Exemplo: Configuração de VPLS (BGP e intertrabalho de LDP)
 de configuração de VPLS
de configuração de VPLS
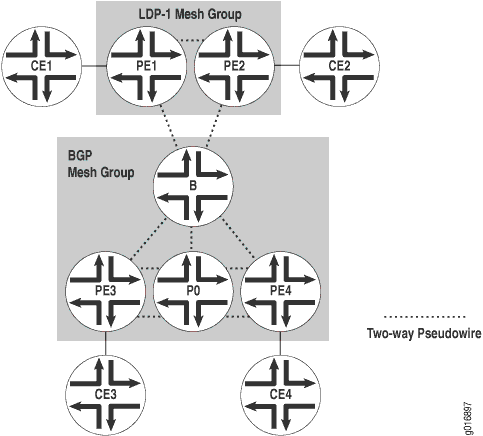
A Figura 1 mostra dois grupos de malha VPLS: LDP-1 e o grupo de malha BGP padrão. A instância VPLS é indicada v1 na configuração. A Tabela 1 mostra os endereços das interfaces do roteador na topologia de exemplo.
Roteador |
Interface |
Endereço |
|---|---|---|
CE1 |
fe-0/0/3 (link para roteador PE1) |
10.12.31.1 |
Loopback |
10.12.53.1 |
|
CE2 |
fe-0/0/1 (link para o Roteador PE2) |
10.12.31.2 |
Loopback |
10.12.53.2 |
|
PE1 |
t1-1/1/1 (link para o Roteador PE2) |
10.12.100.17 |
t1-0/1/0 (link para roteador B) |
10.12.100.2 |
|
Loopback |
10.255.170.106 |
|
PE2 |
t1-0/1/1 (link para Roteador PE1) |
10.12.100.18 |
t1-0/1/3 (link para roteador B) |
10.12.100.6 |
|
Loopback |
10.255.170.104 |
|
B |
t1-0/1/2 (link para Roteador PE1) |
10.12.100.1 |
t1-0/1/3 (link para Roteador PE2) |
10.12.100.5 |
|
so-0/2/2 (link para o Roteador PE3) |
10.12.100.9 |
|
fe-0/0/3 (link para Roteador PE4) |
10.12.100.13 |
|
Loopback |
10.255.170.98 |
|
PE3 |
s0-0/2/1 (link para roteador B) |
10.12.100.10 |
so-0/2/2 (link para o roteador P0) |
10.12.100.21 |
|
Loopback |
10.255.170.96 |
|
P0 |
so-0/2/1 (link para o Roteador PE3) |
10.12.100.22 |
t1-0/1/3 (link para roteador PE4) |
10.12.100.25 |
|
Loopback |
10.255.170.100 |
|
PE4 |
fe-0/0/3 (link para roteador B) |
10.12.100.14 |
t1-0/1/3 (link para o roteador P0) |
10.12.100.26 |
|
Loopback |
10.255.170.102 |
|
CE3 |
ge-1/2/1 (link para PE3) |
10.12.31.3 |
Loopback |
10.12.53.3 |
|
CE4 |
fe-0/0/2 (link para PE4) |
10.12.31.4 |
Loopback |
10.12.53.4 |
No Roteador CE3, o único item que você precisa configurar é a interface Ethernet Gigabit que se conecta ao PE3.
Roteador CE3
[edit]
interfaces {
ge-1/2/1 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.12.31.1/24;
}
}
}
}
No Roteador PE3, prepare o roteador para VPLS configurando BGP, MPLS, OSPF e LDP. (Esses protocolos são a base para a maioria dos aplicativos relacionados à VPN de Camada 2, incluindo VPLS.) Inclua a signaling declaração no nível de hierarquia, porque o [edit protocols bgp group group-name family l2vpn] VPLS usa a mesma infraestrutura para BGP interna que as VPNs de Camada 2.
No Junos OS Release 7.3 e posterior, a signaling declaração substitui a unicast declaração no nível de [edit protocols bgp group group-name family l2vpn] hierarquia. Você deve usar a signaling declaração se quiser configurar domínios VPLS e VPNs de Camada 2 simultaneamente.
Em seguida, configure a marcação VLAN na interface Gigabit Ethernet conectada ao Roteador CE3. Por fim, adicione a interface Gigabit Ethernet em uma instância de roteamento VPLS e especifique a faixa do site, o número do ID do site e o nome do site.
Roteador PE3
[edit]
interfaces {
so-0/2/1 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.12.100.10/30;
}
family mpls;
}
}
so-0/2/2 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.12.100.21/30;
}
family mpls;
}
}
ge-1/3/1 {
encapsulation ethernet-vpls;
unit 0 {
family vpls;
}
}
}
routing-instances {
v1 {
instance-type vpls;
protocols {
vpls {
site 1 {
site-identifier 3;
}
site-range 10;
}
}
interface ge-1/3/1.0;
route-distinguisher 10.255.170.96:1;
vrf-target target:1:2;
}
}
routing-options {
autonomous-system 65000;
}
protocols {
bgp {
group int {
type internal;
local-address 10.255.170.96;
family l2vpn {
signaling;
}
neighbor 10.255.170.98;
neighbor 10.255.170.102;
}
log-updown;
}
ldp {
interface so-0/2/1.0;
interface so-0/2/2.0;
}
mpls {
interface all;
}
ospf {
area 0.0.0.0 {
interface so-0/2/1.0;
interface so-0/2/2.0;
interface lo0.0 {
passive;
}
}
}
}
No Roteador P0, configure MPLS, OSPF e LDP para interconectar PE3 e PE4.
Roteador P0
[edit]
interfaces {
t1-0/1/3 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.12.100.25/30;
}
family mpls;
}
so-0/2/1 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.12.100.22/30;
}
family mpls;
}
}
}
protocols {
mpls {
interface all;
}
ospf {
area 0.0.0.0 {
interface so-0/2/1.0;
interface t1-0/1/3.0;
interface lo0.0 {
passive;
}
}
}
ldp {
interface t1-0/1/3.0;
interface so-0/2/1.0;
}
}
No Roteador PE4, configure BGP, MPLS, OSPF e LDP para complementar a configuração no PE3. Em seguida, configure a marcação VLAN na interface Fast Ethernet conectada ao Roteador CE4. Inclua o encapsulamento VLAN VPLS nos níveis de interface física e lógica. Por fim, adicione a interface Fast Ethernet em uma instância de roteamento VPLS e especifique a faixa do site, o número do ID do site e o nome do site.
Roteador PE4
[edit]
interfaces {
fe-0/0/2 {
encapsulation ethernet-vpls;
unit 0 {
family vpls;
}
fe-0/0/3 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.12.100.14/30;
}
family mpls;
}
}
t1-0/1/3 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.12.100.26/30;
}
family mpls;
}
}
}
}
protocols {
mpls {
interface all;
}
bgp {
log-updown;
group int {
type internal;
local-address 10.255.170.102;
family l2vpn {
signaling;
}
neighbor 10.255.170.96;
neighbor 10.255.170.98;
}
}
ospf {
area 0.0.0.0 {
interface fe-0/0/3.0;
interface t1-0/1/3.0;
interface lo0.0 {
passive;
}
}
}
ldp {
interface fe-0/0/3.0;
interface t1-0/1/3.0;
interface lo0.0;
}
}
routing-instances {
v1 {
instance-type vpls;
interface fe-0/0/2.0;
route-distinguisher 10.255.170.102:1;
vrf-target target:1:2;
protocols {
vpls {
site-range 10;
site 1 {
site-identifier 4;
}
}
}
}
routing-options {
autonomous-system 65000;
}
No Roteador CE4, configure a interface Fast Ethernet que se conecta ao PE4.
Roteador CE4
[edit]
interfaces {
fe-0/0/2 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.12.31.4/24;
}
}
}
}
No roteador B, o roteador de borda da área, configure as interfaces. Em seguida, configure BGP, MPLS, OSPF e LDP. Certifique-se de incluir a interface de loopback na configuração do LDP, incluindo a interface lo0.0 declaração no nível [edit protocols ldp] de hierarquia. Para BGP, inclua a signaling declaração no nível [edit bgp group group-name family l2vpn] de hierarquia. Por último, configure a instância VPLS com sinalização BGP e LDP. Configure o grupo de malha LDP-1 incluindo a mesh-group ldp1 declaração no nível [edit routing-instances v1 protocols vpls] de hierarquia.
Roteador B
[edit]
interfaces {
fe-0/0/3 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.12.100.13/30;
}
family mpls;
}
}
t1-0/1/2 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.12.100.1/30;
}
family mpls;
}
}
t1-0/1/3 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.12.100.5/30;
}
family mpls;
}
}
so-0/2/2 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.12.100.9/30;
}
family mpls;
}
}
}
protocols {
mpls {
interface all;
}
bgp {
log-updown;
group int {
type internal;
local-address 10.255.170.98;
family l2vpn {
signaling;
}
neighbor 10.255.170.96;
neighbor 10.255.170.102;
}
}
ospf {
area 0.0.0.0 {
interface t1-0/1/2.0;
interface t1-0/1/3.0;
interface so-0/2/2.0;
interface fe-0/0/3.0;
interface lo0.0 {
passive;
}
}
}
ldp {
interface fe-0/0/3.0;
interface t1-0/1/2.0;
interface t1-0/1/3.0;
interface so-0/2/2.0;
interface lo0.0;
}
}
routing-instances {
v1 {
instance-type vpls;
route-distinguisher 10.255.170.98:1;
vrf-target target:1:2;
protocols {
vpls {
site-range 10;
site 1 {
site-identifier 1;
}
vpls-id 101;
mesh-group ldp-1 {
neighbor 10.255.170.106;
neighbor 10.255.170.104;
}
}
}
}
}
routing-options {
autonomous-system 65000;
}
Por fim, configure os roteadores LDP PE. No Roteador PE1, prepare o roteador para VPLS configurando LDP, MPLS e OSPF. Em seguida, configure o encapsulamento VPLS na interface Fast Ethernet conectada ao CE1. Por fim, adicione a interface Fast Ethernet à instância de roteamento, especificando o ID VPLS e os endereços de loopback dos roteadores vizinhos.
Roteador PE1
[edit]
interfaces {
fe-0/0/3 {
encapsulation ethernet-vpls;
unit 0 {
family vpls;
}
}
t1-0/1/0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.12.100.2/30;
}
family mpls;
}
}
t1-1/1/1 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.12.100.17/30;
}
family mpls;
}
}
}
protocols {
mpls {
interface all;
}
ospf {
area 0.0.0.0 {
interface t1-0/1/0.0;
interface t1-1/1/1.0;
interface lo0.0 {
passive;
}
}
}
ldp {
interface t1-0/1/0.0;
interface t1-1/1/1.0;
interface lo0.0;
}
}
routing-instances {
v1 {
instance-type vpls;
interface fe-0/0/3.0;
protocols {
vpls {
vpls-id 101;
neighbor 10.255.170.98;
neighbor 10.255.170.104;
}
}
}
}
Em seguida, configure a interface Fast Ethernet no Roteador CE1 que se conecta ao Roteador PE1.
Roteador CE1
[edit]
interfaces {
fe-0/0/3 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.12.31.1/24;
}
}
}
}
No Roteador PE2, prepare o roteador para VPLS configurando LDP, MPLS e OSPF. Em seguida, configure o encapsulamento VPLS na interface Fast Ethernet conectada ao Roteador CE1. Por fim, adicione a interface Fast Ethernet à instância de roteamento, especificando o ID VPLS e os endereços de loopback dos roteadores vizinhos.
Roteador PE2
[edit]
interfaces {
t1-0/1/1 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.12.100.18/30;
}
family mpls;
}
t1-0/1/3 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.12.100.6/30;
}
family mpls;
}
}
fe-1/0/2 {
encapsulation ethernet-vpls;
unit 0 {
family vpls;
}
}
}
protocols {
mpls {
interface all;
}
ospf {
area 0.0.0.0 {
interface t1-0/1/3.0;
interface t1-0/1/1.0;
interface lo0.0 {
passive;
}
}
}
ldp {
interface t1-0/1/1.0;
interface t1-0/1/3.0;
interface lo0.0;
}
}
routing-instances {
v1 {
instance-type vpls;
interface fe-1/0/2.0;
protocols {
vpls {
vpls-id 101;
neighbor 10.255.170.98;
neighbor 10.255.170.106;
}
}
}
}
Por fim, no Roteador CE2 configure a interface Fast Ethernet conectada ao PE2:
Roteador CE2
[edit]
interfaces {
fe-0/0/1 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.12.31.2/24;
}
}
}
}
Verificando seu trabalho
Para verificar a operação adequada do VPLS, use os seguintes comandos:
show bgp summaryshow ldp neighborshow vpls connectionsshow route forwarding-table family vpls (destination | extensive | matching | table)show interfaces vt* terseshow vpls flood extensiveshow vpls statistics
A seção a seguir mostra a saída de alguns desses comandos no Roteador B como resultado do exemplo de configuração.
Use o show bgp summary comando para verificar se a sinalização BGP para VPLS está ativa.
user@B> show bgp summary Groups: 1 Peers: 2 Down peers: 0 Table Tot Paths Act Paths Suppressed History Damp State Pending bgp.l2vpn.0 2 2 0 0 0 0 Peer AS InPkt OutPkt OutQ Flaps Last Up/Dwn State|#Active/Received/Damped... 10.255.170.96 65000 124 125 0 0 54:26 Establ bgp.l2vpn.0: 1/1/0 v1.l2vpn.0: 1/1/0 10.255.170.102 65000 122 124 0 0 54:18 Establ bgp.l2vpn.0: 1/1/0 v1.l2vpn.0: 1/1/0
Use o show ldp neighbors comando para verificar se a sinalização de LDP para VPLS está ativada.
user@B> show ldp neighbors Address Interface Label space ID Hold time 10.255.170.104 lo0.0 10.255.170.104:0 41 10.255.170.106 lo0.0 10.255.170.106:0 38 10.12.100.14 fe-0/0/3.0 10.255.170.102:0 12 10.12.100.10 so-0/2/2.0 10.255.170.96:0 14 10.12.100.2 t1-0/1/2.0 10.255.170.106:0 14 10.12.100.6 t1-0/1/3.0 10.255.170.104:0 13
Para verificar se as conexões VPLS estão ativas, use o show vpls connections comando.
user@B>show vpls connections
Layer-2 VPN connections:
Legend for connection status (St)
EI -- encapsulation invalid NC -- interface encapsulation not CCC/TCC/VPLS
EM -- encapsulation mismatch WE -- interface and instance encaps not same
VC-Dn -- Virtual circuit down NP -- interface hardware not present
CM -- control-word mismatch -> -- only outbound connection is up
CN -- circuit not provisioned <- -- only inbound connection is up
OR -- out of range Up -- operational
OL -- no outgoing label Dn -- down
LD -- local site signaled down CF -- call admission control failure
RD -- remote site signaled down SC -- local and remote site ID collision LN -- local site not designated LM -- local site ID not minimum designated RN -- remote site not designated RM -- remote site ID not minimum designated XX -- unknown connection status IL -- no incoming label
MM -- MTU mismatch MI -- Mesh-Group ID not availble
Legend for interface status
Up -- operational
Dn -- down
Instance: v1
BGP-VPLS State
Local site: 1 (1)
connection-site Type St Time last up # Up trans
3 rmt Up Jan 22 16:38:47 2008 1
Local interface: vt-0/3/0.1048834, Status: Up, Encapsulation: VPLS
Description: Intf - vpls v1 local site 1 remote site 3
Remote PE: 10.255.170.96, Negotiated control-word: No
Incoming label: 800258, Outgoing label: 800000
4 rmt Up Jan 22 16:38:54 2008 1
Local interface: vt-0/3/0.1048835, Status: Up, Encapsulation: VPLS
Description: Intf - vpls v1 local site 1 remote site 4
Remote PE: 10.255.170.102, Negotiated control-word: No
Incoming label: 800259, Outgoing label: 800000 LDP-VPLS State
VPLS-id: 101
Mesh-group connections: m1
Neighbor Type St Time last up # Up trans
10.255.170.104(vpls-id 101) rmt Up Jan 22 16:38:40 2008 1
Local interface: vt-0/3/0.1048833, Status: Up, Encapsulation: ETHERNET
Description: Intf - vpls v1 neighbor 10.255.170.104 vpls-id 101
Remote PE: 10.255.170.104, Negotiated control-word: No
Incoming label: 800001, Outgoing label: 800000
10.255.170.106(vpls-id 101) rmt Up Jan 22 16:38:39 2008 1
Local interface: vt-0/3/0.1048832, Status: Up, Encapsulation: ETHERNET
Description: Intf - vpls v1 neighbor 10.255.170.106 vpls-id 101
Remote PE: 10.255.170.106, Negotiated control-word: No
Incoming label: 800000, Outgoing label: 800000
Para exibir rotas VPLS (endereços MAC) na tabela de encaminhamento de vpls, use o show route forwarding-table family vpls comando.
user@B> show route forwarding-table family vpls
Routing table: v1.vpls
VPLS:
Destination Type RtRef Next hop Type Index NhRef Netif
default perm 0 rjct 540 1
vt-0/3/0.1048832 user 0 comp 587 3
vt-0/3/0.1048833 user 0 comp 587 3
vt-0/3/0.1048834 user 0 comp 589 3
vt-0/3/0.1048835 user 0 comp 589 3
00:17:cb:c2:10:01/48
dynm 0 indr 262143 4
Push 800000 580 2
t1-0/1/3.0
00:17:cb:c2:10:02/48
dynm 0 indr 262145 4
10.12.100.14 Push 800000 594 2
fe-0/0/3.0
00:17:cb:c2:10:03/48
dynm 0 indr 262142 4
Push 800000 576 2
t1-0/1/2.0
00:17:cb:c2:10:bd/48
dynm 0 indr 262144 4
Push 800000 585 2
so-0/2/2.0
Para exibir informações de contabilidade de endereço MAC de origem e destino VPLS, use adestination, extensiveou matchingtable opção com o show route forwarding-table family vpls comando. Ao analisar a saída do display, tenha em mente o seguinte:
A contabilidade de endereço MAC VPLS é tratada em um endereço por MAC para cada instância VPLS. Todas as informações são recuperadas das entradas de endereço MAC na tabela de endereços MAC. A contabilidade de endereços MAC VPLS é realizada apenas em roteadores CE locais.
Os contadores VPLS para endereços MAC de origem e destino aumentam continuamente até que as entradas de endereço MAC mais antigas sejam removidas do buffer de memória, seja quando as entradas saem ou se a instância VPLS for reiniciada.
Para exibir informações de status sobre interfaces virtuais do túnel loopback na instância VPLS, use o show interfaces vt* terse comando.
user@B> show interfaces vt* terse Interface Admin Link Proto Local Remote vt-0/3/0 up up vt-0/3/0.1048832 up up vpls vt-0/3/0.1048833 up up vpls vt-0/3/0.1048834 up up vpls vt-0/3/0.1048835 up up vpls
Para exibir informações de rota VPLS relacionadas ao processo de inundação, use o show vpls flood extensive comando.
user@B> show vpls flood extensive
Name: v1
CEs: 0
VEs: 4
Flood route prefix: 0x4a/32
Flood route type: IFF_FLOOD
Flood route owner: vt-0/3/0.1048834
Flood group name: __ves__
Flood group index: 0
Nexthop type: comp
Nexthop index: 589
Flooding to:
Name Type NhType Index
m1 Group comp 588
Composition: flood-to-all
Flooding to:
Name Type NhType Index
vt-0/3/0.1048832 VE indr 262142
vt-0/3/0.1048833 VE indr 262143
Flood route prefix: 0x4b/32
Flood route type: IFF_FLOOD
Flood route owner: vt-0/3/0.1048835
Flood group name: __ves__
Flood group index: 0
Nexthop type: comp
Nexthop index: 589
Flooding to:
Name Type NhType Index
m1 Group comp 588
Composition: flood-to-all
Flooding to:
Name Type NhType Index
vt-0/3/0.1048832 VE indr 262142
vt-0/3/0.1048833 VE indr 262143
Flood route prefix: 0x48/32
Flood route type: IFF_FLOOD
Flood route owner: vt-0/3/0.1048832
Flood group name: m1
Flood group index: 2
Nexthop type: comp
Nexthop index: 587
Flooding to:
Name Type NhType Index
__ves__ Group comp 586
Composition: flood-to-all
Flooding to:
Name Type NhType Index
vt-0/3/0.1048834 VE indr 262144
vt-0/3/0.1048835 VE indr 262145
Flood route prefix: 0x49/32
Flood route type: IFF_FLOOD
Flood route owner: vt-0/3/0.1048833
Flood group name: m1
Flood group index: 2
Nexthop type: comp
Nexthop index: 587
Flooding to:
Name Type NhType Index
__ves__ Group comp 586
Composition: flood-to-all
Flooding to:
Name Type NhType Index
vt-0/3/0.1048834 VE indr 262144
vt-0/3/0.1048835 VE indr 262145
Para exibir estatísticas de fluxo de pacotes para a instância VPLS, use o show vpls statistics comando:
user@B> show vpls statistics
Instance: v1
Local interface: vt-0/3/0.1048832, Index: 72
Remote PE: 10.255.170.106
Multicast packets: 6
Multicast bytes : 360
Flooded packets : 16
Flooded bytes : 1188
Current MAC count: 1
Local interface: vt-0/3/0.1048833, Index: 73
Remote PE: 10.255.170.104
Multicast packets: 4
Multicast bytes : 240
Flooded packets : 6
Flooded bytes : 398
Current MAC count: 1
Local interface: vt-0/3/0.1048834, Index: 74
Remote PE: 10.255.170.96
Multicast packets: 2
Multicast bytes : 120
Flooded packets : 4
Flooded bytes : 278
Current MAC count: 1
Local interface: vt-0/3/0.1048835, Index: 75
Remote PE: 10.255.170.102
Multicast packets: 1
Multicast bytes : 60
Flooded packets : 2
Flooded bytes : 158
Current MAC count: 1
