负载平衡行为。为了获得简化且稳健的负载平衡方法,每次为负载平衡选择的聚合以太网接口束的成员链路将发挥重要作用。如果需要在单跳中选择 2^n(2 的 n 次方)下一跳之一,则链路选择的平衡模式在预先计算的哈希值中使用“n”位。成员链路或下一跳选择的不平衡模式使用预先计算的散列中的 8 位来选择选择器表中的条目,该过程是使用链路聚合组 (LAG) 或 ae束的成员链路 ID 随机完成的。
术语平衡与不平衡表示选择器表是否用于负载平衡机制。LAG 捆绑包使用非平衡模式(选择器表平衡)来平衡成员链路之间的流量。当流量最小时,非平衡模式可能会出现以下问题: 链路选择逻辑仅使用预计算散列的子集位。无论散列算法的效率如何,它都只是流的压缩表示。由于流间方差非常低,计算的结果哈希值和子集无法提供有效利用所有 LAG 成员链路所需的可变性。哈希计算和选择器表中存在过多的随机性质。因此,当流数越少时,与所选每个子链路的最佳负载均衡技术的偏差就越大。
每个子链路的偏差定义为
Vi = ((Ci - (M/N)))/N
地点
Vi 表示该子链接“i”的偏差。
i 表示子链路成员/索引。
Ci 表示为该子链路“i”传输的数据包。
M 表示该 LAG 束上传输的数据包总数。
N 表示该 LAG 中的子链路数。
由于这些缺点,对于较少的流或流间方差较小的流,链路利用率会发生偏差,并且存在一些子链路未完全利用的可能性。
添加了记录和保留流状态并相应分配流量负载的机制。因此,对于 m 个流量,它们分布在 LAG 束的 n 个成员链路之间,或分布在 ECMP 链路中的单跳下一跳之间。这种在成员链路之间分配负载的方法称为 有状态负载平衡 ,它使用 5 元组信息(源和目标地址、协议、源和目标端口)。此类方法可以直接映射到流,也可以映射到基于流中某些字段的预计算哈希。因此,在每个子链路上观察到的偏差都会减少。
此机制仅对最小流量(大约小于数千个流量)有效。对于较多流量(1000 到 10,000 个流量之间),建议使用基于 Trio 的分布式负载均衡机制。
考虑一个示例情景,其中 LAG 中的“n”个链路使用链路 ID 为 0 到 n-1 来标识。散列表或流表用于记录流的出现时间。散列键是使用唯一标识流的字段构造的。查找结果标识流当前正在使用的link_id。对于每个数据包,将检查基于流标识符的流表。如果找到匹配项,则表示属于之前处理或检测到的流的数据包。链路 ID 与流相关联。如果未找到匹配项,则该数据包属于该流的第一个数据包。链路 ID 用于选择链路,并将流插入到流表中。
要基于哈希值启用按流的负载平衡,请在per-flow层次结构级别包含[edit interfaces aeX unit logical-unit-number forwarding-options load-balance-stateful]该语句。默认情况下,当有多个等价路径可用时,Junos OS 仅使用基于目标地址的散列方法来选择转发下一跃点。默认情况下,所有数据包转发引擎插槽都分配相同的哈希值。要将负载均衡算法配置为使用现有参数动态重新平衡 LAG,请在层次结构级别包含[edit interfaces aeX unit logical-unit-number forwarding-options load-balance-stateful]该rebalance interval语句。此参数通过在一段时间内在所有入口数据包转发引擎 (PFE) 之间提供同步再平衡切换,从而定期对流量进行负载均衡。您可以将间隔指定为每分钟 1 到 1000 流量范围内的值。要配置负载类型,请在层次结构级别包含load-type (low | medium | high)[edit interfaces aeX unit logical-unit-number forwarding-options load-balance-stateful]该语句。
该 stateful per-flow 选项可在 AE 捆绑包上启用负载平衡功能。该 rebalance 选项会按指定的时间间隔清除负载均衡状态。该 load 选项会通知数据包转发引擎要使用的相应内存模式。如果在此聚合以太网接口上的流量数较少(介于 1 到 100 个流量之间),则可以使用关键字 low 。同样,对于相对较高的流量(100 到 1000 个流量之间), medium 可以使用关键字, large 并且关键字可用于最大流量(1000 到 10,000 个流量之间)。用于对每个关键字进行有效负载平衡的大致流量数是一个导数。
该 clear interfaces aeX unit logical-unit-number forwarding-options load-balance state 命令将清除硬件级别的负载均衡状态,并启用从清理后的空状态进行重新平衡。仅当您使用此命令时,才会触发此清除状态。该 clear interfaces aggregate forwarding-options load-balance state 命令将清除所有聚合以太网接口负载平衡状态,然后重新创建这些状态。
为聚合以太网接口或 LAG 束配置有状态负载平衡的准则
为聚合以太网接口配置有状态负载平衡时,请记住以下几点:
移除或添加子链路时,将选择新的聚合选择器,并将流量流向新的选择器。由于选择器为空,因此将在选择器中填充流量。此行为会导致流重新分配,因为旧状态丢失。这是在未启用有状态的按流负载平衡的情况下的现有行为。
如果传入流量到达 MPC1E、MPC2E、MPC3E-3D、MPC5E 和 MPC6E 线卡,则在 AE 接口上实现有状态的按流负载均衡功能。任何其他类型的线卡都不具备此功能。如果 MPC 不支持此功能,则会显示相应的 CLI 错误。
当入口线卡作为 MPC 时,出口线卡作为 MPC 或 DPC,此功能可以正常工作。如果入口线卡是 DPC,而出口线卡是 DPC 或 MPC,则不支持有状态负载平衡。
组播流量(本机/泛滥)不支持此功能。
启用重新平衡选项或清除负载均衡状态可能会导致活动流量的数据包重新排序,因为可以为流量选择不同的链路集。
虽然功能性能很高,但会消耗大量的线卡内存。在受支持的 MPC 上,大约可以有 4000 个逻辑接口或 16 个聚合以太网逻辑接口启用此功能。但是,当数据包转发引擎硬件内存不足时,根据可用内存,它会回退到默认负载平衡机制。在这种情况下,系统日志记录消息将生成并发送至路由引擎。对支持有状态负载均衡的 AE 接口数量没有限制;限制由线卡决定。
如果流量频繁老化,则设备需要移除或刷新负载平衡状态。因此,您必须配置重新平衡或定期运行 clear 命令,以实现适当的负载平衡。否则,可能会发生流量偏差。当子链路关闭或启动时,负载平衡行为不会对现有流发生更改。这种情况是为了避免数据包重新排序。新流会拾取启动的子链路。如果您发现负载分配不是很有效,则可以清除负载均衡状态或使用重新平衡功能自动清除硬件状态。配置再平衡工具时,流量可能会重定向到不同的链路,这可能会导致数据包重新排序。
在聚合以太网接口上配置有状态负载均衡
添加了记录和保留流状态并相应分配流量负载的机制。因此,对于 m 个流量,它们分布在 LAG 束的 n 个成员链路之间,或分布在 ECMP 链路中的单跳下一跳之间。这种在成员链路之间分配负载的方法称为 有状态负载平衡 ,它使用 5 元组信息(源和目标地址、协议、源和目标端口)。此类方法可以直接映射到流,也可以映射到基于流中某些字段的预计算哈希。因此,在每个子链路上观察到的偏差都会减少。
要在接口束上 ae 配置有状态负载平衡,请执行以下作:
配置自适应负载均衡
本文介绍如何配置自适应负载平衡。自适应负载平衡可保持聚合以太网 (AE) 捆绑包的成员链路带宽的有效利用。自适应负载平衡使用反馈机制,通过调整 AE 束内链路上的带宽和数据包流来纠正流量负载不平衡。
开始之前:
配置一组具有协议家族和 IP 地址的接口。这些接口可以组成 AE 捆绑包的成员资格。
通过将一组路由器接口配置为聚合以太网并使用特定的 AE 组标识符,创建 AE 捆绑包。
要为 AE 捆绑包配置自适应负载平衡:
也可以看看
了解用于负载平衡的对称散列
对于依赖于流量对称的功能,在支持此功能的设备上,对称散列会使流量的正向和反向方向保持在同一路径上。对称散列有助于服务维护会话上下文,同时跨 ECMP 下一跃点和 LAG 成员实现负载平衡。
对称散列的好处
- 保持双向路径对称性,以便有状态服务在同一路径上看到流量的两个方向。
- 通过对流量的两个方向使用相同的标准化输入,改进负载平衡的可预测性。
- 减少可能中断服务处理或会话状态的非对称路由问题。
要配置对称散列,请在 symmetric-hash 层次结构中使用 [edit forwarding-options enhanced-hash-key] configuration 语句。使用该 enhanced-hash-key 语句配置散列计算中包含的数据包字段。通过选择稳定的双向字段并排除单向输入,可以对输入进行规范化,以便设备为流量的两个方向导出相同的散列值。
您可以从层次结构的 [edit forwarding-options enhanced-hash-key] hash with no-incoming-port 配置语句中排除单向属性,例如入口接口。
使用 show forwarding-options enhanced-hash-key 命令验证当前散列输入和对称散列状态。
其他注意事项:
- 动态负载平衡 (DLB) 优先。对称散列适用于静态负载平衡;如果启用了 DLB,DLB 将覆盖对称行为。
- 使用第 3 层和第 4 层字段进行对称散列。对称散列中不包含第 2 层标头字段,应根据需要使用
hash-mode配置语句来使用第 2 层数据字段。 - 如果所有设备使用相同的哈希种子和输入,则在级联拓扑中可能会发生哈希极化。在链路抖动或成员发生变化时,可考虑弹性散列和种子分集,以减少极化。
在 MX 系列路由器上的 802.3ad 链路聚合组上配置对称负载均衡
MX 系列路由器上 802.3ad LAG 上的对称负载平衡概述
带有聚合以太网 PIC 的 MX 系列路由器支持在 802.3ad LAG 上实现对称负载平衡。当两台 MX 系列路由器通过 LAG 捆绑包上的深度包检测 (DPI) 设备以透明方式连接时,此功能非常重要。DPI 设备跟踪流,并需要正向和反向给定流的信息。如果 802.3ad LAG 上没有对称负载平衡,DPI 可能会误解流量,从而导致流量中断。通过使用此功能,可以确保相同设备在两个方向上都有给定的流量(双工)。
802.3ad LAG 上的对称负载平衡利用源地址和目标地址互换机制来对字段进行哈希计算,例如源地址和目标地址。在这些字段上计算的散列结果用于选择 LAG 的链路。正向流和反向流的散列计算必须相同。这是通过将源字段与反向流的目标字段交换来实现的。交换作称为补码 哈希计算 或 symmetric-hash complement ,常规(或未交换)作称为 对称哈希计算 或 symmetric-hash。可交换字段包括 MAC 地址、IP 地址和端口。
在 MX 系列路由器上的 802.3ad LAG 上配置对称负载均衡
您可以指定是对称散列还是补码散列来平衡流量负载。要配置对称散列,请在层次结构级别使用[edit forwarding-options hash-key family inet]该symmetric-hash语句。要配置对称散列补码,请在层次结构级别使用symmetric-hash complement[edit forwarding-options hash-key family inet]语句和选项。
也可以通过指定哈希密钥在 PIC 级别执行这些作。要在 PIC 级别配置散列密钥,请在 和 [edit chassis hash-key family multiservice] 层次结构级别使用 symmetric-hash [edit chassis hash-key family inet] or symmetric-hash complement 语句。
考虑 图 1 中的示例。
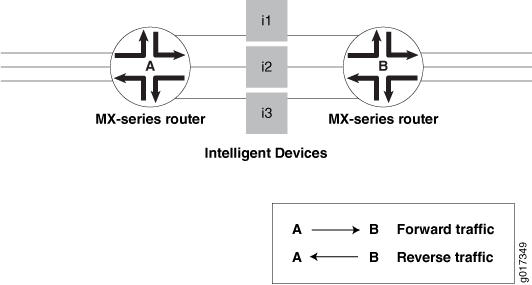
路由器 A 配置了对称散列,路由器 B 配置了对称散列补码。因此,对于给定的流 fx,后散列计算是从路由器 A 到 i2 到路由器 B。同一流 fx 的反向流量通过与其散列相同的 i2 设备从路由器 B 到路由器 A(在交换源字段和目标字段后完成),并返回相同的链路索引;因为它是在互换的源地址和目标地址上执行的。
但是,所选链接可能与附加到 DPI 的内容相对应,也可能不对应。换句话说,散列结果应指向已连接的相同链路,以便流量在两个方向上流经相同的 DPI 设备。为确保发生这种情况,您还需要配置具有相同链路索引的对应端口(连接到相同 DPI-iN 的端口)。在将子链路配置到 LAG 捆绑包中时,会执行此作。这可确保为给定哈希结果选择的链路在任一路由器上始终相同。
请注意,任何两个相互连接的链路都应具有相同的链路索引,并且这些链路索引在给定的捆绑包中必须是唯一的。
在 MX 系列路由器上的 802.3ad LAG 上配置对称负载平衡时,适用以下限制:
可以将数据包转发引擎 (PFE) 配置为以对称或补充模式对流量进行散列处理。单个 PFE 复合体不能在两种作模式下同时工作,这样的配置可能会产生不良结果。
per-PFE 设置仅会覆盖已配置系列的机箱范围设置。对于其他系列,PFE 复合体仍继承机箱范围的设置(配置后)或默认设置。
此功能仅支持 VPLS、INET 和桥接流量。
此功能不能与
per-flow-hash-seed load-balancing该选项协同工作。它要求以互补方式配置的所有 PFE 复合物共享同一种子。两种对应的 PFE 络合物之间的种子变化可能会产生不良结果。
有关更多信息,请参阅 适用于路由设备的 Junos OS VPN 库 和适用于 路由设备的 Junos OS 管理库。
示例配置语句
要在捆绑包级别配置 802.3ad LAG 参数:
[edit interfaces]
g(x)e-fpc/pic/port {
gigether-options {
802.3ad {
bundle;
link-index number;
}
}
}
其中,范围 link-index number 从 0 到 15。
您可以使用以下 show interfaces 命令检查上面配置的链路索引:
[edit forwarding-options hash-key]
family inet {
layer-3;
layer-4;
symmetric-hash {
[complement;]
}
}
family multiservice {
source-mac;
destination-mac;
payload {
ip {
layer-3 {
source-ip-only | destination-ip-only;
}
layer-4;
}
}
symmetric-hash {
[complement;]
}
}
要基于第 3 层字段对第 2 层流量进行负载平衡,可以在每个 PIC 级别配置 802.3ad LAG 参数。这些配置选项在机箱层次结构下提供,如下所示:
[edit chassis]
fpc X {
pic Y {
.
.
.
hash-key {
family inet {
layer-3;
layer-4;
symmetric-hash {
[complement;]
}
}
family multiservice {
source-mac;
destination-mac;
payload {
ip {
layer-3 {
source-ip-only | destination-ip-only;
}
layer-4;
}
}
symmetric-hash {
[complement;]
}
}
}
.
.
.
}
}
在基于 Trio 的 MPC 上配置对称负载平衡
尽管存在一些配置差异,但在具有基于 Trio 的 MPC 的 MX 系列路由器上,支持 802.3ad 链路聚合组上的对称负载平衡。
要在基于 Trio 的 MPC 上实现对称负载平衡,需要执行以下作:
计算对称哈希
两台路由器都必须从正向和反向流动中计算出相同的散列值。在基于 Trio 的平台上,计算出的哈希值与流动方向无关,因此本质上始终是对称的。因此,在基于 Trio 的平台上计算对称哈希值不需要特定配置。
但是,应注意的是,用于配置散列的字段在 LAG 的两端应具有相同的包含和排除设置。
配置链路索引
要允许两台路由器使用相同的哈希值选择相同的链路,必须在两台路由器上为LAG中的链路配置相同的链路索引。这可以通过语句来
link-index实现。启用对称负载平衡
要在基于 Trio 的 MPC 上配置对称负载平衡,请在层次结构级别包含
[edit forwarding-options enhanced-hash-key]该symmetric语句。本声明仅适用于基于 Trio 的平台。该
symmetric语句可与任何协议家族搭配使用,并为路由器上的所有聚合以太网捆绑包实现对称负载平衡。需要在 LAG 的两端启用该语句。默认情况下,此语句处于禁用状态。实现桥接和路由流量的对称性
在某些部署中,需要对称的 LAG 束会由上行方向的第 2 层桥接流量遍历,而下行方向则由 IPv4 路由流量遍历。在这种情况下,每个方向上计算的散列值都不同,因为桥接数据包会考虑以太网 MAC 地址。要克服此问题,您可以从增强型散列密钥计算中排除源和目标 MAC 地址。
要从增强型散列密钥计算中排除源和目标 MAC 地址,请在层次结构级别包含
[edit forwarding-options enhanced-hash-key family multiservice]该no-mac-addresses语句。默认情况下,此语句处于禁用状态。
在基于 Trio 的 MPC 上启用对称负载平衡后,请记住以下注意事项:
流量极化是使用通过相同类型的散列来分配流量的拓扑时发生的一种现象。当路由器级联时,可能会发生流量极化,从而导致流量分配不均。
当在级联路由器上配置 LAG 时,会发生流量极化。例如,在 图 2 中,如果某个流量在设备 R1 和设备 R2 之间使用聚合以太网捆绑包的链路 1,则该流也会在设备 R2 和设备 R3 之间使用聚合以太网捆绑包的链路 1。
图 2:在基于 Trio 的 MPC 上启用对称负载平衡时,级联路由器上的流量极化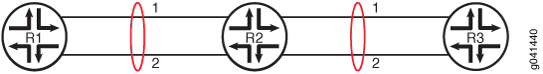
这与随机链路选择算法不同,随机链路选择算法中,流量可能会在设备 R1 和设备 R2 之间使用聚合以太网捆绑包的链路 1,以及设备 R2 和设备 R3 之间的聚合以太网捆绑包的链路 2。
对称负载平衡不适用于基于路由前缀计算散列的按前缀负载平衡。
对称负载平衡不适用于 MPLS 或 VPLS 流量,因为在这些场景中,标签在两个方向上并不相同。
示例配置
机箱范围设置的配置示例
路由器 A
user@host> show configuration forwarding-options hash-key
family multiservice {
payload {
ip {
layer-3;
}
}
symmetric hash;
}
路由器 B
user@host> show configuration forwarding-options hash-key
family multiservice {
payload {
ip {
layer-3;
}
}
symmetric-hash {
complement;
}
}
按数据包转发引擎设置的示例配置
路由器 A
user@host> show configuration chassis fpc 2 pic 2 hash-key
family multiservice {
payload {
ip {
layer-3;
}
}
symmetric hash;
}
路由器 B
user@host> show configuration chassis fpc 2 pic 3 hash-key
family multiservice {
payload {
ip {
layer-3;
}
}
symmetric-hash {
complement;
}
}
配置 PIC 级对称散列,用于 MX 系列路由器的 802.3ad LAG 上的负载平衡
当两台 MX 系列路由器(例如,路由器 A 和路由器 B)通过深度包检测 (DPI) 设备通过 LAG 捆绑包透明连接时,用于在 802.3ad 链路聚合组 (LAG) 上进行负载平衡的对称散列非常有用。DPI 设备跟踪正向和反向的流量流。
如果配置了对称散列,则流量的反向流也将通过 LAG 上的同一子链路,并绑定要流经同一 DPI 设备。这样可以正确核算正向和反向流中流量的 DPI。
如果未配置对称散列,则可能会选择 LAG 上的其他子链路来进行通过不同 DPI 设备的反向流量流。这会导致有关 DPI 设备上流量的正向和反向信息不完整,从而导致 DPI 设备对流量的核算不完整。
对称散列是根据源地址和目标地址等字段计算的。您可以根据家族 INET(IPv4 协议家族)和多服务(交换机或网桥)流量的第 2 层、第 3 层和第 4 层数据单元字段,在机箱级别和 PIC 级别配置对称散列,以实现负载平衡。在机箱级别配置的对称散列适用于整个路由器,并由其所有 PIC 和数据包转发引擎继承。配置 PIC 级对称散列可在数据包转发引擎级别获得更精细的粒度。
对于通过 LAG 捆绑包通过 DPI 设备连接的两台路由器,您可以在一个路由器上配置 对称散列 ,在远程端路由器上配置 对称散列补 码,反之亦然。
要在机箱级别配置对称散列,请在层次结构级别包括 [edit forwarding-options hash-key family] symmetric-hash 或symmetric-hash complement语句。有关在机箱级别配置对称散列和配置链路索引的信息,请参阅适用于路由设备的 Junos OS 网络接口库和适用于路由设备的 Junos OS VPN 库。
在 MX 系列 DPC 上,在 PIC 级别配置对称散列是指在数据包转发引擎级别配置对称散列。
要在入站流量接口(流量进入路由器的位置)上的 PIC 级别配置对称散列,请在层次结构级别包含 symmetric-hash 或 symmetric-hash complement 语句 [edit chassis fpc slot-number pic pic-number hash-key] :
[edit chassis fpc slot-number pic pic-number hash-key]
family multiservice {
source-mac;
destination-mac;
payload {
ip {
layer-3 (source-ip-only | destination-ip-only);
layer-4;
}
}
symmetric-hash {
complement;
}
}
family inet { layer-3; layer-4; symmetric-hash { complement; } }
PIC 级对称散列将覆盖在 [edit chassis forwarding-options hash-key] 层次结构级别配置的机箱级对称散列。
目前仅 VPLS、INET 和桥接流量支持用于 802.3ad 链路聚合组负载平衡的对称散列。
PIC 或数据包转发引擎上的散列密钥配置可以处于“对称散列”或“对称散列补码”模式,但不能同时处于两者。
也可以看看
示例:配置 PIC 级对称散列,以便在 MX 系列路由器上的 802.3ad LAG 上实现负载平衡
这些示例仅适用于 MX240、MX480 和 MX960 路由器上支持的 DPC。有关支持的 DPC 列表,请参阅相关文档部分中的 MX240、MX480 和 MX960 路由器上支持的 DPC 。
以下示例说明如何在 PIC 级别配置对称散列,以便在 MX 系列路由器上实现负载平衡:
在两台路由器上为家族多服务配置对称散列
在流量进入路由器 A 的入站流量接口上,在层次结构级别包含[edit chassis fpc slot-number pic pic-number hash-key family multiservice]该symmetric-hash语句:
[edit chassis fpc 2 pic 2 hash-key]
family multiservice {
source-mac;
destination-mac;
payload {
ip {
layer-3;
layer-4;
}
}
symmetric-hash;
}
在流量进入路由器 B 的入站流量接口上,在层次结构级别包含[edit chassis fpc slot-number pic pic-number hash-key family multiservice]该symmetric-hash complement语句:
[edit chassis fpc 0 pic 3 hash-key]
family multiservice {
source-mac;
destination-mac;
payload {
ip {
layer-3;
layer-4;
}
}
symmetric-hash {
complement;
}
}
在两台路由器上为家族 inet 配置对称散列
在流量进入路由器 A 的入站流量接口上,在层次结构级别包含[edit chassis fpc slot-number pic pic-number hash-key family inet]该symmetric-hash语句:
[edit chassis fpc 0 pic 1 hash-key]
family inet {
layer-3;
layer-4;
symmetric-hash;
}
在流量进入路由器 B 的入站流量接口上,在层次结构级别包含[edit chassis fpc slot-number pic pic-number hash-key family inet]该symmetric-hash complement语句:
[edit chassis fpc 1 pic 2 hash-key]
family inet {
layer-3;
layer-4;
symmetric-hash {
complement;
}
}
在两台路由器上为家族 inet 和家族多服务配置对称散列
在流量进入路由器 A 的入站流量接口上,在层次结构级别包含[edit chassis fpc slot-number pic pic-number hash-key family multiservice]该symmetric-hash语句:
[edit chassis fpc 1 pic 0 hash-key]
family multiservice {
payload {
ip {
layer-3;
layer-4;
}
}
symmetric-hash;
}
在流量进入路由器 B 的入站流量接口上,在层次结构级别包含[edit chassis fpc slot-number pic pic-number hash-key family inet]该symmetric-hash complement语句:
[edit chassis fpc 0 pic 3 hash-key]
family inet {
layer-3;
layer-4;
symmetric-hash {
complement;
}
}
也可以看看
示例:配置聚合以太网负载均衡
示例:配置聚合以太网负载均衡
此示例说明如何配置聚合以太网负载平衡。
要求
此示例使用以下硬件和软件组件:
三台带 MIC 和 MPC 接口的 MX 系列路由器或三台带 PIC 和 FPC 接口的 PTX 系列数据包传输路由器
在所有设备上运行 Junos OS 13.3 或更高版本
概述
当下一跳路由器有多个路径或接口可用时,转发平面需要进行负载均衡,最好在所有可用路径上均衡传入流量,以提高链路利用率。
聚合以太网捆绑包是一种典型应用,它使用负载平衡来平衡捆绑包成员链路之间的流量 (IEEE 802.3ad)。
从 Junos OS 13.3 版开始,聚合以太网负载平衡得到增强,可提供两种解决方案来解决 MX 系列路由器 MIC 或 MPC 上的聚合以太网捆绑包上的真正流量不平衡问题。从 Junos OS 14.1 版开始,聚合以太网负载平衡得到增强,可提供两种解决方案来解决 PTX 系列数据包传输路由器的 PIC 或 FPC 上的聚合以太网捆绑包上的真正流量不平衡问题。
聚合以太网负载平衡解决方案包括:
-
自适应 — 自适应负载平衡用于基于流的散列不足以实现均匀负载分布的场景。此负载平衡解决方案实施实时反馈和控制机制来监控和管理网络负载的不平衡。
自适应负载平衡解决方案通过修改选择器条目并定期扫描 AE 束每个成员链路上的链路利用率以检测任何偏差来纠正流量不平衡。当检测到偏差时,将触发调整事件,并减少映射到受影响成员链路的流量。结果,该成员链路提供的带宽下降。这会导致一个连续的反馈环路,在一段时间内确保向所有成员链路提供相同数量的字节速率,从而在 AE 束中的每个成员链路上提供有效的流量分配。
要配置自适应负载平衡,请在层次结构级别包含
adaptive[edit interfaces aex aggregated-ether-options load-balance]该语句。注意:启用自适应负载平衡可能会导致每个重新平衡间隔对数据包重新排序一次。
该
pps选项可根据每秒数据包数速率实现负载平衡。默认设置为每秒位负载平衡。该
scan-interval值将扫描时间长度配置为 30 秒的倍数。该
tolerance值是流向捆绑包中聚合以太网链路的数据包流量方差的极限。您可以指定最大 100% 的差异。如果未配置容差属性,则会为自适应负载平衡启用默认值 20%。容差值越小,带宽平衡越好,但融合时间越长。 每数据包随机喷射 — 当自适应负载平衡解决方案出现故障时,每数据包随机喷射将作为最后手段。按数据包随机喷射负载平衡解决方案将数据包随机喷射到聚合下一跃点,帮助解决流量不平衡问题。这可确保 AE 捆绑包的所有成员链路都按同等负载,从而对数据包进行重新排序。
此外,每个数据包的随机喷洒可识别导致流量不平衡的入口数据包转发引擎,并消除由于软件错误而发生的流量不平衡(数据包哈希除外)。
要配置每个数据包的随机喷负载平衡,请在层次结构级别包含
per-packet[edit interfaces aex aggregated-ether-options load-balance]该语句。注意:PTX 系列数据包传输路由器不支持用于负载平衡的按数据包选项。
聚合以太网负载平衡解决方案是互斥的。配置多个负载平衡解决方案时,上次配置的解决方案将覆盖之前配置的解决方案。您可以通过发出 show interfaces aex aggregated-ether-options load-balance 命令来验证正在实施的负载均衡解决方案。
拓扑结构
在此拓扑中,R2 和 R3 路由器之间的链路上配置了两个聚合以太网束 - ae0 和 ae1。
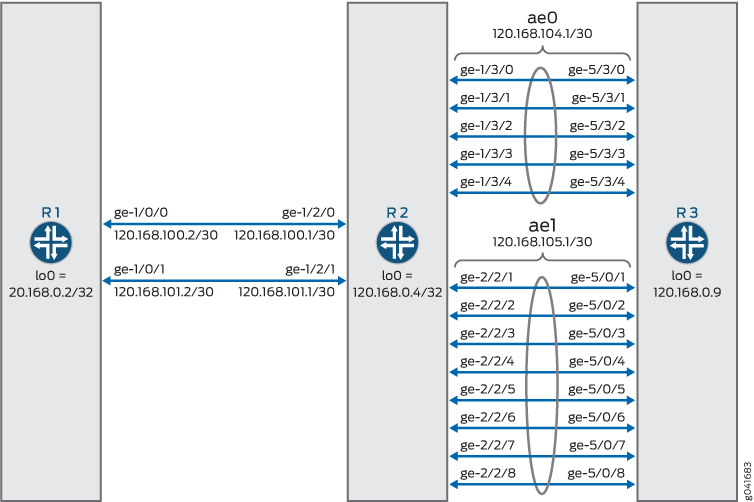
配置
CLI 快速配置
要快速配置此示例,请复制以下命令,将其粘贴到文本文件中,删除所有换行符,更改详细信息,以便与网络配置匹配,然后将命令复制并粘贴到层次结构级别的 [edit] CLI 中。
R1
set chassis aggregated-devices ethernet device-count 12 set interfaces xe-0/0/0 unit 0 family inet address 120.168.1.1/30 set interfaces xe-0/0/0 unit 0 family iso set interfaces xe-0/0/0 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces xe-0/0/1 unit 0 family inet address 120.168.2.1/30 set interfaces xe-0/0/1 unit 0 family iso set interfaces xe-0/0/1 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces ge-1/0/0 unit 0 family inet address 120.168.100.2/30 set interfaces ge-1/0/0 unit 0 family iso set interfaces ge-1/0/0 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces ge-1/0/1 unit 0 family inet address 120.168.101.2/30 set interfaces ge-1/0/1 unit 0 family iso set interfaces ge-1/0/1 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 120.168.0.2/32 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family iso address 49.0001.1201.6800.0002.00 set routing-options router-id 120.168.0.2 set routing-options autonomous-system 55 set protocols rsvp interface ge-1/0/0.0 set protocols rsvp interface ge-1/0/1.0 set protocols mpls label-switched-path videl-to-sweets to 120.168.0.9 set protocols mpls label-switched-path v-2-s-601 to 60.0.1.0 set protocols mpls label-switched-path v-2-s-601 primary v-2-s-601-primary hop-limit 5 set protocols mpls label-switched-path v-2-s-602 to 60.0.2.0 set protocols mpls label-switched-path v-2-s-602 primary v-2-s-602-primary hop-limit 5 set protocols mpls label-switched-path v-2-s-603 to 60.0.3.0 set protocols mpls label-switched-path v-2-s-604 to 60.0.4.0 set protocols mpls path v-2-s-601-primary 120.168.100.1 strict set protocols mpls path v-2-s-601-primary 120.168.104.2 strict set protocols mpls path v-2-s-602-primary 120.168.101.1 strict set protocols mpls path v-2-s-602-primary 120.168.105.2 strict set protocols mpls interface ge-1/0/0.0 set protocols mpls interface ge-1/0/1.0 set protocols bgp group pe-routers type internal set protocols bgp group pe-routers local-address 120.168.0.2 set protocols bgp group pe-routers family inet unicast set protocols bgp group pe-routers family inet-vpn unicast set protocols bgp group pe-routers neighbor 120.168.0.9 set protocols isis traffic-engineering family inet shortcuts set protocols isis level 1 disable set protocols isis interface ge-1/0/0.0 set protocols isis interface ge-1/0/1.0 set protocols isis interface lo0.0 set policy-options policy-statement nhs then next-hop self set policy-options policy-statement vpn-m5-export term 1 from protocol bgp set policy-options policy-statement vpn-m5-export term 1 from protocol direct set policy-options policy-statement vpn-m5-export term 1 then community add vpn-m5-target set policy-options policy-statement vpn-m5-export term 1 then accept set policy-options policy-statement vpn-m5-export term 2 then reject set policy-options policy-statement vpn-m5-import term 1 from protocol bgp set policy-options policy-statement vpn-m5-import term 1 from community vpn-m5-target set policy-options policy-statement vpn-m5-import term 1 then accept set policy-options policy-statement vpn-m5-import term 2 then reject set policy-options community vpn-m5-target members target:55:100 set routing-instances vpn-m5 instance-type vrf set routing-instances vpn-m5 interface xe-0/0/0.0 set routing-instances vpn-m5 interface xe-0/0/1.0 set routing-instances vpn-m5 route-distinguisher 120.168.0.2:1 set routing-instances vpn-m5 vrf-import vpn-m5-import set routing-instances vpn-m5 vrf-export vpn-m5-export set routing-instances vpn-m5 protocols bgp group ce type external set routing-instances vpn-m5 protocols bgp group ce peer-as 100 set routing-instances vpn-m5 protocols bgp group ce as-override set routing-instances vpn-m5 protocols bgp group ce neighbor 120.168.1.2 set routing-instances vpn-m5 protocols bgp group ce neighbor 120.168.2.2 set routing-instances vpn-m5 protocols ospf domain-id 1.0.0.0 set routing-instances vpn-m5 protocols ospf export vpn-m5-import set routing-instances vpn-m5 protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface xe-0/0/1.0 set routing-instances vpn-m5 protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface xe-0/0/0.0
R2
set chassis aggregated-devices ethernet device-count 5 set interfaces ge-1/2/0 unit 0 family inet address 120.168.100.1/30 set interfaces ge-1/2/0 unit 0 family iso set interfaces ge-1/2/0 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces ge-1/2/1 unit 0 family inet address 120.168.101.1/30 set interfaces ge-1/2/1 unit 0 family iso set interfaces ge-1/2/1 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces ge-1/3/0 gigether-options 802.3ad ae0 set interfaces ge-1/3/1 gigether-options 802.3ad ae0 set interfaces ge-1/3/2 gigether-options 802.3ad ae0 set interfaces ge-1/3/3 gigether-options 802.3ad ae0 set interfaces ge-1/3/4 gigether-options 802.3ad ae0 set interfaces ge-2/2/1 gigether-options 802.3ad ae1 set interfaces ge-2/2/2 gigether-options 802.3ad ae1 set interfaces ge-2/2/3 gigether-options 802.3ad ae1 set interfaces ge-2/2/4 gigether-options 802.3ad ae1 set interfaces ge-2/2/5 gigether-options 802.3ad ae1 set interfaces ge-2/2/6 gigether-options 802.3ad ae1 set interfaces ge-2/2/7 gigether-options 802.3ad ae1 set interfaces ge-2/2/8 gigether-options 802.3ad ae1 set interfaces ae0 aggregated-ether-options load-balance adaptive tolerance 10 set interfaces ae0 aggregated-ether-options link-speed 1g set interfaces ae0 aggregated-ether-options lacp active set interfaces ae0 unit 0 family inet address 120.168.104.1/30 set interfaces ae0 unit 0 family iso set interfaces ae0 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces ae1 aggregated-ether-options load-balance adaptive tolerance 10 set interfaces ae1 aggregated-ether-options link-speed 1g set interfaces ae1 aggregated-ether-options lacp active set interfaces ae1 unit 0 family inet address 120.168.105.1/30 set interfaces ae1 unit 0 family iso set interfaces ae1 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 120.168.0.4/32 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family iso address 49.0001.1201.6800.0004.00 set accounting-options selective-aggregate-interface-stats disable set protocols rsvp interface ge-1/2/0.0 set protocols rsvp interface ge-1/2/1.0 set protocols rsvp interface ae0.0 set protocols rsvp interface ae1.0 set protocols mpls interface ge-1/2/0.0 set protocols mpls interface ge-1/2/1.0 set protocols mpls interface ae0.0 set protocols mpls interface ae1.0 set protocols isis traffic-engineering family inet shortcuts set protocols isis level 1 disable set protocols isis interface ge-1/2/0.0 set protocols isis interface ge-1/2/1.0 set protocols isis interface ae0.0 set protocols isis interface ae1.0 set protocols isis interface lo0.0
R3
set chassis aggregated-devices ethernet device-count 5 set interfaces xe-4/0/0 unit 0 family inet address 120.168.9.1/30 set interfaces xe-4/0/0 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces xe-4/0/1 unit 0 family inet address 120.168.10.1/30 set interfaces xe-4/0/1 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces ge-5/0/1 gigether-options 802.3ad ae1 set interfaces ge-5/0/2 gigether-options 802.3ad ae1 set interfaces ge-5/0/3 gigether-options 802.3ad ae1 set interfaces ge-5/0/4 gigether-options 802.3ad ae1 set interfaces ge-5/0/5 gigether-options 802.3ad ae1 set interfaces ge-5/0/6 gigether-options 802.3ad ae1 set interfaces ge-5/0/7 gigether-options 802.3ad ae1 set interfaces ge-5/0/8 gigether-options 802.3ad ae1 set interfaces ge-5/3/0 gigether-options 802.3ad ae0 set interfaces ge-5/3/1 gigether-options 802.3ad ae0 set interfaces ge-5/3/2 gigether-options 802.3ad ae0 set interfaces ge-5/3/3 gigether-options 802.3ad ae0 set interfaces ge-5/3/4 gigether-options 802.3ad ae0 set interfaces ae0 aggregated-ether-options link-speed 1g set interfaces ae0 aggregated-ether-options lacp active set interfaces ae0 unit 0 family inet address 120.168.104.2/30 set interfaces ae0 unit 0 family iso set interfaces ae0 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces ae1 aggregated-ether-options link-speed 1g set interfaces ae1 aggregated-ether-options lacp active set interfaces ae1 unit 0 family inet address 120.168.105.2/30 set interfaces ae1 unit 0 family iso set interfaces ae1 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 120.168.0.9/32 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family iso address 49.0001.1201.6800.0009.00 set routing-options router-id 120.168.0.9 set routing-options autonomous-system 55 set protocols rsvp interface xe-4/0/0.0 set protocols rsvp interface xe-4/0/1.0 set protocols rsvp interface ae0.0 set protocols rsvp interface ae1.0 set protocols mpls label-switched-path to-videl to 120.168.0.2 set protocols mpls interface xe-4/0/0.0 set protocols mpls interface xe-4/0/1.0 set protocols mpls interface ae0.0 set protocols mpls interface ae1.0 set protocols bgp group pe-routers type internal set protocols bgp group pe-routers local-address 120.168.0.9 set protocols bgp group pe-routers family inet unicast set protocols bgp group pe-routers family inet-vpn unicast set protocols bgp group pe-routers neighbor 120.168.0.2 set protocols isis traffic-engineering family inet shortcuts set protocols isis level 1 disable set protocols isis interface ae0.0 set protocols isis interface ae1.0 set protocols isis interface lo0.0 set policy-options policy-statement nhs then next-hop self set policy-options policy-statement vpn-m5-export term 1 from protocol bgp set policy-options policy-statement vpn-m5-export term 1 from protocol direct set policy-options policy-statement vpn-m5-export term 1 then community add vpn-m5-target set policy-options policy-statement vpn-m5-export term 1 then accept set policy-options policy-statement vpn-m5-export term 2 then reject set policy-options policy-statement vpn-m5-import term 1 from protocol bgp set policy-options policy-statement vpn-m5-import term 1 from protocol direct set policy-options policy-statement vpn-m5-import term 1 from community vpn-m5-target set policy-options policy-statement vpn-m5-import term 1 then accept set policy-options policy-statement vpn-m5-import term 2 then reject set policy-options community vpn-m5-target members target:55:100 set routing-instances vpn-m5 instance-type vrf set routing-instances vpn-m5 interface xe-4/0/0.0 set routing-instances vpn-m5 interface xe-4/0/1.0 set routing-instances vpn-m5 route-distinguisher 120.168.0.9:1 set routing-instances vpn-m5 vrf-import vpn-m5-import set routing-instances vpn-m5 vrf-export vpn-m5-export set routing-instances vpn-m5 protocols bgp group ce type external set routing-instances vpn-m5 protocols bgp group ce peer-as 100 set routing-instances vpn-m5 protocols bgp group ce as-override set routing-instances vpn-m5 protocols bgp group ce neighbor 120.168.9.2 set routing-instances vpn-m5 protocols bgp group ce neighbor 120.168.10.2 set routing-instances vpn-m5 protocols ospf domain-id 1.0.0.0 set routing-instances vpn-m5 protocols ospf export vpn-m5-import set routing-instances vpn-m5 protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface xe-4/0/0.0 set routing-instances vpn-m5 protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface xe-4/0/1.0
配置自适应负载均衡
分步程序
下面的示例要求您在各个配置层级中进行导航。有关导航 CLI 的信息,请参阅在 配置模式下使用 CLI 编辑器。
要配置 R2 路由器,请执行以下作:
修改每个路由器的相应接口名称、地址和任何其他参数后,对其他路由器重复此过程。
指定要创建的聚合以太网接口数量。
[edit chassis]user@R2# set aggregated-devices ethernet device-count 5配置将 R2 连接到 R1 的千兆以太网接口链路。
[edit interfaces]user@R2# set ge-1/2/0 unit 0 family inet address 120.168.100.1/30 user@R2# set ge-1/2/0 unit 0 family iso user@R2# set ge-1/2/0 unit 0 family mpls user@R2# set ge-1/2/1 unit 0 family inet address 120.168.101.1/30 user@R2# set ge-1/2/1 unit 0 family iso user@R2# set ge-1/2/1 unit 0 family mpls user@R2# set lo0 unit 0 family inet address 120.168.0.4/32 user@R2# set lo0 unit 0 family iso address 49.0001.1201.6800.0004.00配置 ae0 聚合以太网捆绑包的五个成员链路。
[edit interfaces]user@R2# set ge-1/3/0 gigether-options 802.3ad ae0 user@R2# set ge-1/3/1 gigether-options 802.3ad ae0 user@R2# set ge-1/3/2 gigether-options 802.3ad ae0 user@R2# set ge-1/3/3 gigether-options 802.3ad ae0 user@R2# set ge-1/3/4 gigether-options 802.3ad ae0配置 ae1 聚合以太网捆绑包的 8 个成员链路。
[edit interfaces]user@R2# set ge-2/2/1 gigether-options 802.3ad ae1 user@R2# set ge-2/2/2 gigether-options 802.3ad ae1 user@R2# set ge-2/2/3 gigether-options 802.3ad ae1 user@R2# set ge-2/2/4 gigether-options 802.3ad ae1 user@R2# set ge-2/2/5 gigether-options 802.3ad ae1 user@R2# set ge-2/2/6 gigether-options 802.3ad ae1 user@R2# set ge-2/2/7 gigether-options 802.3ad ae1 user@R2# set ge-2/2/8 gigether-options 802.3ad ae1在 R2 的 ae0 上启用聚合以太网负载平衡。
[edit interfaces]user@R2# set ae0 aggregated-ether-options load-balance adaptive tolerance 10配置 ae0 聚合以太网捆绑包的链路速度。
[edit interfaces]user@R2# set ae0 aggregated-ether-options link-speed 1g在 ae0 聚合以太网捆绑包上配置 LACP。
[edit interfaces]user@R2# set ae0 aggregated-ether-options lacp active为 ae0 聚合以太网捆绑包配置接口参数。
[edit interfaces]user@R2# set ae0 unit 0 family inet address 120.168.104.1/30 user@R2# set ae0 unit 0 family iso user@R2# set ae0 unit 0 family mpls在 R2 的 ae1 上启用聚合以太网负载平衡。
[edit interfaces]user@R2# set ae1 aggregated-ether-options load-balance adaptive tolerance 10配置 ae1 聚合以太网捆绑包的链路速度。
[edit interfaces]user@R2# set ae1 aggregated-ether-options link-speed 1g在 ae1 聚合以太网捆绑包上配置 LACP。
[edit interfaces]user@R2# set ae1 aggregated-ether-options lacp active为 ae1 聚合以太网捆绑包配置接口参数。
[edit interfaces]user@R2# set ae1 unit 0 family inet address 120.168.105.1/30 user@R2# set ae1 unit 0 family iso user@R2# set ae1 unit 0 family mpls禁用选择性聚合以太网统计信息。
[edit accounting-options]user@R2# set selective-aggregate-interface-stats disable在 R2 的所有接口和 AE 捆绑包上配置 RSVP。
[edit protocols]user@R2# set rsvp interface ge-1/2/0.0 user@R2# set rsvp interface ge-1/2/1.0 user@R2# set rsvp interface ae0.0 user@R2# set rsvp interface ae1.0在 R2 的所有接口和 AE 捆绑包上配置 MPLS。
[edit protocols]user@R2# set mpls interface ge-1/2/0.0 user@R2# set mpls interface ge-1/2/1.0 user@R2# set mpls interface ae0.0 user@R2# set mpls interface ae1.0在 R2 的所有接口和 AE 捆绑包上配置 IS-IS。
[edit protocols]user@R2# set isis traffic-engineering family inet shortcuts user@R2# set isis level 1 disable user@R2# set isis interface ge-1/2/0.0 user@R2# set isis interface ge-1/2/1.0 user@R2# set isis interface ae0.0 user@R2# set isis interface ae1.0 user@R2# set isis interface lo0.0
结果
在配置模式下,输入 show chassis、 show interfaces、 show accounting-options和 show protocols 命令以确认您的配置。如果输出未显示预期的配置,请重复此示例中的说明以更正配置。
user@R2# show chassis
aggregated-devices {
ethernet {
device-count 5;
}
}
user@R2# show interfaces
ge-1/2/0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 120.168.100.1/30;
}
family iso;
family mpls;
}
}
ge-1/2/1 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 120.168.101.1/30;
}
family iso;
family mpls;
}
}
ge-1/3/0 {
gigether-options {
802.3ad ae0;
}
}
ge-1/3/1 {
gigether-options {
802.3ad ae0;
}
}
ge-1/3/2 {
gigether-options {
802.3ad ae0;
}
}
ge-1/3/3 {
gigether-options {
802.3ad ae0;
}
}
ge-1/3/4 {
gigether-options {
802.3ad ae0;
}
}
ge-2/2/1 {
gigether-options {
802.3ad ae1;
}
}
ge-2/2/2 {
gigether-options {
802.3ad ae1;
}
}
ge-2/2/3 {
gigether-options {
802.3ad ae1;
}
}
ge-2/2/4 {
gigether-options {
802.3ad ae1;
}
}
ge-2/2/5 {
gigether-options {
802.3ad ae1;
}
}
ge-2/2/6 {
gigether-options {
802.3ad ae1;
}
}
ge-2/2/7 {
gigether-options {
802.3ad ae1;
}
}
ge-2/2/8 {
gigether-options {
802.3ad ae1;
}
}
ae0 {
aggregated-ether-options {
load-balance {
adaptive tolerance 10;
}
link-speed 1g;
lacp {
active;
}
}
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 120.168.104.1/30;
}
family iso;
family mpls;
}
}
ae1 {
aggregated-ether-options {
load-balance {
adaptive tolerance 10;
}
link-speed 1g;
lacp {
active;
}
}
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 120.168.105.1/30;
}
family iso;
family mpls;
}
}
lo0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 120.168.0.4/32;
}
family iso {
address 49.0001.1201.6800.0004.00;
}
}
}
user@R2# show accounting-options
selective-aggregate-interface-stats disable;
user@R2# show protocols
rsvp {
interface ge-1/2/0.0;
interface ge-1/2/1.0;
interface ae0.0;
interface ae1.0;
}
mpls {
interface ge-1/2/0.0;
interface ge-1/2/1.0;
interface ae0.0;
interface ae1.0;
}
isis {
traffic-engineering {
family inet {
shortcuts;
}
}
level 1 disable;
interface ge-1/2/0.0;
interface ge-1/2/1.0;
interface ae0.0;
interface ae1.0;
interface lo0.0;
}
验证
确认配置工作正常。
验证 ae0 上的自适应负载均衡
目的
验证在 ae0 聚合以太网捆绑包上接收的数据包是否在五个成员链路之间实现负载均衡。
行动
在作模式下,运行命令 show interfaces ae0 extensive 。
user@R2> show interfaces ae0 extensive
Logical interface ae0.0 (Index 325) (SNMP ifIndex 917) (Generation 134)
Flags: SNMP-Traps 0x4004000 Encapsulation: ENET2
Statistics Packets pps Bytes bps
Bundle:
Input : 848761 9 81247024 7616
Output: 166067308909 3503173 126900990064983 21423804256
Adaptive Statistics:
Adaptive Adjusts: 264
Adaptive Scans : 27682
Adaptive Updates: 10
Link:
ge-1/3/0.0
Input : 290888 5 29454436 3072
Output: 33183442699 704569 25358563587277 4306031760
ge-1/3/1.0
Input : 162703 1 14806325 992
Output: 33248375409 705446 25406995966732 4315342152
ge-1/3/2.0
Input : 127448 1 12130566 992
Output: 33184552729 697572 25354827700261 4267192376
ge-1/3/3.0
Input : 121044 1 11481262 1280
Output: 33245875402 697716 25405953405192 4265750584
ge-1/3/4.0
Input : 146678 1 13374435 1280
Output: 33205071207 697870 25374651121458 4269487384
意义
ae0 聚合以太网捆绑包的成员链路可通过自适应负载平衡得到充分利用。
特定于平台的聚合以太网负载平衡行为
使用 功能资源管理器 确认平台和版本对特定功能的支持。
使用下表查看平台的特定于平台的行为。
特定于平台的聚合以太网负载平衡行为
| 平台 | 差异 |
|---|---|
| ACX 系列 |
|
| EX 系列 |
|
| MX 系列 |
|
| PTX 系列 |
|
| QFX 系列 |
|
变更历史表
是否支持某项功能取决于您使用的平台和版本。使用 功能资源管理器 确定您的平台是否支持某个功能。
payload 第 2 层流量配置负载平衡散列密钥,以使用第 3 层和第 4 层标头中的字段。
