在本页
修改设备的配置
CLI 允许您修改现有 Junos OS 配置。本节介绍添加语句、删除语句、复制语句和插入新标识符的细节,包括示例。
显示当前正在编辑配置的用户
要显示当前正在编辑配置的用户,请使用 status 配置模式命令:
user@host# status
Users currently editing the configuration:
rchen terminal p0 (pid 55691) on since 2018-03-01 13:17:25 PST
[edit interfaces]
系统将显示谁在编辑配置(rchen)、用户登录的位置(terminal p0)、用户登录的日期和时间(2018-03-01 13:17:25 PST)以及用户正在编辑的层次结构级别([edit interfaces])。
如果发出配置模式命令, status 并且用户已计划候选配置在将来的某个时间变为活动状态,则系统将显示计划提交的人员 (root)、用户登录的位置 (terminal d0)、用户登录的日期和时间 (2018-10-31 14:55:15 PST) 以及提交挂起 (commit at).
[edit]
user@host# status
Users currently editing the configuration:
root terminal d0 (pid 767) on since 2018-10-31 14:55:15 PST, idle 00:03:09
commit at
如果发出 status 配置模式命令,并且用户正在配置独占模式下编辑配置,则系统将显示谁在编辑配置root()、用户terminal d0登录的位置()、用户登录的日期和时间(2018-11-01 13:05:11 PST),以及用户正在配置独占模式下编辑配置(exclusive [edit])。
[edit]
user@host# status
Users currently editing the configuration:
root terminal d0 (pid 2088) on since 2018-11-01 13:05:11 PST
exclusive [edit]
另请参阅
如何修改瞻博网络设备配置
要配置瞻博网络设备或修改现有配置,请使用和set命令向edit配置中添加语句。对于每个语句层次结构,从顶层的语句开始创建层次结构。然后,您继续使用在层次结构中逐渐降低的语句创建层次结构。
要修改层次结构,请使用两个配置模式命令。根据要完成的操作选择相关命令:
edit- 移动到指定的层次结构级别。如果该层次结构级别不存在,该命令将edit创建它。该edit命令具有以下语法:edit <statement-path>
set— 创建配置语句并设置标识符值。发出set命令后,您将保持在层次结构中的同一级别。该set命令具有以下语法:set <statement-path> statement <identifier>
配置语句和语句本身的层次结构为
statement-path。如果已移动到语句的层次结构级别,则可以省略语句路径。配置语句本身为statement。该identifier字符串标识语句的实例。
语句可以是容器语句,也可以是叶语句。容器语句可以包含其他容器语句以及叶语句。然而,叶子声明是独立的。该命令 edit? 显示容器语句,同时 set? 显示容器和叶语句,用于 > 区分它们。
不能使用 edit 命令更改标识符的值。您必须使用 set 命令。
另请参阅
如何添加配置语句和标识符
您可以通过在配置中包含语句来配置瞻博网络设备的所有属性。语句由关键字组成,该关键字是固定文本。还可以在语句中包含标识符。标识符是您定义的标识名称,例如接口名称或用户名,使您能够和 CLI 区分语句集合。
例如,以下列表显示了配置模式下顶层可用的语句:
user@host# set ?
Possible completions:
> accounting-options Accounting data configuration
+ apply-groups Groups from which to inherit configuration data
> chassis Chassis configuration
> class-of-service Class-of-service configuration
> firewall Define a firewall configuration
> forwarding-options Configure options to control packet sampling
> groups Configuration groups
> interfaces Interface configuration
> policy-options Routing policy option configuration
> protocols Routing protocol configuration
> routing-instances Routing instance configuration
> routing-options Protocol-independent routing option configuration
> snmp Simple Network Management Protocol
> system System parameters语句名称前的尖括号 ( > ) 表示它是一个容器语句,您可以在其下面的级别定义其他语句。如果语句名称前没有尖括号 ( > ),则该语句是叶语句;不能在其下的层次结构级别定义其他语句。
语句名称前的加号 (+) 表示它可以包含一组值。要指定集合,请将值包含在括号中。例如:
[edit]
user@host# set policy-options community my-as1-transit members [65535:10 65535:11]
在某些语句中,可以包含标识符。对于某些标识符(如接口名称),必须以精确的格式指定标识符。例如,接口名称 so-0/0/0 是指位于灵活 PIC 集中器 (FPC) 插槽 0、第一个 PIC 位置和物理接口卡 (PIC) 上第一个端口中的 SONET/SDH 接口。
对于其他标识符(如接口描述性文本以及策略和防火墙术语名称),您可以指定任何名称,包括特殊字符、空格和制表符。
必须将标识符括在引号(双引号)中。还必须使用引号将标识符和包含空格、制表符或以下任何字符的任何字符串括起来:
( ) [ ] { } ! @ # $ % ^ & | ' = ?
如果不为需要选项的语句键入选项,则会出现一条消息,指示所需的信息类型。在此示例中,必须键入区域编号才能完成命令:
[edit]
user@host# set protocols ospf area
^
syntax error, expecting <identifier>
另请参阅
如何从设备配置中删除语句
您可以使用 delete 配置模式命令从设备配置中删除语句或标识符。删除语句或标识符会有效地“取消配置”与该语句或标识符关联的功能,并将该功能返回到其默认状态。
user@host# delete <statement-path> <identifier>
删除语句时,将从配置中删除该语句及其所有从属语句和标识符。
对于可以具有多个标识符的语句,删除一个标识符时,只会删除该标识符。语句中的其他标识符将保留。
要删除从当前层次结构级别开始的整个层次结构, delete 请使用命令而不指定语句或标识符。省略语句或标识符时,系统会提示您确认删除:
[edit]
user@host# delete
Delete everything under this level? [yes, no] (no)
Possible completions:
no Don't delete everything under this level
yes Delete everything under this level
Delete everything under this level? [yes, no] (no) 不能使用单个 delete 命令删除层次结构中的多个语句或标识符。您必须使用多个 delete 命令分别删除每个语句或标识符。例如,请考虑层次结构级别的以下配置 [edit system] :
system {
host-name host-211;
domain-name domain-122;
backup-router 192.168.71.254;
arp;
authentication-order [ radius password tacplus ];
}
要从配置中删除 domain-name、 host-name和 backup-router ,必须单独删除每个语句。
user@hostdelete system host-name host-211user@hostdelete system domain-name domain-122user@hostdelete system backup-router 192.168.71.254
不能发出单个 delete 命令。例如,以下命令将不起作用:
user@host> delete system hostname host-211 domain-name domain-122 backup-router 192.168.71.254您可以使用单个命令和正则表达式同时删除相关配置项,例如通道化接口或静态路由。删除语句或标识符会有效地“取消配置”与该语句或标识符关联的功能,并将该功能返回到其默认状态。
您只能删除配置中通常放置多个项目的某些部分,例如接口。但是,您无法删除不同项目的“组”,如以下示例所示:
user@host#show system servicesftp; rlogin; rsh; ssh { root-login allow; } telnet; [edit] user@host#wildcard delete system services *syntax error.
删除语句时,将从配置中删除该语句及其所有从属语句和标识符。
要删除相关配置项,请发出 wildcard 带有选项的 delete 配置模式命令,并指定语句路径、要用正则表达式汇总的项目和正则表达式,如下所示:
user@host# wildcard delete <statement-path> <identifier> <regular-expression>
使用 wildcard 命令删除相关配置项时,正则表达式必须是 final 语句。
如果匹配 Junos OS 八个以上的相关项目,CLI 仅显示前八个项目。
如何从配置中删除接口
您可以使用以下语法删除从 到 t1-0/0/0:0 范围内的 t1-0/0/0:23 多个 T1 接口:
user@host# wildcard delete interfaces t1-0/0/0:.*
matched: t1-0/0/0:0
matched: t1-0/0/0:1
matched: t1-0/0/0:2
Delete 3 objects? [yes,no] (no) no
如何从配置中删除路由
可以使用以下语法删除从 172.0.0.0 到 172.255.0.0 范围内的静态路由:
user@host# wildcard delete routing-options static route 172.*
matched: 172.16.0.0/12
matched: 172.16.14.0/24
matched: 172.16.100.0/24
matched: 172.16.128.0/19
matched: 172.16.160.0/24
matched: 172.17.12.0/23
matched: 172.17.24.0/23
matched: 172.17.28.0/23
...
Delete 13 objects? [yes,no] (no)
示例:从设备配置中删除语句
以下示例说明如何删除语句 ospf ,从而有效地取消配置路由器上的 OSPF:
[edit] user@host#set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface so-0/0/0 hello-interval 5[edit] user@host#showprotocols { ospf { area 0.0.0.0 { interface so-0/0/0 { hello-interval 5; } } } } [edit] user@host#delete protocols ospf[edit] user@host#show[edit] user@host#
从当前级别向下删除所有语句:
[edit] user@host#edit protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0[edit protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0] user@host#set interface so-0/0/0 hello-interval 5[edit protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0] user@host#deleteDelete everything under this level? [yes, no]yes[edit protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0] user@host#show[edit] user@host#
取消配置特定属性。在此示例中,请删除接口速度设置:
[edit] user@host#set interfaces so-3/0/0 speed 100mb[edit] user@host#showinterfaces { so-3/0/0 { speed 100mb; } } [edit] user@host#delete interfaces so-3/0/0 speed[edit] user@host#showinterfaces { so-3/0/0; }
复制配置中的语句
当设备配置中有许多类似的语句时,可以添加一个语句,然后复制该语句。复制语句会复制该语句以及在该语句下配置的整个语句层次结构。配置许多相同类型的物理或逻辑接口时,复制语句非常有用。
要复制配置中的现有语句,请执行以下操作:
- 使用配置模式
copy命令:user@host#
copy existing-statement to new-statement - 复制部分配置后,请立即检查新配置的有效性。
- 如果配置无效,请修改复制的部分或原始部分以生成有效的配置。
示例:复制配置中的语句
此示例说明如何通过复制现有 VC 在接口上创建一个虚拟连接 (VC)。
要求
配置此示例之前,不需要除设备初始化之外的特殊配置。
在开始此示例之前,请配置以下初始配置:
[edit interfaces]
user@host# show
at-1/0/0 {
description "PAIX to MAE West"
encapsulation atm-pvc;
unit 61 {
point-to-point;
vci 0.61;
family inet {
address 10.0.1.1/24;
}
}
}
要快速配置此示例的初始配置,请复制以下命令,将其粘贴到文本文件中,删除所有换行符并更改与您的网络配置匹配所需的任何详细信息,将此命令复制并粘贴到层次结构级别的 CLI [edit] 中,然后进入 commit 配置模式。
set interfaces at-1/0/0 description "PAIX to MAE West" set interfaces at-1/0/0 encapsulation atm-pvc set interfaces at-1/0/0 unit 61 point-to-point set interfaces at-1/0/0 unit 61 vci 0.61 set interfaces at-1/0/0 unit 61 family inet address 10.0.1.1/24
概述
在此说明如何复制语句的示例中,您将添加一个与已配置的虚拟连接非常相似的虚拟连接。
配置
CLI 快速配置
从 [edit interfaces at-1/0/0] 层次结构级别开始。
copy unit 61 to unit 62set unit 62 vci 0.62edit unit 62replace pattern 10.0.1.1 with 10.0.2.1
通过复制进行配置
分步过程
要通过复制配置进行配置,请执行以下操作:
[edit interfaces at-1/0/0]转到层次结构级别并复制单元 61。[edit interfaces at-1/0/0] user@host#
copy unit 61 to unit 62-
查看新配置,了解需要更改哪些内容才能使配置有效。
user@host#
show interfaces at-1/0/0description "PAIX to MAE West" encapsulation atm-pvc; unit 61 { point-to-point; vci 0.61; family inet { address 10.0.1.1/24; } } unit 62 { point-to-point; vci 0.61; family inet { address 10.0.1.1/24; } } 更改配置以使其有效。
在此示例中,您需要重新配置虚拟电路标识符 (VCI) 和虚拟路径标识符 (VPI)。
[edit interfaces at-1/0/0] user@host#
set unit 62 vci 0.62您还希望将新接口的 IP 地址替换为其自己的 IP 地址。
[edit interfaces at-1/0/0] user@host#
edit unit 62user@host#replace pattern 10.0.1.1 with 10.0.2.1
结果
[edit]
show interfaces
at-1/0/0 {
description "PAIX to MAE West"
encapsulation atm-pvc;
unit 61 {
point-to-point;
vci 0.61;
family inet {
address 10.0.1.1/24;
}
}
unit 62 {
point-to-point;
vci 0.62;
family inet {
address 10.0.2.1/24;
}
}
}
示例:替换配置
如果需要更改设备的配置,则始终可以使用命令删除 delete 原始配置设置,然后使用命令添加新 set 的配置设置。但是,还有其他更高效、更易于使用的修改配置的方法。
此示例说明如何使用以下配置模式命令更新现有配置:
rename— 重命名现有配置设置,例如接口名称。向设备添加新接口时,此命令可能很有用。copy— 复制配置设置和在该设置下配置的语句的整个层次结构。配置许多相同类型的物理或逻辑接口时,复制配置语句非常有用。replace- 对配置中的文本模式进行全局更改。例如,如果您始终拼错设备上所有接口的描述语句中通用的单词,则可以通过单个命令修复此错误。
要求
配置此示例之前,不需要除设备初始化之外的特殊配置。
概述
在本主题的第一个示例中,您将进行以下配置更改:
创建一个新界面,其中包含包含键入错误的描述。
从您创建的接口复制配置以创建新接口。
重命名您创建的接口之一。
修复您创建的接口的说明中的键入错误。
在第二个较短的示例中,您将在略有不同的情况下尝试一些相同的命令。
配置
使用复制、重命名和替换命令修改环路接口配置
分步过程
如果现有配置使用此示例中使用的任何环路接口单元号,则必须替换不同的未使用的环路接口单元号。否则,执行这些步骤可能会损坏设备的现有操作状态。
要使用 、 rename和replace命令创建和copy修改环路接口的配置,请执行以下操作:
-
创建新的环路接口单元号并附上描述。
描述中环回拼写中的错误是故意的。
[edit] user@host#
set interfaces lo0 unit 100 description "this is a lopbck interface" -
显示刚刚添加的环路接口的配置。
[edit] user@host#
show interfaces lo0 unit 100description "this is a lopbck interface"; -
将刚刚创建的环路接口(包括错误)从单元 100 复制到单元 101。
[edit] user@host#
copy interfaces lo0 unit 100 to unit 101 -
显示环路接口 lo0 单元 100 和 lo0 单元 101 的配置。
[edit] user@host#
show interfaces lo0 unit 100description "this is a lopbck interface";[edit] user@host#show interfaces lo0 unit 101description "this is a lopbck interface";该
copy命令复制包含任何子语句的接口,例如description。 -
将环路接口 lo0 单元 100 重命名为环路接口 lo0 单元 102。
[edit] user@host#
rename interfaces lo0 unit 100 to unit 102 -
显示环路接口 lo0 单元 100 的配置。
[edit] user@host#
show interfaces lo0 unit 100[edit] user@host#不应看到此命令的任何结果。单元 100 的环路接口 lo0 现已消失。该
rename命令将指示的配置语句替换为新配置。 -
修复环路接口 lo0 单元 101 和 lo0 单元 102 描述中单词 环回 的拼写错误。
[edit] user@host#
replace pattern lopbck with loopback -
显示环路接口 lo0 单元 101 和 lo0 102 的配置,以验证 “环回 ”一词现在拼写是否正确。
[edit] user@host#
show interfaces lo0 unit 101description "this is a loopback interface";[edit] user@host#show interfaces lo0 unit 102description "this is a loopback interface";该
replace命令将替换命令中指定的模式的所有实例,除非以某种方式受到限制。本主题中的下一个示例演示一种限制命令效果replace的方法。 -
在配置模式下,使用
rollback命令将设备配置返回到执行上述步骤之前的状态。[edit] user@host#
rollback
结果
在配置模式下,使用 and show interfaces lo0 unit 101show interfaces lo0 unit 102 命令确保设备配置处于执行此示例中的步骤之前的状态。
[edit]
user@host: show interfaces lo0 unit 101
[edit]
user@host#
不应看到此命令的任何结果。
[edit] user@host# show interfaces lo0 unit 102 [edit] user@host#
不应看到此命令的任何结果。
比较顶级配置层次结构级别的 copy 命令
分步过程
前面的示例显示了copy层次结构级别的 、 rename和replace[edit interfaces interface-name unit logical-interface-number]命令。此示例说明其中一些命令如何在 CLI 配置模式层次结构的顶层工作。
以下示例要求您导航到配置层次结构中的各个级别。有关导航 CLI 的信息,请参阅 在配置模式下使用 CLI 编辑器 。
-
创建以太网接口。
[edit] user@host#
set interfaces et-2/0/0 unit 0 family inet address 192.0.2.2 -
将刚刚创建的接口复制到另一个接口。
[edit] user@host#
copy interfaces et-2/0/0 to et-2/1/0将此命令与上一示例中的命令进行比较
copy,其中命令在copy要复制的值之前获取关键字unit:[edit] user@host#
copy interfaces lo0 unit 100 to unit 101请注意,关键字
interfaces不会在介词to之后和要复制的值之前重复。这发生在带有命令的某些copy顶级语句中。提示:同样,在命令中
rename,您不能在某些顶级语句的新标识符之前重复语句的关键字部分。 -
显示到目前为止的配置。
[edit] user@host#
show interfaceset-2/0/0 { unit 0 { family inet { address 192.0.2.2/32; } } } et-2/1/0 { unit 0 { family inet { address 192.0.2.2/32; } } } -
将 et-2/1/0 的地址替换为另一个 IP 地址。
[edit interfaces et-2/1/0 unit 0 family inet] user@host#
replace pattern 192.0.2.2 with 192.0.2.40请注意,如果只想更改模式的特定匹配项而不是所有匹配项,则必须在使用命令之前
replace导航到该特定层次结构级别。 -
再次显示接口。
[edit] user@host#
show interfaceset-2/0/0 { unit 0 { family inet { address 192.0.2.2/32; } } } et-2/1/0 { unit 0 { family inet { address 192.0.2.40/32; } } } -
在配置模式下,使用命令将
rollback设备配置返回到执行上述步骤之前的状态。[edit] user@host#
rollback
结果
在配置模式下,使用 and show interfaces et-2/0/0show interfaces et-2/1/0 命令确保设备配置处于执行此示例中的步骤之前的状态。
[edit]
user@hostshow interfaces et-2/0/0
[edit]
user@host#
不应看到此命令的任何结果。
[edit]
user@R1# show interfaces et-2/1/0
[edit]
user@host#
不应看到此命令的任何结果。
在设备配置中插入新标识符
配置瞻博网络设备时,您可以按任意顺序输入大多数语句和标识符。无论输入配置语句的顺序如何,CLI 始终严格按顺序显示配置。但是,在少数情况下,语句的顺序很重要,因为配置语句会创建一个按顺序分析的序列。
例如,在路由策略或防火墙过滤器中,您可以定义按顺序分析的术语。此外,在动态 MPLS 中创建命名路径时,需要定义路径中传输路由器的有序列表,从第一个传输路由器开始,到最后一个路由器结束。
要修改语句顺序很重要的配置部分,请使用 insert 配置模式命令:
user@host#insert <statement-path> identifier1 (before | after) identifier2
如果不使用该 insert 命令而是配置标识符,则该标识符将放在类似标识符列表的末尾。
示例:在设备配置中插入新标识符
此示例演示了命令 insert 的用法。
使用命令添加 set 的术语位于现有术语列表的末尾,而您可以使用命令按 insert 指定的顺序添加术语。在顺序很重要的情况下,指定语句的顺序非常重要,因为配置语句会创建一个按顺序分析的序列。
如本示例所示,必须先创建术语(或者它必须已存在),然后才能将其与命令一起使用 insert 。放置术语的参考点也必须存在;例如,要将术语 T1 放在术语 T2 之前,T1 和 T2 必须已存在并已填充。 Junos OS 自动删除空术语。
要求
在插入术语之前,必须配置初始策略。要快速配置此示例的初始策略,请复制以下命令,将其粘贴到文本文件中,删除所有换行符并更改任何必要的详细信息以匹配您的网络配置,将命令复制并粘贴到层次结构级别的 CLI [edit policy-options] 中,然后从配置模式进入 commit 。
set policy-statement statics term term1 from route-filter 192.168.0.0/16 orlonger set policy-statement statics term term1 from route-filter 224.0.0.0/3 orlonger set policy-statement statics term term1 then reject set policy-statement statics term term2 from protocol direct set policy-statement statics term term2 then reject set policy-statement statics term term3 from protocol static set policy-statement statics term term3 then reject set policy-statement statics term term4 then accept
现在检查以验证是否正确配置了层次结构:
[edit policy-options]
user@host# show
policy-statement statics {
term term1 {
from {
route-filter 192.168.0.0/16 orlonger;
route-filter 224.0.0.0/3 orlonger;
}
then reject;
}
term term2 {
from protocol direct;
then reject;
}
term term3 {
from protocol static;
then reject;
}
term term4 {
then accept;
}
}
概述
要修改语句顺序很重要的配置部分,必须使用 insert 配置模式命令。set如果改用命令,则添加的语句或标识符将按顺序位于错误的位置。以正确顺序获取命令条款的唯一其他方法是拆除配置并重新开始。
配置
CLI 快速配置
要快速配置此示例,请复制以下命令,将其粘贴到文本文件中,删除所有换行符并更改与您的网络配置匹配所需的任何详细信息,将命令复制并粘贴到 [编辑策略选项] 层次结构级别的 CLI 中,然后进入 commit配置模式。
[edit] user@host#rename policy-options policy-statement statics term term4 to term term6[edit] user@host#set policy-options policy-statement statics term term4 from protocol local[edit] user@host#set policy-options policy-statement statics term term4 then reject[edit] user@host#set policy-options policy-statement statics term term5 from protocol aggregate[edit] user@host#set policy-options policy-statement statics term term5 then reject[edit] user@host#insert policy-options policy-statement statics term term4 after term term3[edit] user@host#insert policy-options policy-statement statics term term5 after term term4
配置为插入术语
分步过程
-
确定配置条款需要遵循的顺序。请考虑原始条款和您计划添加的新条款。
在原始配置中,策略名为
statics,共有四个术语。前三个术语中的每一个都以不同的匹配标准匹配,并且生成的匹配将被拒绝。最后一个术语接受所有其他流量。在此示例中,您需要添加两个术语来消除其他类型的流量。这两个术语都需要在原始配置中的最后一个术语之前。
将原始术语 4 重命名为术语 6。
[edit] user@host#
rename policy-options policy-statement statics term term4 to term term6此步骤将保留原来的最后一个术语(现在重命名为 term6)作为最后一个术语。
创建新术语4.
[edit] user@host#
set policy-options policy-statement statics term term4 from protocol localuser@host#set policy-options policy-statement statics term term4 then reject添加了一个新术语,用于匹配来自本地系统地址的流量并拒绝它。
创建新术语5.
[edit] user@host#
set policy-options policy-statement statics term term5 from protocol aggregateuser@host#set policy-options policy-statement statics term term5 then reject将添加一个新术语,用于匹配来自聚合路由的流量并拒绝它。
在术语 3 之后插入术语 4。
[edit] user@host#
insert policy-options policy-statement statics term term4 after term term3在术语 4 之后插入术语 5。
[edit] user@host#
insert policy-options policy-statement statics term term5 after term term4
结果
[edit]
user@host# show policy-options policy-statement statics
term term1 {
from {
route-filter 192.168.0.0/16 orlonger;
route-filter 224.0.0.0/3 orlonger;
}
then reject;
}
term term2 {
from protocol direct;
then reject;
}
term term3 {
from protocol static;
then accept;
}
term term4 {
from protocol local;
then reject;
}
term term5 {
from protocol aggregate;
then reject;
}
term term6 {
then accept;
}
停用和重新激活设备配置中的语句和标识符
在配置中 Junos OS ,您可以停用语句和标识符,使其在发出 commit 命令时不会生效。任何已停用的语句和标识符都标有 inactive 标记。它们仍保留在配置中,但在发出 commit 命令时不会激活。
要停用语句或标识符,请使用 deactivate 配置模式命令:
user@host# deactivate( statement | identifier )
要重新激活语句或标识符,请使用 activate 配置模式命令:
user@host# activate ( statement | identifier )
在这两个命令中, statement 您指定的 和 identifier 必须位于当前层次结构级别。停用语句时,发出命令时 commit 将忽略该特定语句,并且根本不应用该语句。
要禁用语句,请使用 disable 配置模式命令。
在配置层次结构的某些部分中,可以包含用于 disable 禁用功能的语句。例如,通过在层次结构级别包含 disable 语句 [edit interface interface-name] 来禁用接口。禁用某个函数时,它会在您发出 commit 命令时重新激活,但会被视为已关闭或被管理性禁用。
示例:停用和重新激活设备配置中的语句和标识符
此示例显示了使用 and activate 配置模式命令的deactivate常见用例。它涉及配置了平滑路由引擎切换 (GRES) 的双路由引擎(主引擎和备份引擎)。两个路由引擎上的软件都需要升级。这可以通过停用 GRES、更新路由引擎,然后重新激活 GRES 轻松实现。
您还可以使用相同的设置执行类似的升级,只是配置了不间断活动路由 (NSR) 而不是 GRES。在重新激活 NSR 之前,您需要停用 NSR,然后升级路由引擎。
要求
此示例要求使用具有可升级的双路由引擎的设备。
在开始此示例之前,请确保已配置 GRES。
概述
在此示例中,有两个路由引擎。GRES 已配置,需要升级路由引擎。要完成升级,您需要停用 GRES 功能,升级每个路由引擎,然后再次激活 GRES。
配置
配置 GRES 的停用和重新激活
分步过程
要停用并重新激活用于路由引擎升级的 GRES:
显示已为路由器启用 GRES。
[edit] user@host#
show chassisredundancy { graceful-switchover; } fpc 2 { pic 0 { tunnel-services { bandwidth 1g; } } }停用 GRES。
[edit] user@host#
deactivate chassis redundancy graceful-switchoveruser@host#commit显示 GRES 已停用。
[edit] user@host#
show chassisredundancy { inactive: graceful-switchover; } fpc 2 { pic 0 { tunnel-services { bandwidth 1g; } } }-
逐个升级路由引擎。
有关在双路由引擎上升级 Junos OS 的说明,请参阅 在具有冗余路由引擎的设备上安装软件包。
重新激活 GRES。
[edit] user@host#
activate chassis redundancy graceful-switchoveruser@host#commit
结果
验证是否再次激活了 GRES 功能。
[edit]
user@host# show chassis
redundancy {
graceful-switchover;
}
fpc 2 {
pic 0 {
tunnel-services {
bandwidth 1g;
}
}
}
如何在设备配置中进行全局更改
您可以使用配置模式命令对 replace 设备配置中的变量和标识符进行全局更改。此命令将配置中的一个模式替换为另一个模式。例如,当 PIC 移动到路由器中的另一个插槽时,您可以使用此命令查找并替换接口名称的所有匹配项。
user@host# replace pattern pattern1 with pattern2 <upto n>
选项 pattern pattern1 是一个文本字符串或正则表达式,用于定义要在配置中替换的标识符和值。
该 pattern2 选项是一个文本字符串或正则表达式,用于替换位于 中的 pattern1标识符和值。
CLI 使用标准 UNIX 样式的正则表达式语法(如 POSIX 1003.2 中所定义)。如果正则表达式包含空格、运算符或通配符,请用引号将表达式括起来。支持贪婪限定符(尽可能匹配)。不支持惰性限定符(尽可能少匹配)。
该 upto n 选项指定替换的对象数。的值 n 控制配置中替换的对象总数(而不是模式出现的总次数)。首先替换相同层次结构级别的对象(同级)。给定对象中模式的多次出现被视为单个替换。例如,如果配置包含 010101 文本字符串,则该命令 replace pattern 01 with pattern 02 upto 2 将替换为 010101020202 (而不是 020201)。替换为 010101020202 被视为单个替换 (n = 1),而不是三个单独的替换 (n =3)。
如果未指定 upto 选项,则会替换配置 pattern1 中匹配的所有标识符和值。
该 replace 命令可在任何层次结构级别的配置模式下使用。所有匹配项都区分大小写。
与命令一起使用的 replace 常用正则表达式
操作人员 |
功能 |
|---|---|
|
指示匹配可以是管道两侧的两个术语之一。 |
|
在表达式的开头使用,表示匹配的开始位置。 |
|
在表达式末尾使用,表示术语必须完全匹配到字符点 |
|
指定要匹配的字母或数字范围。若要分隔范围的开始和结束,请使用连字符 ( - )。 |
|
指定要匹配的一组术语。存储为编号变量。用于反向引用,如 |
|
表示 0 个或多个术语。 |
|
表示一个或多个术语。 |
|
表示除空格 (“ ”) 之外的任何字符。 |
|
反斜杠转义特殊字符以抑制其特殊含义。例如\。匹配 |
|
与第 th 组匹配 n的反向引用。 |
|
匹配整个匹配项的反向引用。 |
下表列出了一些替换示例。
命令 |
结果 |
|---|---|
|
火柴: 成果: |
|
火柴: 成果: |
|
火柴: 成果: |
|
火柴: 成果: |
示例:如何在设备配置中使用全局替换 - \n 反向引用
此示例说明如何使用反向引用来替换模式。
要求
配置此示例之前,不需要除设备启动之外的特殊配置。
在开始之前,请配置以下内容:
[edit]
user@host# show interfaces
xe-0/0/0 {
unit 0;
}
fe-3/0/1 {
vlan-tagging;
unit 0 {
description "inet6 configuration. IP: 2000::c0a8::1bf5";
vlan-id 100;
family inet {
address 17.10.1.1/24;
}
family inet6 {
address 2000::c0a8:1bf5/3;
}
}
}
要快速配置此初始配置,请复制以下命令并将其粘贴到文本文件中,删除所有换行符,更改任何必要的详细信息以匹配您的网络配置,然后将命令复制并粘贴到层次结构级别的 CLI [edit] 中:
set interfaces xe-0/0/0 unit 0set interfaces fe-3/0/1 vlan-taggingset interfaces fe-3/0/1 unit 0 description "inet6 configuration IP: 2000::c0a8::1bf5"set interfaces fe-3/0/1 unit 0 vlan-id 100set interfaces fe-3/0/1 unit 0 family inet address 17.10.1.1/24set interfaces fe-3/0/1 unit 0 family inet6 address 2000::c0a8:1bf5/3
概述
正则表达式最有用的功能之一是反向引用。反向引用提供了一种识别字符串中重复字符或子字符串的便捷方法。找到模式后,您可以重复它而无需再次编写。您仅使用(其中#是一个数字,表示您希望模式匹配的次数)来\#引用先前捕获的模式。
您可以使用反向引用来调用或查找数据并将其替换为其他内容。通过这种方式,您可以使用单个替换命令重新格式化大型数据集,从而节省手动查找和替换模式所需的时间。
配置
使用命令中的反向引用配置替换
分步过程
要使用反向参照替换配置中的 Junos OS 模式:
使用
replace命令。[edit] user@host#
replace pattern pattern1 with pattern2在本例中,我们要替换为
:1bf51bf5.[edit] user@host#
replace pattern "(.*):1bf5" with "\11bf5"请注意反向引用 (\1),它指示应仅搜索和替换一次模式。
结果
下面是生成的配置:
[edit]
user@host# show interfaces
xe-0/0/0 {
unit 0;
}
fe-3/0/1 {
vlan-tagging;
unit 0 {
description "inet6 configuration. IP: 2000::c0a8:1bf5";
vlan-id 100;
family inet {
address 17.10.1.1/24;
}
family inet6 {
address 2000::c0a8:1bf5/3;
}
}
}
在此示例中,模式 2000::c0a8::1bf5 替换为 2000::c0a8:1bf5 一次。
示例:设备配置中的全局替换 — 替换接口名称
此示例说明如何使用命令在 replace 配置中全局替换接口名称。
使用该 replace 命令可以更快、更好地更改配置。例如,PIC 可能会移动到路由器中的另一个插槽,这会更改接口名称。使用一个命令,您可以更新整个配置。或者,您可能希望使用其他类似配置(例如类似接口)快速扩展配置。
通过使用和replace命令的组合copy,您可以添加到配置中,然后替换新复制的配置的某些方面。该 replace 命令适用于正则表达式。正则表达式快速、灵活且无处不在。您可以修改可能需要搜索的任何模式,并且大多数编程语言都支持正则表达式。
要求
配置此示例之前,不需要除设备初始化之外的特殊配置。
开始之前,请在路由器上配置以下层次结构。要快速配置此层次结构,请参见 CLI 快速配置 。
user@host#show interfacesso-0/0/0 { dce; } user@host#show protocolsospf { area 0.0.0.0 { interface so-0/0/0.0 { hello-interval 5; } } }
概述
此示例说明如何使用命令在 replace 配置中全局替换接口名称。这是一个简单的例子。
以前的配置是此配置更新的起点。在此示例中,您将使用一个命令更改整个配置中初始接口的名称。
配置
CLI 快速配置
要快速配置此示例的初始配置,请复制以下命令,将其粘贴到文本文件中,删除所有换行符并更改与您的网络配置匹配所需的任何详细信息,将这些命令复制并粘贴到层次结构级别的 CLI [edit] 中,然后从配置模式进入 commit 。
set interfaces so-0/0/0 dce set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface so-0/0/0.0 hello-interval 5
配置接口名称更改
分步过程
要更改接口名称:
确保您位于配置模式层次结构的顶部。
user@host#
top-
替换为
so-0/0/0so-1/1/0使用replace命令,命令使用pattern关键字。user@host#
replace pattern so-0/0/0 with so-1/1/0
结果
进行所需的更改后,请使用和show protocols配置模式命令验证show interfaces配置。
[edit] user@host#show interfacesso-1/1/0 { dce; } user@host#show protocolsospf { area 0.0.0.0 { interface so-1/1/0.0 { hello-interval 5; } } }
确认配置正确后,输入 commit 命令。
示例:设备配置中的全局替换 — 最新选项
请考虑 中 图 1所示的层次结构。文本字符串 010101 显示在三个位置:、 ge-0/0/0.0和 fe-0/0/1的说明ge-0/0/0部分。这三个实例是三个对象。以下示例说明如何使用该 upto 选项在设备配置中执行替换:
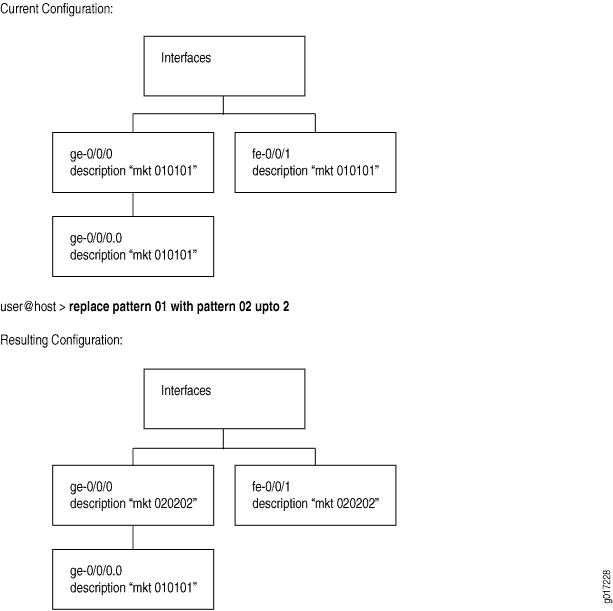
upto 2命令中的一个replace选项将0102转换为两个对象实例。主接口 ge-0/0/0 下的对象将 fe-0/0/1 首先被替换(因为这些是层次结构级别的同级)。由于此 upto 2 限制,该 replace 命令将替换层次结构中第一个和第二个实例(同级)中的模式,但不替换第三个实例(第一个实例的子实例)中的模式。
user@host#show interfacesge-0/0/0 { description "mkt 010101"; #First instance in the hierarchy unit 0 { description "mkt 010101"; #Third instance in the hierarchy (child of the first instance) } } fe-0/0/1 { description "mkt 010101"; #second instance in the hierarchy (sibling of the first instance) unit 0 { family inet { address 200.200.20.2/24; } } } [edit] user@host#replace pattern 01 with 02 upto 2[edit] user@host#commitcommit complete
[edit]
user@host# show interfaces
ge-0/0/0 {
description "mkt 020202"; #First instance in the hierarchy
unit 0 {
description "mkt 010101"; #Third instance in the hierarchy (child of the first
instance)
}
}
fe-0/0/1 {
description "mkt 020202"; #second instance in the hierarchy (sibling of the first
instance)
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 200.200.20.2/24;
}
}
}
在设备配置中添加注释
您可以在设备配置中包含注释,以描述配置中的任何语句。您可以在 CLI 中和通过编辑 ASCII 配置文件以交互方式添加注释。
配置接口时,可以通过在层次结构级别包含 description 语句 [edit interfaces interface-name] 来添加有关接口的注释。您包含的任何注释都会显示在命令的show interfaces输出中。
在 CLI 中添加注释
在配置模式下添加注释时,这些注释与当前级别的语句相关联。每个语句都可以有一个与之关联的单行注释。在将注释与语句关联之前,该语句必须存在。注释放在语句前面的行上。
要向配置添加注释,请使用 annotate 配置模式命令:
user@host# annotate statement "comment-string"
statement 是要附加注释的配置语句;它必须位于当前层次结构级别。如果指定的 statement 注释已存在,则会将其删除并替换为新注释。
comment-string 是注释的文本。注释文本可以是任意长度,您必须在一行上键入它。如果注释包含空格,则必须用引号将其括起来。在注释字符串中,可以包含注释分隔符 /* */ 或 #。如果未指定任何注释字符串,则注释字符串将用注释分隔符括起来 /* */ 。
要删除现有注释,请指定一个空注释字符串:
user@host# annotate statement ""
如果使用命令添加注释 annotate ,则可以通过输入 show 配置模式命令或 show configuration 操作模式命令来查看配置中的注释。
Junos OS 支持配置层次结构中最后一个级别的注释,包括单行代码。但是,不支持对单行的部件(单行中的子语句或标识符)进行注释。例如,在以下示例配置层次结构中,父层次结构支持 level 1 注释,但子语句不支持 metric 注释:
[edit protocols]
isis {
interface ge-0/0/0.0 {
level 1 metric 10;
}
}
}
在文件中添加注释
编辑 ASCII 配置文件并添加注释时,可以是一行或多行,并且必须位于与之关联的语句之前。如果将注释放在文件的其他位置(如语句后面的同一行或语句后面的单独行上),则在使用命令将 load 配置打开到 CLI 中时,注释将被删除。
以下配置示例摘录说明了如何在配置文件中放置和不放置注释:
/* This comment goes with routing-options */
routing-options {
/* This comment goes with routing-options traceoptions */
traceoptions {
/* This comment goes with routing-options traceoptions tracefile */
tracefile rpd size 1m files 10;
/* This comment goes with routing-options traceoptions traceflag task */
traceflag task;
/* This comment goes with routing-options traceoptions traceflag general */
traceflag general;
}
autonomous-system 10458; /* This comment is dropped */
}
routing-options {
rib-groups {
ifrg {
import-rib [ inet.0 inet.2 ];
/* A comment here is dropped */
}
dvmrp-rib {
import-rib inet.2;
export-rib inet.2;
/* A comment here is dropped */
}
/* A comment here is dropped */
}
/* A comment here is dropped */
}
直接在配置文件中包含注释时,可以通过以下方式设置注释的格式:
注释以 开头,以
*/./*注释文本可以位于一行上,也可以跨越多行。注释以 a
#开头,以新行(回车)结尾。
示例:使用 CLI 在设备配置中包含注释
向设备配置添加注释可使配置文件可读且更易于用户理解。您可以在使用语句进行 annotate 配置时包括注释。在此示例中,通过使用 CLI 对现有配置添加注释:
要求
配置此示例之前,不需要除设备初始化之外的特殊配置。
在添加注释之前,必须在路由器上配置以下层次结构。
要快速配置此示例的初始配置,请复制以下命令,将其粘贴到文本文件中,删除所有换行符并更改与您的网络配置匹配所需的任何详细信息,将此命令复制并粘贴到层次结构级别的 CLI [edit] 中,然后从配置模式进入 commit 。
set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface so-0/0/0.0 hello-interval 5
现在验证是否已配置此层次结构。
user@host# show protocols
ospf {
area 0.0.0.0 {
interface so-0/0/0 {
hello-interval 5;
}
}
}
概述
使用 CLI 添加注释时,可以使用语句 annotate 在配置模式下执行此操作。您添加的每个注释都与当前级别的语句相关联。每个语句都可以有一个与之关联的单行注释。
要配置语句, annotate 请移动到要与注释关联的语句级别。要查看注释,请转到配置层次结构的顶部并使用 show 命令。
配置
CLI 快速配置
要快速配置此示例的注释,请复制以下命令,将其粘贴到文本文件中,删除所有换行符并更改与网络配置匹配所需的任何详细信息,从层次结构级别开始 [edit] 将命令复制并粘贴到 CLI 中,然后从配置模式进入 commit 。
edit protocols ospfannotate area 0.0.0.0 "Backbone area configuration added June 15, 2018"edit area 0.0.0.0annotate interface so-0/0/0.0 "Interface from router sj1 to router sj2"
请注意,当您批注层次结构的不同部分时,命令会将您向下移动层次结构。
在 CLI 配置模式中包含注释
分步过程
此过程假定您已经配置了初始配置。
要向配置添加注释:
移动到需要向其添加注释的第一个层次结构级别。
[edit] user@host#
edit protocols ospf使用
annotate配置语句向配置语句添加注释area。[edit protocols ospf] user@host#
annotate area 0.0.0.0 "Backbone area configuration added June 15, 1998"向下移动一个级别到
interface配置语句。[edit protocols ospf] user@host#
edit area 0.0.0.0-
使用该
annotate语句向接口so-0/0/0.0添加注释。[edit protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0] user@host#
annotate interface so-0/0/0.0 "Interface from router sj1 to router sj2"
结果
移动到层次结构的顶部,然后使用 show 命令查看您添加的注释。注释位于与其关联的语句之前。
[edit]
user@host# show protocols
ospf {
/* Backbone area configuration added June 15, 2018 */
area 0.0.0.0 {
/* Interface from router sj1 to router sj2 */
interface so-0/0/0.0 {
hello-interval 5;
}
}
}
确认配置正确后,输入 commit 命令。
示例:将通配符命令与范围选项一起使用
如果需要更改设备的配置,则始终可以使用命令删除 delete 原始配置设置,然后使用命令添加新 set 的配置设置。但是,还有其他更高效、更易于使用的修改配置的方法。
此示例说明如何使用通配符命令以及激活、停用、删除、保护、设置、显示和取消保护配置命令的范围。
通配符命令无法创建配置层次结构。您可以使用它来修改现有语句。当您尝试在空层次结构上设置参数(如停用)时,预计会出现表单 warning: statement not found 的 CLI 错误。
要求
在设备上运行的 Junos OS 12.1 或更高版本。
概述
使用带有通配符命令的范围选项,可以在激活、停用、删除、保护、设置、显示和取消保护命令中指定范围。您可以使用范围来指定接口、逻辑单元、VLAN 和其他编号元素的范围。通配符范围选项将您输入的命令扩展为多个命令,每个命令对应于范围中的一个项目。
通配符范围选项使您能够使用单个 set 命令配置多个配置语句,而不是单独配置每个配置语句。例如,要使用不同的端口号配置 24 个千兆以太网接口,可以使用单个通配符范围 set 命令,而不是 24 个单独的 set interfaces 命令。
同样,要停用一组 30 个逻辑接口,您可以使用通配符范围停用命令,而不是单独停用每个逻辑接口。
配置
- 将通配符命令与 range 语句一起使用,以执行各种配置任务。
- 使用 range 选项为配置语句配置一系列命名标识符
- 在语法中指定多个范围
- 在语法中指定范围和唯一编号
- 从范围中排除某些值
- 使用步骤号指定范围
- 使用通配符删除策略 p1-p10
将通配符命令与 range 语句一起使用,以执行各种配置任务。
分步过程
- 您可以将通配符范围与活动、停用、删除、保护、设置、显示和取消保护配置命令配合使用。
[edit] user@host#
wildcard range ? Possible completions: activate Remove the inactive tag from a statement annotate Annotate the statement with a comment deactivate Add the inactive tag to a statement delete Delete a data element protect Protect the statement set Set a parameter show Show a parameter unprotect Unprotect the statement -
可以使用完整的配置层次结构来限定该
wildcard语句。停留在配置层次结构中时,通配符命令相对于该层次结构支持的选项。[edit] user@host#
wildcard range set interfaces ? Possible completions: <interface-name> Interface name + apply-groups Groups from which to inherit configuration data + apply-groups-except Don't inherit configuration data from these groups > interface-range Interface ranges configuration > interface-set Logical interface set configuration lo0 Interface name > stacked-interface-set Stacked interface set configuration > traceoptions Interface trace options xe-0/0/0:0 Interface name xe-0/0/0:1 Interface nameuser@host# edit interfaces [edit interfaces]wildcard range set ? Possible completions: <interface-name> Interface name + apply-groups Groups from which to inherit configuration data + apply-groups-except Don't inherit configuration data from these groups > interface-range Interface ranges configuration > interface-set Logical interface set configuration lo0 Interface name > stacked-interface-set Stacked interface set configuration > traceoptions Interface trace options xe-0/0/0:0 Interface name xe-0/0/0:1 Interface name在第一种情况下,接口层次结构的完整路径是使用通配符语句指定的。在第二种情况下,用户停放在接口层次结构中。这两种方法支持的选项相同。
使用 range 选项为配置语句配置一系列命名标识符
分步过程
要使用不同的端口号(0 到 23)配置一系列相同类型的接口,请使用以下格式指定端口号的范围。
-
[edit] user@host# wildcard range set interfaces ge-0/0/[0-23] unit 0 family vpls
-
显示结果。范围通配符范围扩展到 24 个不同的 set 命令,用于配置端口号范围为 0 到 23 的接口。在这种情况下,
vpls将创建接口以添加协议家族。如果已经定义了接口,则只添加家族。root@R1# show | compare [edit interfaces] + ge-0/0/0 { + unit 0 { + family vpls; + } + } + ge-0/0/1 { + unit 0 { + family vpls; + } + } + ge-0/0/2 { + unit 0 { + family vpls; + } + } . . . + ge-0/0/23 { + unit 0 { + family vpls; + }
在语法中指定多个范围
分步过程
可以在通配符范围命令中指定多个范围。每个范围必须用逗号分隔。您还可以有重叠的范围。
对于其余示例,您将创建包含十个策略语句的配置的临时副本。具有这些语句可避免在尝试操作层次结构的空部分中的属性时报告的 CLI 错误。
[edit] user@device# set policy-options policy-statement p1 then reject set policy-options policy-statement p10 then reject set policy-options policy-statement p2 then reject set policy-options policy-statement p3 then reject set policy-options policy-statement p4 then reject set policy-options policy-statement p5 then reject set policy-options policy-statement p6 then reject set policy-options policy-statement p7 then reject set policy-options policy-statement p8 then reject set policy-options policy-statement p9 then reject [edit] user@device# save temp Wrote 254 lines of configuration to 'temp'
- 若要在语法中指定多个范围,请包括每个范围的最小值和最大值,用逗号分隔。
[edit] user@host# wildcard range deactivate policy-options policy-statement p[1-3,5-7,6-9]
-
显示结果。通配符范围将展开,以将
deactivate语句添加到名称与指定范围匹配的策略中。值得注意的是,候选配置的更改列表中没有 p4 和 p10 。注:如果配置中尚不存在指定的策略名称,则会返回错误。这是因为您无法将 deactivate 语句添加到配置层次结构的空白部分。
[edit] show | compare [edit policy-options] ! inactive: policy-statement p1 { ... } ! inactive: policy-statement p2 { ... } ! inactive: policy-statement p3 { ... } ! inactive: policy-statement p5 { ... } ! inactive: policy-statement p6 { ... } ! inactive: policy-statement p7 { ... } ! inactive: policy-statement p8 { ... } ! inactive: policy-statement p9 { ... }
在语法中指定范围和唯一编号
分步过程
可以在通配符范围命令的语法中指定范围和唯一数字的组合。
-
重新加载 临时配置。
[edit] user@host# load override temp load complete
- 要指定范围和唯一编号,请用逗号分隔。在此示例中,10 作为唯一编号添加到一系列范围中。
[edit] user@host# wildcard range deactivate policy-options policy-statement p[1-3,5,7,10]
-
显示结果。通配符范围将展开,以将
deactivate语句添加到名称与指定范围匹配的策略以及唯一编号。因此, p10 在此示例中,策略也被停用。注:如果配置中尚不存在指定的策略名称,则会返回错误。这是因为您无法将 deactivate 语句添加到空的配置层次结构中。
[edit] user@host# show | compare [edit policy-options] ! inactive: policy-statement p1 { ... } ! inactive: policy-statement p10 { ... } ! inactive: policy-statement p2 { ... } ! inactive: policy-statement p3 { ... } ! inactive: policy-statement p5 { ... } ! inactive: policy-statement p7 { ... }
从范围中排除某些值
分步过程
可以通过使用感叹号标记要排除的数字或要排除的数字范围来从范围中排除某些值。
-
重新加载 临时配置。
[edit] user@host# load override temp load complete
- 要从范围中排除某些值,请使用 !在语法中。
[edit] user@host# wildcard range deactivate policy-options policy-statement p[1-5,!3-4]
-
显示结果。通配符范围将展开,以将
deactivate语句添加到名称与指定范围匹配的策略中。请注意,对候选配置所做的修改列表中没有策略 p3 和 p4 。它们已从通配符范围中排除。注:如果配置中尚不存在指定的策略名称,则会返回错误。这是因为您无法将 deactivate 语句添加到空的配置层次结构中。
[edit] user@host# show | compare [edit policy-options] ! inactive: policy-statement p1 { ... } ! inactive: policy-statement p2 { ... } ! inactive: policy-statement p5 { ... }
使用步骤号指定范围
分步过程
您可以提供一个步长编号,以便在范围内具有恒定的间隔。步长值对第一个匹配项进行计数,然后跳过后续匹配项,直至达到指定的步长值。
-
重新加载 临时配置。
[edit] user@host# load override temp load complete
- 若要提供步骤,请在语法中包含步骤值,前面加上正斜杠 (/)。在这里,我们指定 1-10 的范围,使用步长值 2 在每次匹配之间跳过 1 个数字。效果是跳过所有偶数匹配,因为我们从匹配奇数 (1) 开始。
[edit] user@host# wildcard range deactivate policy-options policy-statement p[1-10/2]
-
显示结果。通配符范围将扩展以将该
deactivate语句添加到所有其他匹配语句中,从第一个匹配项开始。注:如果配置中尚不存在指定的策略名称,则会返回错误。这是因为您无法将 deactivate 语句添加到空的配置层次结构中。
[edit] user@host# show | compare [edit policy-options] ! inactive: policy-statement p1 { ... } ! inactive: policy-statement p3 { ... } ! inactive: policy-statement p5 { ... } ! inactive: policy-statement p7 { ... } ! inactive: policy-statement p9 { ... }为了更好地说明 step 函数,恢复临时配置并重复通配符命令,这次的步长值为 4。现在,每次初始匹配后都会跳过 3 个条目。
[edit] user@host# load override temp load complete user@host## wildcard range deactivate policy-options policy-statement p[1-10/4] \
-
显示结果。通配符范围将扩展为将语句添加到
deactivate每四个匹配语句(从第一个匹配项开始)。[edit] user@host# show | compare [edit policy-options] ! inactive: policy-statement p1 { ... } ! inactive: policy-statement p5 { ... } ! inactive: policy-statement p9 { ... }
使用通配符删除策略 p1-p10
分步过程
删除为测试通配符功能而添加的临时策略。
-
delete将语句与通配符范围语句一起使用,可通过 删除p10策略p1。[edit] user@host# wildcard range delete policy-options policy-statement p[1-10]
-
显示结果。我们的
policy-options节仅 p1 包含通过 的策略 p10。这将导致配置层次结构为空policy-options。[edit] user@host# show policy-options
